26
DecChristmas Offer : Get Flat 35% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
Imagine those busy weekends before Diwali, when your mom asks you to clean your room and rearrange all your belongings in a proper order. Your room otherwise are cluttered, with belongings lying anywhere and everywhere. It is very difficult to find anything in that mess. But after the day long work of removing the unnecessary things and moving around rest of your belongings in a proper way, you realize searching things has now become very easy. Same thing can happen to your data if you do not store them in a proper way. There can be data loss, redundancy and duplicity .To avoid all this we have normalization.
A database anomaly is a fault in a database that usually emerges as a result of shoddy planning and storing everything in a flat database. In most cases, this is removed through the normalization procedure, which involves the joining and splitting of tables.
There are namely three types of anomalies:
Let us now understand about them in more details. For that let us create a table called Emp and fill it up with some data. Following are the code to create the table and insert data into it.
SQL Server Training & Certification

create table Emp
(
Emp_id varchar(100),
Emp_name varchar(100),
Emp_Address varchar(100),
Emp_dept varchar(100)
)
To insert data into EMP table
insert into Emp(Emp_id,Emp_name,Emp_Address,Emp_dept)
select '101','Rick','Delhi','D001'
union
select '101','Rick','Delhi','D002'
union
select '123','Maggie','Agra','D890'
union
select '166','Glenn','Chennai','D900'
union
select '166','Glenn','Chennai','D004'
The output looks like below

An insertion anomaly is the inability to add data to the database due to the absence of other data.
Here in this example, if a person joins as a trainee, who has not been assigned a department it will be very difficult to enter his data into the table based on the current design as all the fields in the current table is mandatory and for the new joinee there is no department assigned.
An update anomaly is a data inconsistency that results from data redundancy and a partial update.
Glenn currently looks after two department and leaves in Chennai. Suppose Glenn decides to change his address from Chennai to Kolkata. Since Glenn works in multiple departments and there are multiple entries for him in the table, data for the all the rows has to be changed. If by any chance, we miss out on one of the rows, it will create an error which we term as update anomaly.
A deletion anomaly occurs when you delete a record that may contain attributes that shouldn't be deleted. In the above example, if we delete department D890, all the data related to that department will be deleted.
To remove all these above mentioned anomalies, we implement normalization.
Normalization is the process of organizing data in a database. This includes creating tables and establishing relationships between those tables according to rules designed both to protect the data and to make the database more flexible by eliminating redundancy and inconsistent dependency.
A large database defined as a single relation may result in data duplication. This repetition of data may result in:
So to handle these problems, we should analyze and decompose the relations with redundant data into smaller, simpler, and well-structured relations that are satisfying desirable properties. Normalization is a process of decomposing the relations into relations with fewer attributes.
In short normalization means:
The main reason for normalizing the relations is removing these anomalies. Failure to eliminate anomalies leads to data redundancy and can cause data integrity and other problems as the database grows. Normalization consists of a series of guidelines that helps to guide you in creating a good database structure.
Normalization works through a series of stages called Normal forms. The normal forms apply to individual relations. The relation is said to be in particular normal form if it satisfies constraints.
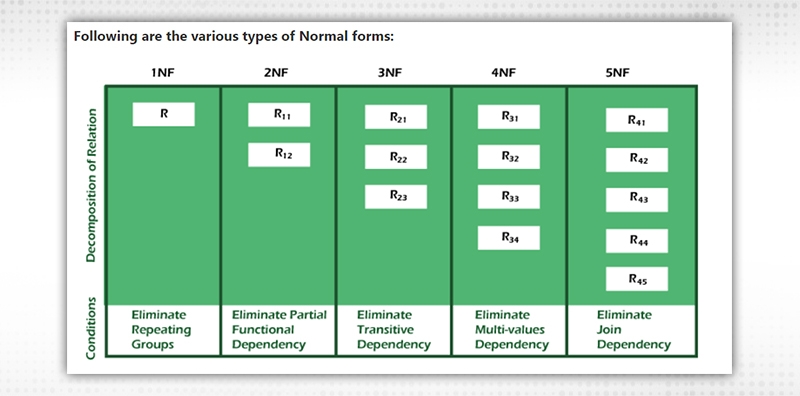
|
Normal Form |
Description |
|
1NF |
A relation is in 1NF if it contains an atomic value. |
|
2NF |
A relation will be in 2NF if it is in 1NF and all non-key attributes are fully functional dependant on the primary key |
|
3NF |
A relation will be in 3NF if it is in 2NF no transition dependency exist |
|
BCNF |
A stronger definition of 3NF is known as Boyce Codd normal form |
|
4NF |
A relation will be in 4 NF if it is in BCNF and has no multi valued dependency |
|
5NF |
A relation is in 5NF if it is in 4NF and does not contain any join dependency, joining should be lossless. |
Next we will discuss about this above mentioned normal forms in more details.
