Introduction
If you're a marketer or student, then you've likely heard the term "cloud computing" being thrown around. It's everywhere these days and everyone is talking about it - but what does that actually mean for the future? Cloud Computing has undoubtedly changed how businesses move their applications and data storage from on-premise servers to cloud-based systems, offering unprecedented scalability, flexibility and cost savings. Cloud computing has transformed how businesses and users utilize and access technology, making it easier and more economical than ever before. In this blog post we'll take an in-depth look at exactly what is cloud computing all about and how its latest trends can be such an important factor in shaping technology’s future.
The Current State of Cloud Computing: An Overview
Cloud computing has become a critical technology infrastructure for businesses and individuals alike. As a result, the cloud computing market has grown rapidly in recent years, with more and more companies offering cloud services. Here's an overview of the current state of cloud computing:
- Market size and growth: The global public cloud services market is expected to grow 20.7% to a total of $590, up from $490 billion in 2022, according to Gartner. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of cloud services by businesses of all sizes.
- Key players: Three key players have majority control over the cloud market. They are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These companies offer a range of cloud services, from infrastructure to software applications, and are continuously expanding their offerings.
- Popular use cases: Cloud computing is used in various ways, including data storage and backup, website hosting, application development and deployment, and big data analytics. Many businesses are also using cloud services to support remote work and collaboration.
- Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud: Many businesses are adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, which involve combining public and private cloud services from different providers. This approach allows businesses to take advantage of the benefits of different cloud services while mitigating risks associated with relying on a single provider.
- Security: Security is a major concern for cloud computing, as public networks and shared resources can pose risks. Cloud service providers are continually improving their security measures, and businesses are also taking steps to ensure the security of their data in the cloud.
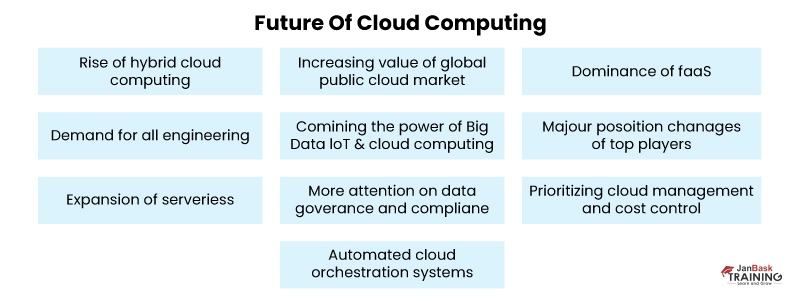
Key Trends That Will Shape Cloud Computing Of The Future

The future of cloud computing looks bright and promising, with many experts predicting continued growth and innovation in the industry. Cloud computing is expected to play an increasingly important role in the digital economy as businesses and consumers turn to cloud-based services for their computing needs.
One of the key trends in the future of cloud computing is the continued growth of hybrid cloud environments, where businesses use a combination of public and private cloud services to meet their needs.
Another trend in the future of cloud computing is the rise of edge computing, where data processing and storage are done closer to the data source rather than in centralized data centers. Cloud computing is also expected to majorly develop emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. Cloud-based AI and ML platforms are already being used by businesses to power advanced analytics and predictive modeling, and this trend is only expected to continue.
Let us look at each prediction individually.
1. Increased Adoption of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies.
Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies are becoming increasingly popular in cloud computing as businesses increasingly rely on cloud-based services and applications. A hybrid cloud is an approach where businesses use a combination of public and private cloud services to meet their needs, while multi-cloud is where businesses use more than one public cloud provider for different applications or services. This approach allows businesses to avoid vendor lock-in and take advantage of the unique strengths of different cloud providers.
The future of cloud computing looks bright for those who adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies. One of the main drivers behind the increased adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies is greater flexibility and agility in the face of rapidly changing business needs. By combining public and private cloud services, businesses can quickly scale their computing resources up or down as needed without making major changes to their infrastructure.
Another factor contributing to the popularity of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies is the growing complexity of IT environments. As businesses rely more heavily on cloud-based services and applications, they are finding that managing these environments can be challenging, especially if they are using multiple cloud providers. Businesses can simplify their IT environments and reduce complexity using a hybrid or multi-cloud approach.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The future of cloud computing is set to become even more exciting with the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies. AI and ML are going to enhance the cloud of the future in a number of ways. Cloud providers are already leveraging these technologies to develop intelligent cloud services, such as automated machine learning, natural language processing, image recognition, and predictive analytics. This will enable businesses to leverage the power of AI and ML without having to build complex models and algorithms.
