Introduction
In today's changing work environments, the concept of leadership has evolved to encompass a range of individuals. Whether overseeing a project, navigating challenges, or holding a management position, motivating and bringing out the best in people is essential to achieving success.
When it comes to project management, leadership goes beyond communication. It entails understanding team dynamics and encompasses theories and styles that shape influential leaders. These leadership theories focus on identifying qualities and behaviors that set leaders apart, making leadership indispensable in project management.
What is Leadership?

Leadership is guiding and motivating a group of people toward an objective. It's not just about making decisions; it's about fostering collaboration, effective communication and motivation. A good leader understands when to take charge and when to listen, creating an environment where everyone can give their best.
Importance of Leadership and its Impact on the Workforce
Effective leadership is vital for many reasons, and its influence on the workplace is essential. Strong leadership serves as the foundation for a successful workplace. Its influence extends across employee satisfaction levels, teamwork dynamics, innovation capabilities, adaptability traits, and overall organizational achievements. A competent leader sets a tone for their team while fostering an environment that allows individuals to thrive – enabling them to contribute their best efforts towards achieving collective goals.
Take the example of a Business Analyst; leadership roles are among the most significant opportunities in their career progression. I led teams, managed departments, led projects, and more. They continually step up and step in in various aspects, just as a few we have mentioned below.
1. Employee Engagement:
- Strong leadership cultivates a work environment that fosters employee engagement.
- Engaged employees are more motivated, dedicated, and passionate about their work, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
2. Team Morale and Job Satisfaction:
- Competent leaders inspire trust and confidence among team members, establishing security and job satisfaction
- Motivated morale contributes to a positive work atmosphere, reducing turnover rates while fostering long-term relationships with employees
3. Innovation and Creativity:
- Good leadership promotes a culture that encourages innovation and creativity by enhancing communication channels and embracing ideas
- Teams led by influential leaders feel empowered to take risks and contribute their unique perspectives
4. Adapting to Change:
- Strong leaders play a role in guiding and supporting teams through periods of change in the workplace
- Leaders who possess adaptability and resilience bring stability during times of uncertainty, making it easier for the team to embrace and adjust to circumstances
5. Effective Communication:
- Exceptional leaders excel in communication, ensuring that team members understand goals, expectations, and feedback
- By fostering communication channels, collaboration is encouraged while minimizing misunderstandings, ultimately enhancing the team's performance
6. Conflict Resolution:
- Leaders who possess strong conflict resolution skills foster a work environment
- Addressing conflicts promptly and effectively prevents issues from escalating, thereby maintaining a positive and collaborative atmosphere within the team
7. Strategic Vision and Goal Achievement:
- Influential leaders establish a vision for the organization and effectively communicate actionable goals
- Under leadership, teams work cohesively towards objectives, driving overall success and accomplishment
8. Employee Development:
- Great leaders prioritize investing in the growth of their team members
- Providing opportunities for development and learning enhances employee skills, contributing to the capability and competitiveness of the organization
9. Organizational Culture:
- According to the behavioral theory of leadership, organizational culture is shaped by leadership style in management, which influences the values, norms, and behaviors within the organization
- A positive and inclusive culture can attract talent, encourage collaboration, and create a sense of belonging among employees
10. Ethical Decision Making:
- Effective leaders prioritize upholding standards and integrity when making decisions. They understand that ethical leadership is crucial for building trust, credibility, and a positive reputation for the organization.
11. Customer Satisfaction:
- Great leadership goes beyond managing teams: it directly impacts customer satisfaction. When employees feel satisfied and motivated, they are more likely to deliver customer service. This, in turn, fosters customers and enhances the brand image of the organization.
12. Financial Performance:
- Effective leadership plays a role in driving performance within an organization. Teams led by leaders tend to be more productive, efficient and innovative – all of which contribute to the company's profitability.
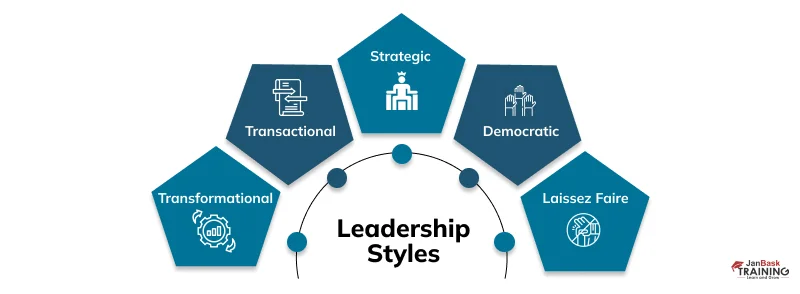
What are Leadership Styles?

