02
JanYear End Sale : Get Upto 50% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
Jenkins is a popular automation server that allows continuous integration and delivery of projects. This does not matter on which platform you are currently working on, Jenkins is compatible with all builds or applications. Jenkins is installed on the central server where your current builds are already taking place.
This is an open source automation server that has the capability to support continuous integration for all builds or projects. Further, Jenkins can be integrated with various testing environments or deployment technologies too as per your requirements.
In this blog, we will discuss how to use, install or configure Jenkins on Ubuntu Linux. This blog covers the most fundamental concepts of the Jenkins program. If you had a technical background or complete knowledge of Software development life cycle then it can be an extra advantage for you while learning Jenkins.
Here is a simple flowchart that will demonstrate the working of Jenkins for different builds. 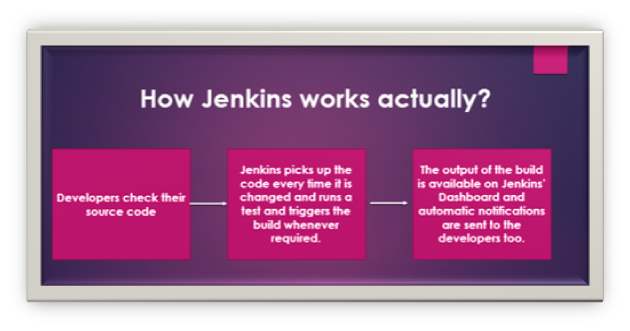
This is the best development practice that demands to integrate code to a central repository at regular time spans. The practice detects build life cycle issues at the earliest stage so that deployment of the particular product can be accelerated. Also, the continuous integration enables developers to release builds frequently.

In brief, every time changes in the code committed by the developer, build should be triggered. Jenkins works in the same way as discussed in the flowchart and triggers the build every time changes are committed by the developers.
Read: Top 20 Git Interview Questions and Answers for 2025
As discussed earlier, Jenkins offers wonderful support to accelerate deployments and project deliveries. Let us closely understand the process of continuous deployment with the help of a flowchart shown below – 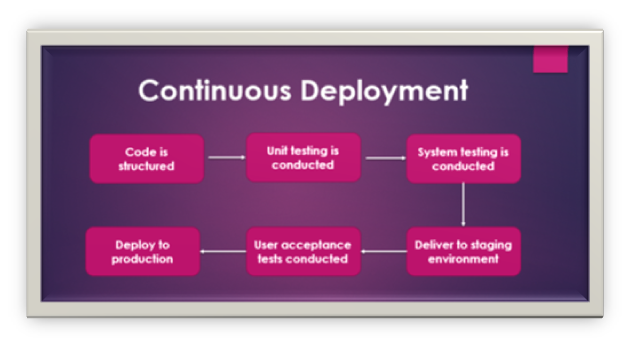 The main part of continuous deployment is that complete process as shown above in the flowchart should be automated. Jenkins achieve the automation through various plug-ins and help in the continuous deployment of the project.
The main part of continuous deployment is that complete process as shown above in the flowchart should be automated. Jenkins achieve the automation through various plug-ins and help in the continuous deployment of the project.
First of all, set up the latest Ubuntu version before you start with the Jenkins installation. Here, we will install Jenkins by adding Debian package repository and apt-get package.
Add the repository key to the system by using the following command.  As soon as, the key will be added to the system, it will return a command OK as shown above. The second command will be used to add the Debian package repository to the Jenkins server source list.
As soon as, the key will be added to the system, it will return a command OK as shown above. The second command will be used to add the Debian package repository to the Jenkins server source list.
Once you are done with both of the steps successfully, now we will run update command to inform apt-get about the new repository.In the end, install Jenkins including Java with the install command as shown below in the screenshot. 
Once you have installed the Jenkins, its dependencies including Java, this is the right time to start the Jenkins with proper commands usage.

We can use ‘system ctl’ to start the Jenkins since this single command does not show any output so we need to use another command ‘status’ to verify either it has been started successfully or not.  If everything is managed well with commands then the output will show you a message that service has been activated and configured to start a boot.
If everything is managed well with commands then the output will show you a message that service has been activated and configured to start a boot.  With all these steps, Jenkins has been installed and started correctly, now you need to configure a firewall so that you can access Jenkins through a web browser and your initial setup guide will be completed.
With all these steps, Jenkins has been installed and started correctly, now you need to configure a firewall so that you can access Jenkins through a web browser and your initial setup guide will be completed.
Read: What Should You Know About Azure Devops?
The default port is 8080, where Jenkins application runs, you can open the port and check the status of new rules with ‘ufw’ command.  Once you will check the status then it should the output that traffic is allowed to the port from anywhere. Here, is an example for your reference how output should look alike –
Once you will check the status then it should the output that traffic is allowed to the port from anywhere. Here, is an example for your reference how output should look alike –  If the firewall is inactive then you have to use ‘openSSH’ to enable it and access the Jenkins through a web browser. Here is the command example how you can use it.
If the firewall is inactive then you have to use ‘openSSH’ to enable it and access the Jenkins through a web browser. Here is the command example how you can use it.  Once the installation is complete, you can start as the administrator user or create a separate user at the moment. In the beginning, Jenkins server is not encrypted and data shared with the server is not safe because it is not stored in the encrypted form.
Once the installation is complete, you can start as the administrator user or create a separate user at the moment. In the beginning, Jenkins server is not encrypted and data shared with the server is not safe because it is not stored in the encrypted form.
For this purpose, you have to work on the SSL setting first then start sharing data on Jenkins server. In this way, information and your personal credentials would be completely safe even when they are exchanged across the network.
Congratulation, at this point your Jenkins set up is installed successfully and you could start working on the application. Obviously, you have to focus on certain points like security, firewall configuration, user creation etc. still, Jenkins is just the perfect choice to get your job done within minutes.
The application has a user-friendly interface that can be understood even by the non-technical user. Also, the build details are given on the same interface and notifications are sent from time to time to the developers working on the build.
Next important concept is Jenkins plug-ins that are helpful to manage the builds and testing precisely. As of now, there are more than 1300 plug-ins offered by the Jenkins and you can use any of them as per your project requirements.

To manage the plug-ins, there is one plug-in manager that allows to add, remove or install plug-ins with a single click only. Also, there is a search option in the beginning where you just need to enter the name of plug-in and it will appear in front of you like a search engine does.
Read: Popular Tenets to Learn DevOps
Final Words:
Jenkins is a powerful automation server tool that is easy to set up and nice to manage like any other build servers but the best part of Jenkins is that it is available for free of costs. You have nothing to complaint about the tool when so many features and flexibility options are available to you without paying anything.
So, congratulation guys, you are ready to explore the tool with JanBask Training with this simple setup guide and the installation process.
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on DevOps Course
Interviews