 New Year Special : Self-Learning Courses: Get any course for just $49! - SCHEDULE CALL
New Year Special : Self-Learning Courses: Get any course for just $49! - SCHEDULE CALL

 New Year Special : Self-Learning Courses: Get any course for just $49! - SCHEDULE CALL
New Year Special : Self-Learning Courses: Get any course for just $49! - SCHEDULE CALL

Searching, reporting, monitoring and visualizing now has become easy with Splunk- a software for your enterprise data.Your machine data is taken as input by Splunk to turn them into powerful operational intelligence through real-time insight to your data in the form of achart, reports, alerts etc. To reach higher in your career goals, you can take different certifications available and handle theexcess amount of data. Implementing Splunk can take your business to a next level but the question is do you possess the skills to be a Splunker? If yes then be prepared for the intense competition and tough interview questions. In this blog, let’ have a look at some of the most common Splunk interview questions. The questions covered in this blog post have been shortlisted after collecting inputs from many industry experts to help you ace your interview.
Answer: The platform of Splunk allows you to get visibility into machine data generated from different networks, servers, devices, and hardware. It can give insights into the application management, threat visibility, compliance, security, etc. so it is used to analyze machine data.
Answer: The data is collected from the forwarder from the source and forwarded to the indexer. The data is stored locally on a host machine or cloud. Then on the data stored in the indexer the search head searches, visualizes, analyzes and performs various other functions.
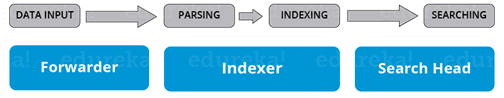
Answer: The main components of Splunk are Forwarders, Indexers and Search Heads.Deployment Server(or Management Console Host) will come into the picture in case of a larger environment.
Deployment servers act like an antivirus policy server for setting up Exceptions and Groups so that you can map and create adifferent set of data collection policies each for either window based server or a Linux based server or a Solaris based server.
Answer: Splunk has a lot of competition in the market, for performing IT operations, for analyzing machine logs, providing security and doing business intelligence. But, there is no one single tool other than Splunk that can do all of these operations and that is where Splunk comes out of the box and makes a difference. Splunk helps in scaling up infrastructure and get professional help from a firm supporting the platform.
Answer: Most of the riles can be shared on the same machine including Indexer, Search Head and licensed Master. However, in case of larger deployments, the preferred practice is to host each role on stand-alone hosts.
Answer: The benefits of getting data into Splunk via forwarders are bandwidth throttling, TCP connection and anencrypted SSL connection for transferring data from a forwarder to an indexer. The data forwarded to the indexer is also load balanced by default and even if one indexer is down due to network outage or maintenance purposes, that data can always be routed to another indexer instance in a very short time.
Answer: In Splunk, license master ensures that perfect amount of data gets indexed. It is important to ensure that the environment stays within the limits of the purchased volume as Splunk license is based on the data volume that comes to the platform within a 24-hour window.the purchased volume
Answer: Splunk DB is a general SQL database plugin which enables adding database information with Splunk reports. It helps in providing scalable and reliable integration between relational databases and Splunk Enterprises.
Answer: A ‘license violation’ error appears if you surpass the data limit. This license warning stays upto 14 days. In a commercial license, there are 5 warnings within a period of 30 days window before which your Indexer’s search results and reports stop triggering
Answer: The Summary index is the default summary index. If you decide to run many types of summary index reports you may need to create additional summary indexes.
Answer: Look at the below image which gives a consolidated view of the architecture of Splunk.
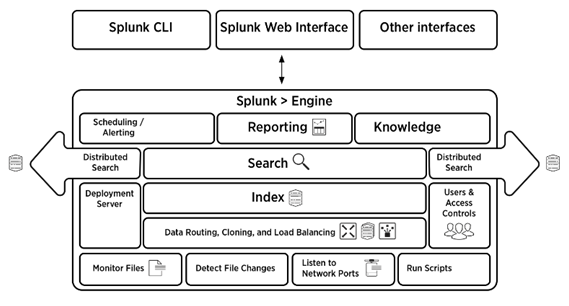
Answer: There are four components in the Splunk architecture. They are:
Answer: If the license master is unreachable, then it’s not possible to search the data. The activities of incoming data into the indexer would be normal but you would receive a warning message saying that you have exceeded the indexing volume and so you either need to purchase a high capacity of license or reduce the amount of incoming data.
Answer: Knowledge objects can be used in many domains. Few examples are:
Answer: Questions regarding Search Factor and Replication Factor are most likely asked when you are interviewing for the role of a Splunk Architect. SF & RF are terminologies related to Clustering techniques
Answer: You can start explaining Workflow actions by first telling why it should be used.You can create workflow actions which will automate certain tasks. For example:
Answer: A Splunk bucket is the directory that contains indexed data. Splunk buckets also have events of a certain period. Bucket lifecycle includes following stages:
Answer: Alert manager enables you to view the link to have alook at the search results. It displays the list of most recently fired alerts, for example, alert instances.
Answer: Search head pooling connects server and shares load, configuration and client data. Search head clustering is a part of Splunk enterprise search.
Answer: The transaction command is useful in two areas. Two transactions are not identified by unique id anymore. In this case, the identifier is re-used to identify web sessions. Here, time span or pauses are used to divide data into transactions. In cases when an identifier is used again, a specific message may identify the beginning or end of a transaction. Usually, stats command is used in a distributed search environment as it performs better. If a unique id is an identifier, stats can be used.
Answer: This is a common question aimed at candidates appearing for the role of a Splunk Administrator. When you want to notify an enormous condition in your system, time alerts can be used.
For example, send an email notification to the admin when there are more than three failed login attempts in a twenty-four hour period. Different options that are available while setting up alerts are:
Answer: There are three ways of doing this.
Answer: To reset the admin password, log into the server on which Splunk is installed and rename the password file, and then restart Splunk. After doing this, you can log in using the default username: admin password: change me
Answer: For creating a structured hierarchical model of your data Data Models are used. When you want to want to make use of that information without using complex search queries or you have a large amount of unstructured data, you can use Data Models.
On the other hand with pivots, you have the flexibility to create the front views of your results and then pick and choose the most appropriate filter for a better view of results.
Answer: There will be a lot of events coming to Splunk in a short time. Thus it is a little complicated task to search and filter data. But, thankfully there are commands like ‘search’, ‘where’, ‘sort’ and ‘rex’ that come to the rescue. That is why filtering commands are also among the most commonly asked Splunk interview questions.
Answer: Lookup command is the topic into which most interview questions dive, with questions like: Can you enrich the data? How do you enrich the raw data with external lookup?
If you want to receive some fields from an external file, you can use Lookup commands. It is usually used to narrow the search results. An inputlookup basically takes an input as the name suggests.
Answer: Eval’ and ‘stats’ are among the most common as well as the most important commands within the Splunk SPL language and they are used interchangeably in the same way as ‘search’ and ‘where’ commands.
| Stats | Chart | Timechart |
| Stats is a reporting command which is used to present data in a tabular format. | The chart displays the data in the form of a bar, line, or area graph. It also gives the capability of generating a pie chart. | A time chart allows you to look at bar and line graphs. However, pie charts are not possible. |
| In the Stats command, you can use multiple fields to build a table. | In Chart, it takes only 2 fields, each field on the X and Y axis respectively. | In Timechart, it takes only 1 field since the X-axis is fixed as the time field. |
Answer:
Answer: You can extract fields from either event lists, sidebar or from the settings menu via the UI. The other way is to write your own regular expressions in props.conf configuration file.
Answer: As the name suggests, Search time field extraction refers to the fields extracted while performing searches whereas, fields extracted when the data comes to the indexer are referred to as Index time field extraction.
Splunk training includes training in basic search, sharing and saving of results, creating tags and event types, generating reports, and chart creation hope this set of Splunk interview questions and answers will help you in preparing for your interview.

Apache Spark Interview Questions and Answers for 2024

Hive Interview Question And Answers


Teradata Interview Questions and Answers

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Download Syllabus
Get Complete Course Syllabus
Enroll For Demo Class
It will take less than a minute
Tutorials
Interviews
You must be logged in to post a comment