Leadership styles in management refer to how leaders behave and influence their teams. These styles can vary depending on the situation, and influential leaders adapt their approach accordingly. Let's explore some leadership styles:
1. Transformational Leadership:
Transformational Leadership inspires and motivates by sharing a vision that promotes growth and encourages innovation. Leaders with charisma, emotional intelligence, and a commitment to change establish a culture of shared purpose and high performance among team members for long-term success.
2. Transactional Leadership
Transactional Leadership relies on established structures, reward systems, and consequences to influence team members.
Leadership entails establishing expectations, monitoring performance, and providing incentives for accomplishments and contributions. This approach emphasizes achieving goals while simultaneously ensuring day-to-day operations within an organization.
3. Democratic Leadership
Democratic Leadership entails making decisions by considering input from your team, appreciating their perspectives, and fostering teamwork. This style enhances creativity, engagement, and team satisfaction, fostering a workplace culture that's democratically empowered and aligned with objectives.
4. Laissez-Faire Leadership
Laissez-faire Faire Leadership takes a hands-off approach where leaders grant autonomy to team members. With interference, it places trust in the expertise of individuals promoting independence.
This Leadership style in management proves effective within self-motivated teams as it allows creativity to thrive and harnesses the strengths of each team member.
5. Strategic Leadership
Strategic Leadership revolves around term goals, envisioning the future, and guiding overall direction. Leaders adopt a forward-thinking mindset, excel at planning, and inspire a shared vision among their teams. This style involves aligning resources and actions with a vision to navigate challenges effectively and achieve success in a dynamic business landscape.
Additional Leadership Styles in Management
According to the personal research Board at Ohio University, the following are a few more leadership styles used in management.
- Bureaucrat: Bureaucratic Leadership thrives within organizations that rely on responsibilities and established rules. It emphasizes a chain of command with strict standards and follower adherence. This style suits regulated entities where adherence to established procedures is paramount.
- Diplomat: Diplomatic leaders embrace a collaborative approach that fosters team accountability while emphasizing harmony. Compassionate and empathetic, they form connections. Diplomats handle issues harmoniously. Prioritize conflict prevention as a bond to unite their teams in a collaborative environment.
- Expert: This type of leadership style revolves around knowledge and skill. Leaders rely on their expertise, expecting team members to be matter specialists. While encouraging autonomy, coordinating can be challenging. The emphasis is on leveraging expertise to contribute to the organization's success.
- Quarterback:Quarterback leadership is a concept that draws inspiration from football, where the quarterback plays a crucial role in leading the team's offensive plays. In a sense, quarterback leadership refers to a style of Leadership where an individual takes on an influential role, similar to how a quarterback directs plays on the field. Quarterback directing a play, this leadership style varies among leaders. Some lead with authority, while others guide through attention. Leading by example, they demonstrate how to inspire and cultivate a culture driven by success. Actions speak louder than words, making results and deeds the measure of Leadership.
What Defines an Honest Leader?

The responsible leader goes beyond leading: they possess a captivating combination of charm, courage, and unwavering ambition.
For instance, imagine a leader whose personality is so intriguing that it brightens the room with a vision. These leaders motivate their teams to achieve greatness and shape success through their determined resolve. Critical qualities of leadership include:
- Transparency plays a role in team communication. It goes beyond sharing information. It involves engaging in open discussions and collaborative strategizing to achieve common goals. Being honest about decisions and actions helps foster an environment of trust and unity.
- Integrity is about staying true to our principles when making choices. It means ensuring that our words align with our actions and building a foundation of trustworthiness and credibility. When we act by our stated values, we contribute to a team dynamic that's reliable and trustworthy.
- Authenticity involves creating an environment where individuals can be themselves. This means taking ownership of mistakes and demonstrating accountability. Cultivating authenticity within the team helps promote a culture of openness and continuous improvement.
- Trustworthiness is an element in team dynamics as it involves establishing and maintaining trust among team members. This encourages honesty, reliability, setting goals, and finding ways to fulfill promises and commitments.
- Accountability is taking responsibility for our actions as the consequences of our decisions. It also entails holding ourselves to standards while expecting the same from others. Doing so fosters a sense of responsibility and commitment within the team.
