10
JanYear End Sale : Get Upto 50% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
Year End Sale : Get Upto 50% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
A/B testing has become crucial for companies looking to boost conversion rates and improve user experience. It is a vital part of the development cycle to guarantee quality and boost the confidence to release the software to the buyers. This blog on AB test interview questions and answers are for you, whether you're an aspiring analyst getting ready for your following interview or an experienced expert trying to improve your skills.
In this blog, you'll have everything about A/B testing and will be thoroughly prepared for your upcoming interview with a/b testing interview questions. So let's get started and learn how to ace your following A/B testing interview!
Key takeaways:
Now, let's proceed to understand what is meant by a/b testing.
QA Software Testing Training

Wondering what is a/b testing in data science? A/B testing identifies the basic version of a product trait that works better to reach the aim. This is known as split testing, and it can be utilized to refine the product development process and user interface. Here’s an example to help you better understand the topic.
An instance is to a/b test a button present at the screen’s bottom with two colors, and the goal is to determine the button that got higher clicks. The goal is to determine the button that got higher clicks. Another example is a two-flow in an item where the treatment and control group visualizes two features. The target is to identify the feature contributing to more lavish in-app spending for two weeks after use.
Preparing for an interview calls for a lot of hard work and sincerity. Your work experience and data science certification are useless if you can’t crack the interview process. Now, look at some of the a/b testing interview questions to help you ace the interview.
Ans. To run an A/B test, you must create two renditions of one piece of content, with changes to a single variable. Then, you'll show these two versions to two similarly sized audiences and analyze which one executed better over a specific period (long enough to make accurate conclusions about your results). This is amongst the other common ab testing interview questions.
Ans. This is the basic way to conduct an A/B test. Anyone prepping for ab test interview questions should be able to answer them immediately.
Ans. Testing incremental changes, such as UX adjustments, new features, ranking, and page load times, is where A/B testing excels. You may compare the results before and after the modifications to decide whether the adjustments have the expected outcome.
When testing significant shifts, such as new products, new branding, or entirely new user experiences, A/B testing must function more effectively. In certain situations, impacts might promote stronger-than-usual engagement or emotional reactions influencing users' behavior. It surely is one of the frequently asked a/b testing questions.
Ans. The average recommended A/B testing time is two weeks, but you should always identify key factors relevant to your conversion goals to determine the best length for a test to meet your goals.
Ans. Analytics is at the heart of planning, execution, and performance recommendation throughout the lifecycle of any A/B test.
The outcome of a test hypothesis demands a strong foundation in analytics. You need to understand current performance and traffic levels. In terms of web analytics (for example), there are some key data points that your analytics system will provide during the planning process, including
Without this grounding in analytics, any test scenario or performance assessment will likely be based on personal preferences or impressions. Testing will often prove those assumptions to be incorrect. Ensure to learn about this topic when preparing for a/b test interview questions.
Read more: Top 100 Business Analyst Interview Questions And Answers
Ans. This might be one of the most crucial ab testing interview questions. Here are the steps to consider with small sample size issues while a/b testing.
1. Skip A/B testing
When testing for the direct reasons of estimation and business risk management there is scarcely any reason to A/B test. In such scenarios, you are likely better off skipping A/B testing entirely and simply implementing the fix.
2. Accept higher uncertainty.
It should be well-known that we can lower the required sample size by
3. Use a sequential testing procedure.
Utilizing sequential testing statistics is an extended strategy that can result in 20%-80% faster tests, indicating that a sequential test would, on average, demand 20% to 80% fewer users to operate compared to an equivalent fixed-sample size test.
4. Use conversion to the next step as the primary KPI.
It is to see if it makes sense to measure the outcome from the step you are optimizing in terms of people who make it to the next step, e.g., adding a product to the cart or starting the checkout, instead of in terms of the final measurable outcome, e.g., purchase rate or average revenue per user.