AI and ML will also play a key role in optimizing resource management in the cloud. These technologies will automatically allocate resources based on demand, traffic, and other variables, reducing costs and improving performance. Integrating AI and ML technologies will also improve the performance of cloud services by optimizing resource allocation, reducing latency, and improving data processing efficiency. This will enable businesses to access and process data faster, enabling faster decision-making. Moreover, AI and ML will enable cloud providers to develop customized solutions based on the unique needs of individual customers. These solutions will be tailored to specific industries, business processes, and use cases, providing businesses with a competitive edge.
3. Advancements in Cloud Security.
Cloud computing is essential for modern business operations, allowing organizations to store and process data scalable and cost-effectively. However, there are risks associated with cloud computing, such as data breaches and other security threats. In recent years, there has been a focus on advancing cloud security measures to help mitigate these risks. These include end-to-end encryption, zero-knowledge encryption, artificial intelligence and machine learning, and enhanced security controls and features. Additionally, there is a growing focus on compliance and regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA for healthcare providers and GDPR for organizations that handle the personal data of EU residents.
The future cloud computing is closely tied to the continued advancement of cloud security measures. As businesses continue to rely more heavily on cloud-based services and applications, they will need to be able to trust that their data is secure and protected. By adopting advanced security measures, such as encryption, AI, and machine learning, and enhanced security controls and features, cloud providers can help ensure the continued growth and adoption of cloud computing in the years to come.
4. Expansion of Edge Computing
Edge computing is an emerging trend in cloud computing that is poised to transform how organizations process and analyze data. It is beneficial for IoT devices, which generate massive amounts of data that must be processed quickly to extract insights and enable real-time decision-making.
One of the key drivers of the expansion of edge computing is the increasing demand for real-time data processing. 5G networks offer faster data transfer speeds, lower latency, and greater bandwidth, making it possible to process data locally rather than sending it to a central data center. As more organizations adopt 5G networks, edge computing will likely become more prevalent.
5. Increased Focus on Sustainability for Cloud Computing.
Cloud computing has become an essential technology for many organizations, offering numerous benefits such as scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. However, as the demand for cloud computing services grows, so does the environmental impact.
To address this issue, many organizations and industry leaders are taking steps to reduce the environmental impact of cloud computing, such as investing in renewable energy sources and carbon offset programs. These programs enable organizations to offset the carbon emissions generated using cloud computing services.
6. Serverless Computing and Containers
Cloud computing has become essential to many organizations' IT strategies, offering numerous benefits such as scalability, flexibility, and cost savings.
As the demand for cloud computing services continues to grow, the cloud industry is rapidly evolving with the emergence of new cloud technologies and services. Serverless computing is a model of cloud computing in which the cloud service provider maintains the infrastructure and seamlessly allocates resources as required, enabling developers to concentrate on writing code rather than managing servers. Another emerging trend is Containers, which offer a lightweight and portable way to package and deploy applications, enabling developers to move applications between different cloud environments easily.
7. Kubernetes
Cloud computing has a highly promising future. More businesses will be moving to the cloud as a result of Kubernetes. Due to how simple it is to manage and deploy apps in the cloud, Kubernetes is a game changer. You may scale your application up or down with Kubernetes as necessary. By simply purchasing the resources you actually need, you can save money.
8. Cloud Orchestration
The process of automating and managing the deployment, configuration, integration, and upkeep of cloud computing resources is known as cloud orchestration. Making sure those resources are utilized as effectively as feasible through cloud optimization. Together, these two procedures may ensure that a company's cloud infrastructure can efficiently accommodate it's evolving needs.
9. SAES Adoption
Increased SASE use appears to be the trend of cloud computing in the future. In comparison to conventional networking methods, SASE, or software-defined networking, has a variety of benefits. One benefit is that since all network components are contained within a single platform, it is considerably easier to maintain and administer.
SASE is also far more versatile and adaptive than traditional networking, which makes it a good fit for the dynamic world of cloud computing.
10. Cloud Mitigation and Data Privacy
As more organizations and individuals utilize cloud-based solutions for data processing and storage, data privacy and security worries are only increasing. One of the main difficulties facing cloud computing is safeguarding data from misuse and unauthorized access.
Mitigating the effects of disruptions to cloud services, like outages or natural catastrophes, is another difficulty.
11. Recovery After Disaster
Numerous advantages of cloud computing include improved flexibility, scalability, and dependability. However, disaster recovery is one of the most significant advantages of cloud computing. Businesses can still access their data and carry on without interruption during a natural disaster or power loss. So any company that wishes to guarantee continuity in the case of a disaster must use cloud computing.