- Fairness is about treating everyone without favoritism or bias. In our workplace, we prioritize making decisions based on merit and objective criteria to ensure fairness and inclusivity.
- Effective communication plays a role in overcoming challenges when working in a team. Creating an environment that values and encourages honest dialogue is essential, allowing information to be shared transparently and efficiently.
- Empathy is about understanding and considering the emotions and viewpoints of others. It is not reflected in how we interact but in making decisions. Fostering empathy contributes to a team culture that values understanding and compassion.
- Consistency is crucial for maintaining a fair and harmonious team dynamic. Treating everyone equally without exceptions demonstrates our commitment to behavior and decision-making across all situations.
- An honest leader cultivates trust where team members feel safe, appreciated, and motivated. This behavior fosters a work environment and strengthens the leader's ability to guide the team towards shared goals.
What is Leadership Theory?
Leadership Theory is a roadmap that helps us understand and practice leadership. It provides a framework for comprehending the dynamics involved in leading a team emphasizing the significance of qualities such as communication, decision making and empathy. Essentially it serves as a toolkit that enables individuals to become leaders and contribute to the success and unity of any group or organization.
Why are Leadership Theories Critical?
- Insights and Tools: Leadership theories offer insights and practical tools for leaders
- Framework: They provide a structure for understanding leadership styles, methods of communication, and approaches to decision-making
- Skill Enhancement: Studying and applying these theories helps leaders improve their skills
- Adaptability: Leaders demonstrate adaptability by incorporating lessons from leadership theories in different situations
- Positive Work Environment: The application of leadership theories contributes to creating a work environment that is positive and fosters productivity
- Guidebook: Leadership theories serve as a valuable guide for both aspiring and experienced leaders, providing insights into effective practices
- Navigation: These theories assist leaders in navigating the complexities of leadership with competence and confidence
What are Leadership Theories?
1. Theory of Management Theory:
Originating during the Industrial Revolution, the theory aimed to enhance company productivity. This leadership approach emphasizes the importance of hierarchy in achieving effectiveness. Managers who employ leadership prioritize structure. Use their authority to enforce rules while rewarding workers for meeting objectives. In contrast, these leaders focus on goals and standardized processes. They are not catalysts for company expansion. Instead, their focus revolves around upholding policies and standards.
2. Theory of Transformation:
Transformational theory is a concept in management that highlights the importance of the relationship between leaders and staff in driving success. According to this theory, influential leaders can inspire their employees to surpass their perceived capabilities. These leaders need to create a vision for their team. Also, motivate and guide them towards achieving it.
Transformational leaders play a role in boosting employee morale, which ultimately leads to performance in the workplace. They focus on taking action rather than relying on words: they emphasize the importance of leading by setting up examples.
Practitioners of leadership exhibit qualities such as self-control, setting standards, prioritizing communication, actively engaging with employees, promoting their development, being open to new ideas, and having the courage to make difficult decisions and take calculated risks.
Unlike leaders who prioritize day-to-day operations and individual goals, transformational leaders prioritize improving processes and unifying teams to achieve organizational objectives. Furthermore, these influential leaders prioritize the organization's and its employees' needs over interests.
3. The Contingency Theory:
According to the contingency hypothesis, there isn't a one-size-fits-all approach to running an organization. Leadership effectiveness depends on external factors, which require leaders to adapt their styles based on specific circumstances. Factors such as management approach, work pace, organizational policies, and employee morale influence the leadership style significantly, highlighting the importance of leaders aligning their strategies with the situation.
4. The Situational Theory:
Similar to contingency theory, situational theory emphasizes that leadership should adapt to changing contexts to achieve objectives and make decisions. Situational leadership entails establishing a connection with employees, motivating them to recognize when different leadership approaches are necessary, and building teams. Four main leadership styles—Telling, Selling, Participating, and Delegating—are identified in this theory, each requiring qualities like problem-solving skills, trustworthiness, adaptability, insightfulness, and coaching abilities.
5. The Great Man Theory:
The Great Man Theory is one of the theories about leadership. Suggests that certain qualities associated with influential leaders are innate and cannot be acquired through learning.
Leaders are often thought to possess charm, decisiveness, wisdom, courage, assertiveness, and charisma. According to this theory, exceptional leaders emerge when these traits are needed and remain consistent over time, applicable to all types of organizations.