First normal form says an attribute (column) of a table cannot hold multiple values. It should only contain atomic values.
Let us assume a table called Empfirstnormal which contains fields called Empid,Emp_Name,Emp_Address and Emp_mobile.The query will be as follows.
create table EmpFirstnormalform
(
Emp_id varchar(100),
Emp_name varchar(100),
Emp_Address varchar(100),
Emp_mobile varchar(100)
)Let us also insert some data into it.The insert query are as follows.
insert into EmpFirstnormalform(Emp_id,Emp_name,Emp_Address,Emp_mobile)
select '101','Rick','Delhi','88859121' union select '101','Rick','Delhi','86251028,8677892410' union select '123','Maggie','Agra','88845555' union select '166','Glenn','Chennai','87445577,87465542'
The final output looks like below.
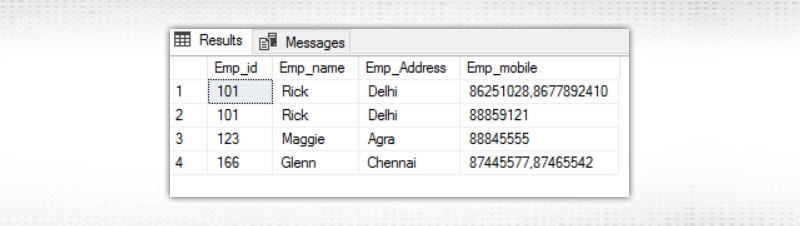
As you can see that in the Emp_mobile column, there are multiple phone numbers separated by a comma. First normal form does not allow that. So the modified table will look like below

The query to create the table is as below.
create table EmpFirstnormalformmodified
(
Emp_id varchar(100),
Emp_name varchar(100),
Emp_Address varchar(100),
Emp_mobile varchar(100)
)
And the following are the insert statements.
insert into EmpFirstnormalformmodified(Emp_id,Emp_name,Emp_Address,Emp_mobile)
select '101','Rick','Delhi','88859121'
union
select '101','Rick','Delhi','86251028'
union
select '101','Rick','Delhi','8677892410'
union
select '123','Maggie','Agra','88845555'
union
select '166','Glenn','Chennai','87445577'
union
select '166','Glenn','Chennai','87465542'
Second normal form says
For this let us assume a table called Teachersecondnormalform with the fields like teacher_id,subject and teacherage.The query for creating the tables are as follows:
create table Teachersecondnormalform
(
teacher_id varchar(100),
subject varchar(100),
teacherage varchar(100),
)
And the query to enter data is as follows
insert into Teachersecondnormalform(teacher_id,subject,teacherage)
select '101','Maths',38
union
select '111','Physics',40
union
select '222','Biology',50
union
select '333','Physics',50
union
select '333','Chemistry',50
The output is as follows
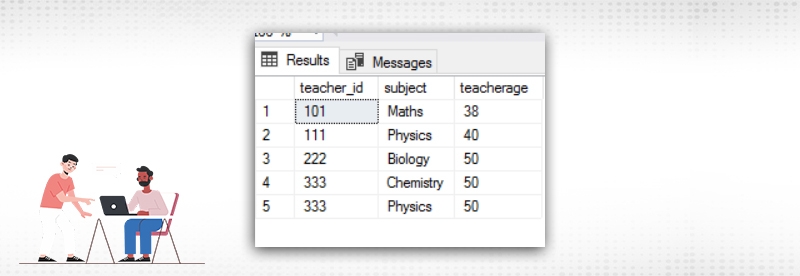
Here both the subject and the teacherage column are individually dependent on the teacher_id column. Second normal form does not allow this. To bring the table into second normal form we have to break the single table into two separate tables. The output will be as below.
