09
JanChristmas Offer : Get Flat 50% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
Enterprise Analysis is a critical activity performed by business analysts at an enterprise level to understand the overall needs of the business, its strategy, architecture and steps to fulfill those strategies. This analysis starts after the business team completed working on strategic vision, plans, and goals. These details hold valuable information from the project development angle and that’s why they are crucial for business analysts.
Remember, enterprise analysis not only focuses on business problems and its proposed business solutions but also on risks, feasibility, market impacts and sudden changes in the organization.
The industry-level analysis is the analysis approach performed by business analysts or business owners to assess the current status of our business with respect to the competitors in the market. This analysis paves the path to understand the economic elements of the marketplace and benefits which can be taken out of it.
The industry-level analysis is very important for any research analyst, example – equity research analyst. It is preferable to do Industry-level analysis in a report format as this report would throw some insights on the economic health of the organization.
The steps for by analyst for Industry Level Analysis are –
Important functions performed in Industry-level analysis
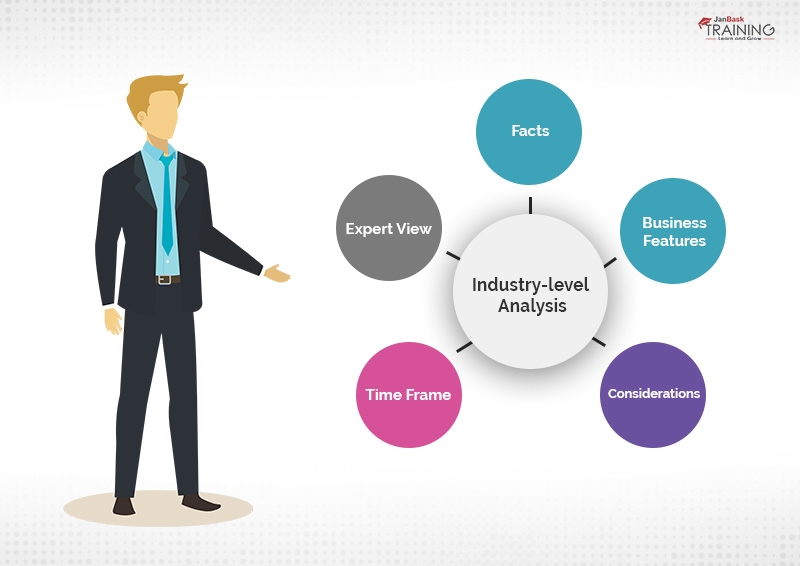
We already got some overview of enterprise-level analysis. The main focus is on the enterprise level and considerations are across the firm. There is some core skill which a business analyst should possess to perform enterprise-level analysis. They are -
Read: What Are The Requirements To Become A Business Analyst?
Project Analysis is totally based on the project and its dimensions. Imagine what step we would perform to figure out if the project will be successful or not, or post-project completion? The steps performed would be called as project analysis.
Project analysis for IT software would differ from any networking company, so would be different for any other domain. Even analysis behind your college project would count as project analysis. At the enterprise level, it gets drill down to granular projects which are handled by different business functions.
Project Level Analysis may not need senior business analysts, but surely the business analyst involved should have a good command of the project.
Process analysis is an analysis method to check on the effectiveness and journey of a business process. It is done to identify each and every part of the structure, the stakeholders involved, the data flow, the changes implemented and the end result is produced.
Process analysis revolved around –understanding of the process, quality of the process being followed and efficiency of the process. Process Analysis is very important as it constantly checks for improvements in the current process. This helps organizations to prepare themselves for a formularized process built from various feedbacks, analysis, and experiences with the current process.
At an enterprise-level, these are the steps to be followed for process analysis –
By now, you might be thinking what actually is an Enterprise? There are multiple meanings to word enterprise, it could be any project, business, company, venture, economic activity, etc. But mostly enterprise is associated with entrepreneurial ventures or simply another name for business. As a matter of fact, it can be detailed as a set of actions performed by someone(initiator), who takes up some risk, by setting, putting some investment and running the business. So this person is called an entrepreneur and that’s the reason it is associated with entrepreneurial ventures.
An enterprise always comes with an idea and a zeal to do something and make a profit out of it. An enterprise business runs very differently in today’s market. With so much diversity and economic uplift, it is not always possible that one person can arrange everything – land, capital, resource, infrastructure, networking, etc. Here the role enterprise comes, who plays like an aggregator and works collaboratively.
Read: How IT Enterprise Analysis Advance Is Going To Change Your Business Strategies.
The way enterprise functions is illustrated below –
These are five mantras responsible for the success of any Enterprise. All five of them go hand in hand and are interconnected to each other.
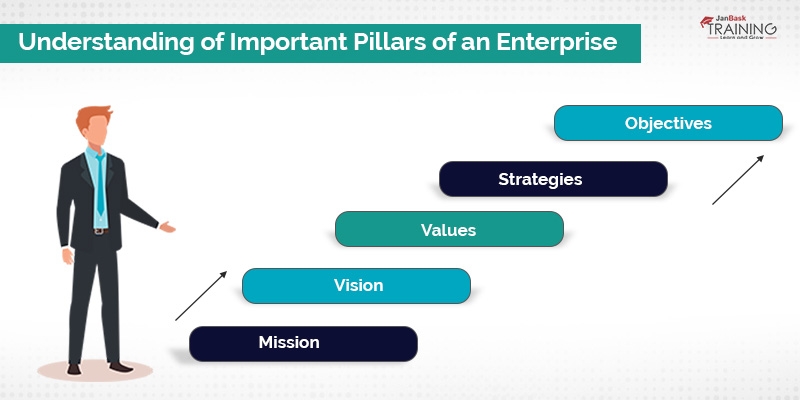
Any business analysts have a visualization towards these pillars -
Remember, the 5W’ and H concept. This concept has always helped to solve many problems and so are they helpful in the analysis world as well. The what, when, why, how and by/for whom is also similar and very beneficial because it gives answers to multiple questions. Let’s see the way each one of them would help in enterprise analysis.
What details need to be analyzed? This question would sort out problems like at what level, what are the factors affecting any enterprise, what is the market place and what all would be the impact of this analysis.
When analysis should be done, is it before forming any business enterprise or post-formation of enterprise, or both?
Why these analysis are important? This would help to fetch and finalize the benefits of enterprise analysis.
Read: Master The Skills Of Project Management Tools & Be Successful
How this analysis has to be carried out. What tools need to be used? What all documentation, processes, and meetings needs to be done for this?
And last, who would this analysis and for whom it would be done. Example - A Senior Business Analyst would perform this analysis and present it before the board of directors.
Business Analysts performed multiple activities as part of enterprise analysis -
Enterprise Analysis is not an easy task to do as it revolves around an entrepreneur. But a proper and complete enterprise analysis marks the success of any business. It helps the analyst to visualize the firm from all aspects and present a holistic view of it. I hope you had a great time learning this topic with us. I would conclude with the words of Sir APJ Abdul Kalam -
“Thinking is the capital, Enterprise is the way, Hard Work is the solution”
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
How to Be the Best Business Analyst?
![]() 4.7k
4.7k
What is Requirement Management? Top 13 Tools for Requirement Management
![]() 539.6k
539.6k
How Important is to Have Domain Knowledge of a Business Analyst?
![]() 7.1k
7.1k
The Ultimate Revelation Of Activity Diagram In UML
![]() 5.9k
5.9k
What is Comparative Analysis: Importance, Examples and Tips
![]() 2.3k
2.3k
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on Business Analyst Course
Interviews