6. The Trait Theory:
Expanding on the Great Man Theory, the trait theory of leadership suggests that influential leaders have personality traits and behavioral qualities. These inherent qualities allow leaders to excel in situations, indicating that some individuals are naturally more inclined to be leaders. Key characteristics of a leader include stability, a sense of responsibility, competency in their field, the ability to recognize challenges and obstacles, motivational skills, practical communication abilities, perseverance, adaptability, and making confident decisions.
7. Behaviorist Theory:
In contrast to the belief in the trait theory of leadership, the behaviorist theory asserts that a person's leadership abilities are shaped by their environment. Leadership qualities are learned rather than predetermined, with behavior being the driving factor. Managers can be categorized based on their recognized leadership styles, such as task-oriented focus or people-first approach, along with classifications, like effective ones.
8. Behavioral Theory:
The behavioral theory of leadership focuses on actions rather than traits, suggesting that influential leaders can be developed through teachable behaviors. This theory emphasizes styles of leadership based on patterns of conduct, such as task-oriented leaders, club leaders, people-oriented leaders, dictatorial leaders, status quo leaders, and more.
9. Functional Theory:
The functional theory of leadership highlights how organizations or workplaces are led rather than solely relying on leader designations. It recognizes that achieving goals and tasks is an effort supported by the behaviors of individuals rather than depending on one person alone.
10. Integrated Psychological Theory:
Integrative leadership represents an approach that promotes cooperation across societal spheres to achieve common goals. It combines leadership theories from five domains: industry, government, nonprofits, media, and the community. This integrative approach aims to create synergy by blending leadership theories and techniques.
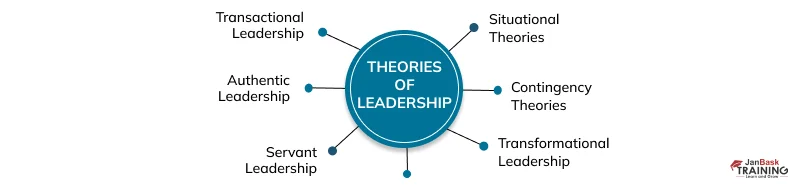
Different Types of Leadership Theories and Models

Numerous leadership theories have been developed throughout the years to analyze and understand the intricacies of leadership styles and behaviors. Let's delve into some leadership theories:
- Situational Theories: Situational theories suggest that effective leadership depends on the context. They advocate for adapting leadership styles based on the characteristics of followers and situational requirements.
- Contingency Theories: Expanding on theories, contingency theories propose that leader traits, behaviors, and situations interact to determine leadership. These theories emphasize the need to tailor leadership styles to suit circumstances.
- Transformational Leadership: Transformational leadership theory highlights inspiration and motivation and focuses on a leader's ability to drive followers beyond self-interest for the organization's benefit. Key elements include vision, charisma, intellectual stimulation, and individualized consideration.
- Transactional Leadership: Transactional leadership theory revolves around the exchange relationship between leaders and followers. Leaders in this model are motivated through rewards, recognition, and a system of performance-based incentives and consequences.
- Authentic Leadership: Authentic leadership theory emphasizes leaders being genuine, self-aware, and faithful to their values. Building trust is essential in leadership, and one way to achieve this is through transparency and ethical behavior. Leaders must inspire their followers by being genuine and authentic.
- Servant Leadership: The theory of leadership emphasizes the importance of prioritizing the needs of followers over self-interest. Leaders who adopt this approach focus on serving and supporting their team members, fostering a sense of community, and promoting growth and development.
How can you determine which Leadership Style is Right for you?
Selecting the leadership style requires self-awareness, adaptability, and a comprehensive understanding of your team dynamics and the context in which you operate. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Self Assessment: Take time to reflect on your values, strengths, weaknesses, and personal philosophy on leadership. Identify your inclinations and preferences when it comes to leading others.
- Understand Your Team: Consider the strengths, preferences, and working styles of each team member. A successful leader tailors their approach to align with the dynamics within the team.
- Evaluate the Situation: Assess the context in which you operate and identify challenges or goals. Different situations may call for leadership approaches.
- Familiarize Yourself with Leadership Theories: Gain knowledge about leadership theories such as transformational, transactional, and situational, among others. Understand their principles and how they align with your values and objectives.
- Being adaptable: It's essential to be flexible and willing to adjust your leadership style according to the changing needs of your team and the circumstances. Taking an approach may yield results in something other than dynamic situations.