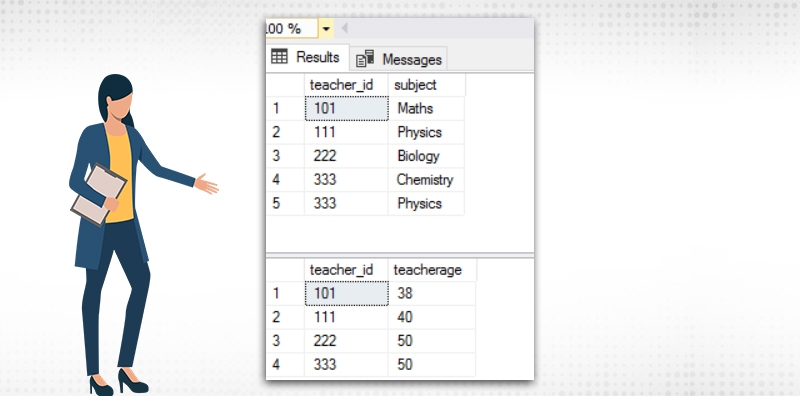
The query to create the table and insert the data into those two tables as as below.
create table Teachersage
(
teacher_id varchar(100),
teacherage varchar(100),
)
create table Teacherssubject
(
teacher_id varchar(100),
subject varchar(100),
)
insert into Teacherssubject(teacher_id,subject)
select '101','Maths'
union
select '111','Physics'
union
select '222','Biology'
union
select '333','Physics'
union
select '333','Chemistry'
insert into Teachersage(teacher_id,teacherage)
select '101',38
union
select '111',40
union
select '222',50
union
select '333',50
Third normal form says
To discuss about this let us take the example of the table empthirdnormalform with the following fields empid, empname, empzip, empstate, empcity, empdistrict.The query for the table creation is as follows.
create table empthirdnormalform
(
empid varchar(100),
empname varchar(100),
empzip varchar(100),
empstate varchar(100),
empcity varchar(100),
empdistrict varchar(100)
)
And the query to enter data is as follows
insert into empthirdnormalform(empid,empname,empzip,empstate,empcity,empdistrict)
select '101','John','282005','UP','Agra','Dayalbagh'
union
select '111','Sara','282006','West Bengal','Kolkata','Lake Gardens'
union
select '112','Sara1','282007','Maharastra','Mumbai','Bandra'
union
select '113','Sara2','282008','Tamil Nadu','Chennai','RT Nagar'
The output of the table looks like below.
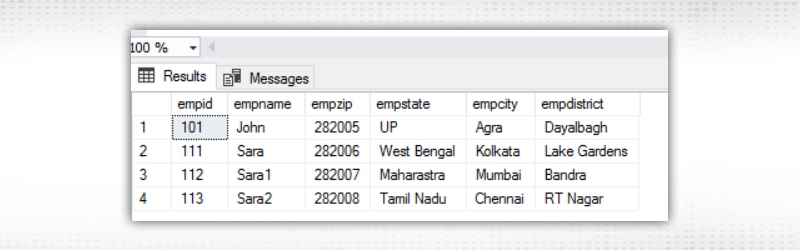
If you look closely at the table, the fields empstate,empcity,empdistrict are individually dependant on empzip.To remove this anamoly we have to create two separate tables employee and employeezip one containing empid,empname and empzip and other empzip,empstate ,empcity and empdistrict.
The query for the two new tables are as follows.
create table employee
(
empid varchar(100),
empname varchar(100),
empzip varchar(100),
)
create table employee_zip
(
empzip varchar(100),
empstate varchar(100),
empcity varchar(100),
empdistrict varchar(100)
)
Following are the query to insert data in those two tables.
insert into employee(empid,empname,empzip)
select '101','John','282005'
union
select '111','Sara','282006'
union
select '112','Sara1','282007'
union
select '113','Sara2','282008'
and
insert into employee_zip(empzip,empstate,empcity,empdistrict)
select '282005','UP','Agra','Dayalbagh'
union
select '282006','West Bengal','Kolkata','Lake Gardens'
union
select '282007','Maharastra','Mumbai','Bandra'
union
select '282008','Tamil Nadu','Chennai','RT Nagar'/p>
Over the last few paragraphs, we have learned about different aspects of normalization, its utility, advantages and disadvantages with practical examples. Hope this blog will help you to understand normalization and give you enough interest to learn normalization in more details in future.
SQL Server Training & Certification

With fact-finding market research & solicitous words, Nandita helps our digital learners globally navigate their way to profound career possibilities in IT and Management.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Interviews