12. Economic
By shifting a portion of these initial fixed costs to variable costs, cloud computing lowers all businesses' initial fixed costs of entry and output. It also helped reduce entry barriers that lead to more market entrants; as each market becomes more competitive, markups tend to be kept to a minimum.
The total factor productivity (TFP) is not directly increased by cloud computing as a GPT, but Information and Communication Technology (ICT) capital does so gradually over time.
13. Modular Software
Individual programs are constantly growing in size and complexity. Therefore, the use of Cloud technologies will soon require sophisticated system thinking. Software development can be viewed from various angles since, in the future, programs will be stored elsewhere besides the cloud.
This application will run on many Cloud Service servers in different modules. This can minimize software expenses because storing program components in multiple locations is economical.
14. Data Security
Cloud storage is safe for data storage. Cloud services provided by small organizations may or may not guarantee proper data security. Therefore, by enhancing security in the future, we can stop cyber-attacks. Cloud providers offer Improved security measures, creating new opportunities to stop cyberattacks.
In addition, many cloud providers now offer end-to-end encryption, ensuring that data remains encrypted during transmission and while it is stored in the cloud. Additionally, some cloud providers are now offering "zero-knowledge" encryption, which means that only the data owner has access to the encryption keys, ensuring the highest level of security.
15. Quantum Computing
Incomparable changes are brought about by quantum computing in the commercial world. Companies like Google encourage innovation by using quantum physics to create the newest consumer items. The best illustration of how quantum computing functions when done correctly is provided by supercomputers. In order to compete, businesses like IBM, Microsoft, Google, and AWS have adapted to new quantum technologies.
Quantum computers use quantum physics to speed up the processing of enormous data sets and enable complicated algorithmic calculations. A supercomputer can boost network security and offer strong encryption capabilities for electronic communications.
Financial firms can use quantum computing to accelerate transaction processing. This strategy reduces waiting time and improves workflow.
16. Green Cloud
A company's environmental effect is considerably increased by the enormous infrastructure, electricity, and cooling needed for cloud computing. According to the US Department of Energy, data centers utilize 2% of the nation's electricity. On average, a typical commercial office block uses 10 to 50 times less energy per floor than a data center.
Cloud service providers are always seeking methods to improve the effectiveness of their infrastructure and software. Over time, even minor adjustments and enhancements can result in considerable energy savings. Because outdated electronics generate millions of tonnes of rubbish yearly, e-waste is also a concern. The desire for more effective computer hardware recycling is driven by shortages in the rare earth mineral market and interruptions in supply chains.
17. Cloud Region
Regulations, trade protectionism, and industry standards are geographically fragmented, developing new, distinct compliance ecosystems. Cloud ecosystems and regional and specialized data services are becoming consolidated.
Utilizing cloud providers outside their own nation helps consumers reduce lock-in and single points of failure. There are not enough platform services available locally in some areas. This is paving the way for legislation that governs the cross-border interchange of cloud services.
For instance, projects like GAIA-X have surfaced in European nations due to growing concerns among researchers, lawmakers, and technology vendors.
Cloud Computing and Safer Collaboration

As technology advances at an unprecedented rate, cloud computing is undoubtedly becoming the future of computing. In recent years, cloud computing has shown its potential as a powerful and reliable data storage and processing tool. However, as we all know, with great power comes great responsibility. Cloud computing security has been a significant cause of concern for many people, especially regarding collaboration.
Fortunately, cloud computing future is heading toward a safer collaboration environment. The adoption of advanced encryption methods and access controls, along with secure collaboration tools, makes it possible to safely share sensitive information with colleagues and partners, regardless of their location. As the future remains bright for cloud computing, the need for a safe and efficient collaboration environment will remain a top priority.
The Future Of Cloud Computing in 2030
In the fast-paced world of technology, the future of cloud computing is a topic of conversation that always seems to be at the forefront of people's minds. With advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things, the potential for cloud computing to transform our world in the next decade is substantial-
- Some experts predict that by 2025, the global cloud computing market will be worth over $1 trillion.
- By 2030, cloud computing could account for over 20% of the world's energy consumption.
The future of cloud computing is exciting, and as technology continues to evolve, it's likely what kind of world we'll be living in by then. However, one thing is certain - cloud computing will likely play a significant role in shaping our future.
Conclusion
The blog post "Predictions for the Future of Cloud Computing" explores the potential developments and trends in the field of cloud computing in the coming years. It discusses how the current state of the technology is rapidly evolving and how cloud computing is becoming increasingly important to businesses and organizations of all sizes. The post predicts that cloud computing will continue to grow in popularity and become even more ubiquitous, with more businesses migrating their operations to the cloud. It also anticipates that there will be an increased focus on hybrid cloud solutions, with companies utilizing both public and private clouds to manage their IT infrastructure. Additionally, the importance of data security and predicts that cloud providers will increasingly emphasize security features and certifications to reassure their customers. The future of cloud computing is bright, with the potential to revolutionize how businesses operate and interact with their customers. If you wish to make a career in cloud computing, you can enroll to any professional certification course to give yourself an edge over other candidates.