- Communication approach: Customize your communication style to resonate with your team. Influential leaders communicate, listen, and adapt their communication based on the preferences of their team members.
- Feedback and continuous learning: Regularly seek feedback from your team. Understand what leadership style works best for them and be open to making adjustments. Continuous learning and improvement are crucial.
- Alignment with culture: Ensure that your leadership style aligns with the values and culture of the organization. Consistency in leadership promotes a supportive work environment.
- Emotional intelligence: Develop intelligence to understand and manage both your emotions and those of your team members. This ability enables you to navigate relationships effectively.
- Experimentation and evaluation: Don't hesitate to try leadership styles in situations. Afterwards, evaluate the outcomes. Learn from those experiences. This iterative process helps you refine your approach over time.
- Seek guidance from mentors: Connect with leaders or mentors who can offer guidance based on their experiences. Learning from others can expand your perspective on leadership.
- Be True to Yourself: While it's essential to adapt to situations, it is crucial to stay authentic. Being genuine and staying true to your values establishes trust and credibility with your team. Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to leadership. Successful leaders are those who can adapt their styles depending on the team's needs and the circumstances.
How to Apply Leadership Theories in the Workplace?
Implementing leadership theories in a work environment requires a thoughtful approach. Here is a step by step guide on applying leadership theories:
1. Educate Your Team
- Introduce essential leadership theories to your team ensuring everyone has a shared understanding.
- Conduct training sessions or workshops explaining the principles and concepts of leadership models.
2. Assess Organizational Requirements
- Evaluate the organization's challenges, objectives, and culture.
- Identify areas where specific leadership theories can address needs and enhance performance.
3. Align, with Values
- Ensure that the chosen leadership theories align with the organization's core values and mission.
- Incorporate leadership principles that reinforce goals and objectives.
4. Leadership Development Programs
- Integrate the principles of chosen theories into leadership development programs.
- Offer resources, workshops and mentoring opportunities to help leaders enhance their skills based on frameworks.
5. Role Model Desired Behaviors
- Leaders should exemplify the behaviors and qualities outlined in the selected leadership theories.
- Set an example by demonstrating the desired leadership style for others to follow.
6. Foster a Culture of Continuous Learning
- Cultivate an environment that promotes learning and development.
- Encouragement. Team members to stay updated on emerging leadership theories and best practices.
7. Address good Leadership Styles
- Highlight the significance of adapting leadership styles based on situational demands.
- Train leaders to assess their team's readiness and maturity adjusting their approach accordingly.
8. Feedback and Evaluation
- Establish a feedback system to evaluate the effectiveness of implementing leadership theories in practice.
- Review and assess leadership strategies to identify areas for improvement.
9. Recognition and Rewards
- Implement recognition programs that acknowledge and reward leaders who effectively apply leadership theories.
- Link performance evaluations and incentives, with the demonstration of desired leadership behaviors.
10. Encourage Collaboration:
- Foster a culture of decision making and problem solving.
- Incorporate strategies, like democratic or participative leadership theories to actively involve team members in decision making processes.
11. Cultivate a Supportive Atmosphere
- Create an environment that upholds the principles of leadership.
- Prioritize the well being and growth of team members.
12. Communicate with Effectiveness
- Highlight the significance of transparent communication.
- Train leaders to adapt their communication styles according to the team's needs and specific situations.
13. Personalize Leadership Development Plans
- Acknowledge that different individuals may respond better to leadership approaches.
- Tailor leadership development plans based on each leader's strengths and requirements.
14. Monitor and Adjust Accordingly
- Regularly assess the impact of implemented leadership theories, on team dynamics and performance.
- Be prepared to modify strategies based on feedback and evolving needs.
15. Promote Ethical Leadership
- Emphasize the considerations outlined in leadership theories.
- Foster a culture characterized by integrity, accountability and responsibility.
By incorporating these steps into your organization's culture you can effectively implement leadership theories that align with your workplaces values and goals.
Consistently evaluating performance and continuously striving for improvement are factors in achieving long term success.
Conclusion
As we can see, theories of leadership originate from perspectives. Emphasize traits, qualities and the influence of situations, on leadership behavior. Given its nature, effective leadership involves navigating dimensions with the human element being the most crucial factor that impacts organizational success. In today's changing business environment leadership continues to be valued.