Ans. When we are in a dilemma between two features, we test them against each other in the real world: we give feature A to a random set of members and feature B to another set and compare the results. Are users of feature A more engaged? Do they have a better experience with our products? If so, feature A wins.
A/B testing is a common practice in many settings; however, most methods rely on a strong assumption: when comparing features, The activity of feature B users does not impact A and feature B, the behavior of feature A users. In other words, most methods assume no interference, sometimes called the "network effect," between features.
Still having cold feet about the interviews and worried about ab test interview questions? Check out some common, most frequently asked questions in all the interviews!
Ans. Even in an ideal data world, concluding a test can still be difficult. Let’s say, this time, the experiment hits the sample size required, but there is an unclear winner. An unclear winner is a less-than-desired lift, if any, with no benefits as you funnel down to secondary and behavioral metrics. All of those could be possible options, but first, we must dive deep into the data to see what action we need to take.
There are four primary options to take with your inconclusive test data.
1. Segment your data:
2. Removing multivariate impacts test data:
Isolate the visitors in multiple tests, or if possible, target and omit a step in your data flow that another test was measuring.
3. Move Upstream:
After looking at the various segments and removing crossover test data, you still may not know if the test is a success or failure. Conversion rates still appear flat. You may want to look upstream to see how users interacted with the larger part of your funnel. There is a possibility that the KPI being analyzed could be too far down the funnel to see the statistical impact.
4. Remove Biases:
Were there biases during your A/B test? This occurred when visitors who historically spent more per purchase were unevenly distributed into the variant group. Neglecting to see this type of bias could result in rolling out a test based on bad data. If you realize you have tested with a biased audience group, some tools may allow you to remove biased data segments, but more than likely, it may be best to retest a test without biases.
A/B Testing can be exciting. You never know until you test something that you’re going to get. However, you can maintain control even when results surprise you through preparation and planning. Remember to practice a/b test interview questions and answers before your big interview.
Ans. To decide the duration of a test, we need to obtain the sample size of a test, which requires three parameters. These parameters are
The rule of thumb is that sample size n approximately equals 16 (based on α = 0.05 and β = 0.8) multiplied by sample variance divided by δ square, whereas δ is the difference between treatment and control:
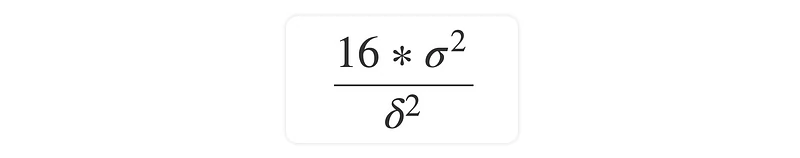
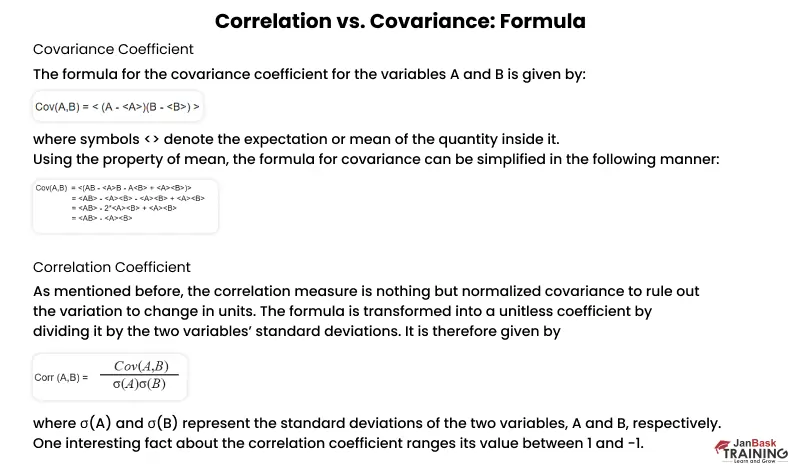
Ans. Covariance values represent the ability of two variables to increase or decrease concerning their mean values. Covariance values can be positive, negative, or zero.
