Year End Sale : Get Upto 50% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
Every time you sit to design a specific course of study, the first point which has to be catered to is the end result. The most efficient way to be able to reach a conclusive end is to write it down in terms of measurable, learning objectives. Objectives are the basic goal statements which define what will be the outcome of the entire learning process. They are generally linked to the desired outcomes and not the process which helps to achieve the outcomes. These often carry action verbs, which will clearly define what you want the makers of the course to exhibit at the end of the journey. The best way is to align various assessments with expectations from the course, to begin with.
What are Learning Objectives?
Learning objectives refer to clear and measurable results which one seeks to achieve after the end of the learning activity or process. Here the word clear may have different meanings for different people, but the underlying objective remains the same, i.e., to be a better version of yourself in terms of the course taken. Defining specific learning objectives also helps to design the curriculum. Two of the most important facts about learning objectives are:
Although both of the form vital information but they are not important to be placed in learning objectives. Thus, it becomes clear that the only thing which has to be kept in mind while developing the learning objectives is the knowledge outcomes and other benefits which your students will gain by subscribing or taking up the learning activity.

Read: The Secrets of Continuing to Learn at Work
Components of Learning Objectives
There are three major components of the Learning Objectives:
Learning Domains
The learning objectives can be grouped into three major domains:
Classification of Learning Objectives
Read: Top 10 Career Options After BCA in 2025
Learning objectives were classified by Bloom’s Taxonomy on the basis of various cognitive processes which were involved in a student’s mind. Latter was edited for the first time by an American educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom. The objectives as earmarked by the same are as follows:
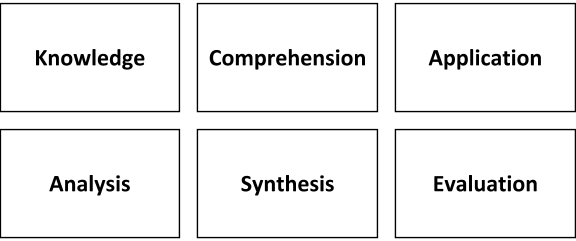
This taxonomic approach is vital for development or defining the learning objectives as it helps to understand the level of various cognitive processes which are involved during learning in humans. This will thus define the natural order by which the target audience will be able to process the information. All the objectives outlined above are ranked as per their importance from lower to higher levels in the hierarchy. In terms of online learning, many experts often suggest ignoring the lower levels as unimportant. Contrarily, these are the ones which are most essential to be able to proceed to higher levels. One can always add in a pre-test to ensure there are no gaps in knowledge. The scores so obtained in the latter can suggest to the learners that they are ready for the next module.

Verbs which Help Write Learning Objectives
Knowledge of Bloom’s taxonomy and the cognitive processes which comprise the learning are a great help when you sit to define and write your learning objectives. Another notable part about learning objectives is their communication to the target audience so that the latter can get a clear picture of the course which they are going to take-up. It was in 2001 when Anderson and Krathwohl were able to present a revised version of Bloom’s taxonomic levels so that the instructional designers can come up with clear objectives. The designers suggested a list of verbs to help the target audience know what has to be expected. Below is a list of verbs which are helpful for the creation of suitable learning objective for every level of Bloom’s taxonomy.
Read: How To List A Certificate On Your Resume: A Complete Guide (With Examples and Samples)
Additional Tips to Keep in Mind
Thus, you now know what to consider while you are writing your learning objectives to the level of cognitive processes which comprise the learning. It will be helpful to also keep the following key pointers in mind when you design the above:
Conclusion
The Learning Objectives form a vital part of every learning process. They have to be clearly defined and laid out in simple and effective language intended for the ultimate target audience. Bloom’s Taxonomic classification serves as a great help in recognition of these and should be kept in mind when writing them. You should also remember that these are different from learning goals, which only give a broader direction in which the objectives have to be written. One should have clarity of thought when writing them as any ambiguity will kill the purpose of learning objectives.
Read: Changing Careers at 40 - Here are the Benefits , Challenges & Tips
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
How to Become a Certified IT Professional?
![]() 582.5k
582.5k
How to Achieve your Career Goals?
![]() 4.8k
4.8k
7 Easiest Programming Languages to Make a Growing IT Career With
![]() 6k
6k
Best Careers For Women: Follow Your Passion & Become Financially Independent
![]() 4.1k
4.1k
Empowering Professionals: Top Certifications for Professionals
![]() 3.8k
3.8k
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on Worth To Visit Course
Interviews