FAQs
Q1. Comment on cloud computing future aspects.
Ans:- While talking about cloud computing future, there are some assumptions that can be predicated regarding the upcoming era of cloud computing. Let’s have a look:
- The application of hybrid and multi-cloud- When businesses get more accustomed to utilizing several cloud providers, we can visualize a rise in the utilization of hybrid and multi-cloud methods.
- Greater AI and machine learning- Cloud providers will keep investing in AI and ML technologies. This will let them have advanced features including automatic scaling systems. Hence future cloud computing is bound to see a vast expansion in the technology. So, next time while asking is cloud computing the future, be sure that cloud computing is the future.
Q2. What are the ongoing trends of cloud computing?
Ans:- The recent trends of cloud computing include Edge Computing, AI and ML, Disaster Recovery, Multi and Hybrid Cloud Solution, Cloud Security and Resilience, Cloud gaming, Kubernetes, Serverless Computing, Blockchain and IoT.
Q3. What are the benefits of Cloud Computing Course?
Ans:- Cloud Computing is a leading industry providing several benefits for businesses but as a worker, a career in this domain can prove really beneficial. Some of the benefits of Cloud Computing Course include adaptability for developers, higher salary, greater job opportunities, challenging domain and creating individual startup.
Q4. What are the career opportunities that can be explored through the Cloud Computing Training Online?
Ans:- Cloud Computing Training Online opens the gate to a vast option of careers including Cloud Administartor, Cloud Support Engineer, Cloud Security Analyst, Cloud network engineer, Cloud software engineer, Cloud automation engineer, Cloud engineer, Cloud Consultant, Cloud Data Scientist and Cloud architect.
Q5. Is Cloud Computing Online courses worth it?
Ans:- Cloud Computing Online courses are extremely beneficial because it allows you to learn the concept of cloud computing from the comfort of your home without having the need to travel to a physical location.
AWS Course
Upcoming Batches
Trending Courses
Cyber Security
- Introduction to cybersecurity
- Cryptography and Secure Communication
- Cloud Computing Architectural Framework
- Security Architectures and Models
Upcoming Class
7 days 08 Jan 2026
QA
- Introduction and Software Testing
- Software Test Life Cycle
- Automation Testing and API Testing
- Selenium framework development using Testing
Upcoming Class
1 day 02 Jan 2026
Salesforce
- Salesforce Configuration Introduction
- Security & Automation Process
- Sales & Service Cloud
- Apex Programming, SOQL & SOSL
Upcoming Class
5 days 06 Jan 2026
Business Analyst
- BA & Stakeholders Overview
- BPMN, Requirement Elicitation
- BA Tools & Design Documents
- Enterprise Analysis, Agile & Scrum
Upcoming Class
8 days 09 Jan 2026
MS SQL Server
- Introduction & Database Query
- Programming, Indexes & System Functions
- SSIS Package Development Procedures
- SSRS Report Design
Upcoming Class
8 days 09 Jan 2026
Data Science
- Data Science Introduction
- Hadoop and Spark Overview
- Python & Intro to R Programming
- Machine Learning
Upcoming Class
1 day 02 Jan 2026
DevOps
- Intro to DevOps
- GIT and Maven
- Jenkins & Ansible
- Docker and Cloud Computing
Upcoming Class
1 day 02 Jan 2026
Hadoop
- Architecture, HDFS & MapReduce
- Unix Shell & Apache Pig Installation
- HIVE Installation & User-Defined Functions
- SQOOP & Hbase Installation
Upcoming Class
1 day 02 Jan 2026
Python
- Features of Python
- Python Editors and IDEs
- Data types and Variables
- Python File Operation
Upcoming Class
2 days 03 Jan 2026
Artificial Intelligence
- Components of AI
- Categories of Machine Learning
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Recurrent Neural Networks
Upcoming Class
16 days 17 Jan 2026
Machine Learning
- Introduction to Machine Learning & Python
- Machine Learning: Supervised Learning
- Machine Learning: Unsupervised Learning
Upcoming Class
8 days 09 Jan 2026
Tableau
- Introduction to Tableau Desktop
- Data Transformation Methods
- Configuring tableau server
- Integration with R & Hadoop
Upcoming Class
9 days 10 Jan 2026