Correlation is a normalized version of covariance. Covariance is a quantity that depends on the units of the variables used. Thus, if the units of either or both variables are changed, the digits of covariance also change. To solve this problem of units, correlation was introduced. Correlation values can be positive, negative, or neutral like covariance values.
We will now dive into correlation and covariance math to understand how the two are mathematically different.
Ans. Finding a proper A/B testing tool isn’t a problem anymore. Here is a list of the top A/B testing tools, with corresponding reviews from A/B testing experts to help you decide.
Cleared your written test round, yet dreading the HR round? HR interviews measure a candidate's personality- whether he or she can take the job role. Look at the top HR interview questions and answers that will boost your confidence. Let us move to the advanced a/b testing interview questions.
Ans: When you prepare for interviews, you must complete these a/b testing questions. The prime consideration is that the probability of false positives (Type I errors) rises while multiple t-tests are run aggressively. Here aggressively does not indicate “a lot.” If each test includes false-positive probability ψ, the probability of never receiving a false positive in n many tests is (1-ψ)n, which becomes zero since n→∞. In this case, the two excellent ways to consider are
Ans: First, you need to comprehend what you wish to measure. Then you can design and perform the test. The four factors in consideration include:
Ans: A user-tied test refers to a numerical test where the experiment divides the users into two groups on the user level, while a user-untied test refers to the test where they are not split on the user level. In a user-untied test on a search engine, traffic is bucketed at the search level because a search engine does not require you to sign in to utilize the item. But it still needs to a/b test various algorithms to understand which is better.
A con of a user-untied test is partiality since the users aren’t split and can observe both treatments. Be well prepared with these a/b testing interview questions and answers.
Ans: The significance level of a test is 0.05, and the power is 0.8, but these numerals vary according to the amount of adaptation that requires to be identified for design alteration. The amount of adaptation required can be linked to external aspects like the time required to design the change after the decision. A p-value of <0.05 depicts that the hypothesis is correct and the outcomes are not invalid.
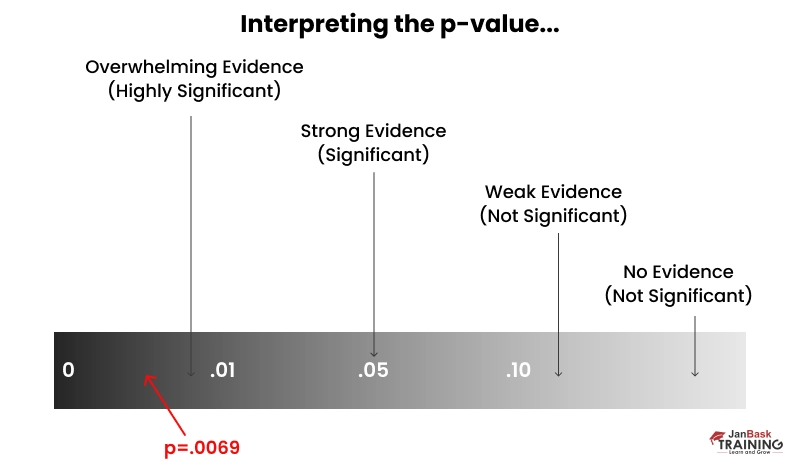
Ans: If you observe the fundamental metric of the p-value, you know that the industry standard is .05, which indicates that 19 out of 20 times you experiment, you will understand that there is a difference between the populations. But you should also include extra considerations such as the experiment's sample size, the time it consumed before the manager measured the p-value, and the manager's approach to measuring the p-value. Make sure to remember while prepping with ab test interview questions.
Ans: There can be cases where bucket testing will provide inappropriate results. Some causes you might stop AB testing leading to its failure, include
Ans: While testing multiple variants, the probability that you attained significance coincidentally is high. To understand this, you can calculate the probability of a significant outcome by considering the inverse of the p-value. Suppose P(one significant outcome) = 1 - P(no. of significant outcome) = 1 - (1 - 0.05) = 0.05. There's a 5% probability of getting a significant outcome coincidentally. When you test 20 results are get a variant back, you can question its significance or the possibility of its coincidence.