To enhance your skills and develop leadership capabilities, JanBask offers advanced programs such as Business Analyst courses online that equip both aspiring professionals and experienced individuals with contemporary leadership skills that are essential for success across different industries. The program covers sought after business management, leadership skills. Provides specializations in areas such, as Digital Marketing, Business Analysis, Design Thinking and Digital Transformation. Discover the potential of this program today.
FAQs
Q: How does leadership theory impact the training of business analysts?
Ans: The training of business analysts is influenced by leadership theories as they shape how professionals lead teams communicate effectively and drive projects forward. Integrating leadership principles, into BA training equips learners with skills that prepare them to handle scenarios in the business world.
Q: How will understanding leadership styles benefit my career as a business analyst?
Ans: Having an understanding of leadership styles can greatly benefit business analysts. It enhances their ability to effectively lead teams navigate projects successfully and make strategic contributions to organizational success. You can explore platforms like Janbask for business analyst training that ensure you are well equipped to excel in your career as a business analyst.
Begin your journey towards becoming a business analyst by enrolling in courses that combine expert knowledge in business analysis with invaluable leadership skills!
Q: What is meant by "leadership theories"? Can you explain the concept of trait theory in relation to leadership?
Ans: "Leadership theories" refers to explanations of how leadership functions and operates. They delve into the characteristics, behaviors and situations that define leadership. From trait theory to contingency models these theories offer insights for aspiring leaders and those, with experience.
Trait theory suggests that leadership is influenced by qualities and characteristics.
Q: What types of leadership styles are discussed in theories of leadership?
Ans: Leadership theories encompass a variety of leadership styles, such, as transformational, transactional, democratic, autocratic, laissez faire and more. Each style emphasizes approaches to decision making, communication and fostering teamwork.
Q: What is the concept of leadership theory? How does the behavioral theory of leadership fit into it?
Ans: Leadership theory explores the models and concepts that help us understand what makes a leader effective. It delves into traits, behaviors and styles that contribute to leadership while providing insights for individuals in positions of authority.
The behavioral theory of leadership focuses on leaders actions and behaviors, than their traits. It proposes that effective leadership can be acquired and developed through behaviors. This theory highlights how different leadership styles can impact team dynamics and performance.
Trending Courses
Cyber Security
- Introduction to cybersecurity
- Cryptography and Secure Communication
- Cloud Computing Architectural Framework
- Security Architectures and Models
Upcoming Class
7 days 30 Dec 2025
QA
- Introduction and Software Testing
- Software Test Life Cycle
- Automation Testing and API Testing
- Selenium framework development using Testing
Upcoming Class
6 days 29 Dec 2025
Salesforce
- Salesforce Configuration Introduction
- Security & Automation Process
- Sales & Service Cloud
- Apex Programming, SOQL & SOSL
Upcoming Class
3 days 26 Dec 2025
Business Analyst
- BA & Stakeholders Overview
- BPMN, Requirement Elicitation
- BA Tools & Design Documents
- Enterprise Analysis, Agile & Scrum
Upcoming Class
3 days 26 Dec 2025
MS SQL Server
- Introduction & Database Query
- Programming, Indexes & System Functions
- SSIS Package Development Procedures
- SSRS Report Design
Upcoming Class
3 days 26 Dec 2025
Data Science
- Data Science Introduction
- Hadoop and Spark Overview
- Python & Intro to R Programming
- Machine Learning
Upcoming Class
4 days 27 Dec 2025
DevOps
- Intro to DevOps
- GIT and Maven
- Jenkins & Ansible
- Docker and Cloud Computing
Upcoming Class
1 day 24 Dec 2025
Hadoop
- Architecture, HDFS & MapReduce
- Unix Shell & Apache Pig Installation
- HIVE Installation & User-Defined Functions
- SQOOP & Hbase Installation
Upcoming Class
10 days 02 Jan 2026
Python
- Features of Python
- Python Editors and IDEs
- Data types and Variables
- Python File Operation
Upcoming Class
11 days 03 Jan 2026
Artificial Intelligence
- Components of AI
- Categories of Machine Learning
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Recurrent Neural Networks
Upcoming Class
4 days 27 Dec 2025
Machine Learning
- Introduction to Machine Learning & Python
- Machine Learning: Supervised Learning
- Machine Learning: Unsupervised Learning
Upcoming Class
17 days 09 Jan 2026
Tableau
- Introduction to Tableau Desktop
- Data Transformation Methods
- Configuring tableau server
- Integration with R & Hadoop
Upcoming Class
10 days 02 Jan 2026