Ans: Test length is a function of sample size because you will require considerable time to run the test on X users every day till you get the overall sample size. But time brings variance into an a/b test. The longevity of the experiment is related to traffic volume and the respective variables being experimented with. There can be such factors that are only available in a particular week. The thumb rule is to run the experiment for two weeks, given that you attain the sample size within that time. Split tests usually run for 2-8 weeks. One of the most asked ab testing interview questions.
Ans: The following tests can be implemented while looking for options other than a/b testing:
Learn more about Data Science and what is a/b testing in data science.
Ans: Guaranteeing proper distribution of users with many attributes is necessary to ensure the a/b test results are correct. More randomization will lead to clearer variables later. Specific considerations are vital when a/b tests are provided to users, such as, is every new user provided the test? How is it influencing the assessment of the present users? If the tests are given to every user, and few signed up for the website this week, and the rest have been longer, is the ratio of new users to present users indicative of the more significant population?
To ensure proper randomization, you need to confirm that the control and Variant groups are of the same size so that they can be adequately compared.
Ans: Some generic metrics you need to consider while running an a/b test are mentioned below.
The variable must be used based on the hypothesis and what you are testing. While testing a button variation, button hover time and CTR are the suitable options, but while experimenting with messaging choices, time spent on the page and bounce rate are good metrics. All these a/b testing interview questions and answers will land you your dream job.
Ans: a/b testing or split testing works well to implement UI design changes, but you can also use it for:
Ans: The main reason for the failure of an a/b testing lies in the wrong goals of the test. Utilization of a/b testing to test a theory is a good idea. For example: Would providing an image to the landing page raise conversions? Are people more inclined to click a red or blue button? Such alterations are quantifiable. a/b testing is a bad idea to test lame theories, such as testing two different designs with different variants. A proper landslide winner must exist, or testing various designs will lead to uncertainty. Be prepared for these a/b test interview questions with confidence.
Ans: A null hypothesis refers to the hypothesis contributing to a difference in results due to a sampling mistake or standard variation. For example, flipping a coin is an excellent instance to help you understand the term. There is a 50/50 probability for the coin to land on heads, but often the result is 51/49. The more the coin is tossed, the greater the probability of getting a 50/50 result. Statistics include proving or disproving a fact to debate the null hypothesis. This means running the test longer to knock off any coincidental results. It is a sure shot of one of the crucial a/b testing interview questions.
Ans: a/b testing worsens search engine rankings as it can be categorized as duplicate content, which search engines don’t approve. However, this myth is wrong. Google’s Matt Cutt says such an experiment upgrades the website's functionality.
Ans: It is one of the frequently asked a/b testing interview questions. Yes, it is also possible to run a/b tests on emails, PPC campaigns, and calls-to-action. The details are below:
Ans: Replay tools receive pertinent details about website user activities. Replay tools also let you click maps and heat maps of user clicks and verify the extent to which the user is browsing the site. Replay tools such as Mouse Flow let you see a visitor’s session as if you are with the visitor. Video replay tools offer better insight into the aspect of the visitor browsing several pages on the website.
QA Software Testing Training

Ans: The detailed workflow for a/b testing is as follows:
Ans: The other term for Confidence interval in a/b Testing is the measurement of deviation from the average on several counts of samples. For instance, 22% of individuals prefer product A, with +/- 2% of a confidence interval. This interval depicts the upper and lower limits of the individuals who prefer product A and is also called the margin of error. The margin of error should be tiny to attain a preferable outcome in the average survey. And you should be confident while you answer the a/b testing interview questions.
Ans: A/b testing is helpful for businesses to understand the technique of improvisation in their products, websites, and bottom lines. It further offers proper knowledge for organizations to reduce risk factors, engage customers, convert buyers, and accelerate sales. a/b Tests will represent how businesses can utilize the available resources in the best way to upgrade the Return On Investment. The organizations that maximize the maximum profits are the ones that become most successful, and hence a/b Testing is an important place for business people all over the globe. You should be prepared for all kinds of a/b testing interview questions.
Ans: Several variations can be utilized in an object, such as using bullets, altering the numbering of the prime elements, altering the font size and color, and others. Different a/b Testing tools in the market consist of a visual editor to help these changes be done correctly. The right tools must be chosen for the a/b testing to be run successfully.
Frequently used tools that can be applied include Visual Website Optimizer, Google Content Experiments, and Optimizely.
Ans: VWO helps you to test various versions of the same web page. It contains an editor known as WYSIWYG, which implies, “What you see is what you get.” This allows you to make the changes and run experiments without altering the page's HTML code. The headlines and numbering of the text can be updated, and an a/b test can be run without changing the IT resources.
The process of creating variations through WYSIWYG is simple. First, open the webpage in the WYSIWYG editor and implement as many changes as you want to a web page. The changes include Change Text, URL, Edit/Edit HTML, Rearrange and Move. Mark it crucial while you revise before your interview with important a/b testing interview questions.
Ans: SRM happens when the count of individuals or traffic categorized in the control and treatment groups in a split test or a/b Test fluctuates significantly from the desired or planned allocation ratio. For example, if we plan to categorize 50% of the traffic to the control group and the rest 50% to the treatment group, but the allocations become 60% for the control group and 40% for treatment due to some error, then there is an SRM. It is depicted in the image below.
Ans: SRM has a significant impact in a/b testing, as mentioned below:
Ans: A Test is a null or dummy test, a split test variation. Users are split into two similar control groups. Both groups get the same experience with no alterations. AA test is used in the following cases:
Ans: The Statistical Test to be used for a split test on Click Through Rate can be the two-proportion z-test. This is the correct test to compare the ratio between two groups, like CTRs in a split test. The test predicts that the data follows a binomial distribution and that the sample sizes are sufficient for applying the Central Limit Theorem. This lets us use a generic distribution to assume the binomial distribution. You might want to remember while revising a/b testing interview questions.
Ans: P-Hacking is the manipulation of data analysis to report the outcome selectively to get statistically significant findings when they may not exist. It’s the kind of research misconduct that contributes to erroneous discoveries and false conclusions. P-Hacking can happen due to multiple testing, selective reporting, data peeking, or cherry-picking.
Ans: Peeking has several effects on the test results:
Ans: Memorize all these elements for a/b test interview questions. The main elements of an a/b Test are as follows:
Ans: The sample size for an a/b test can be determined by the below-mentioned formula:

Ans: The following method helps to select the appropriate metrics to measure the success rate of a split test:
Ans: It is a very common yet one of the crucial a/b testing interview questions. The following metrics are usually implemented in an a/b Test:
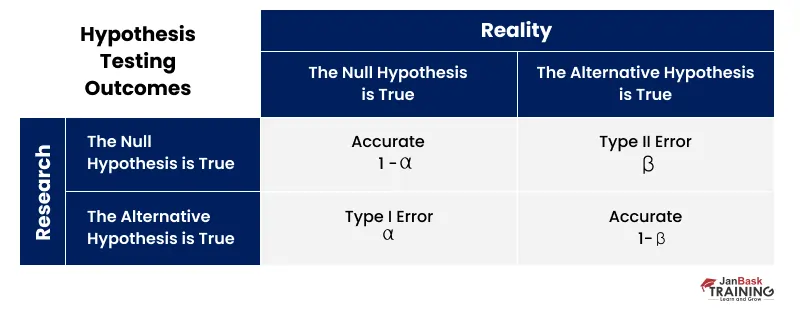
Ans: Type I error is seen when one rejects a true null hypothesis for the population. It denotes that the test and control could not be differentiated. Type II errors occur when a null hypothesis that is false for the population is rejected. It denotes that the test and control could be differentiated, but the differences could not be detected.
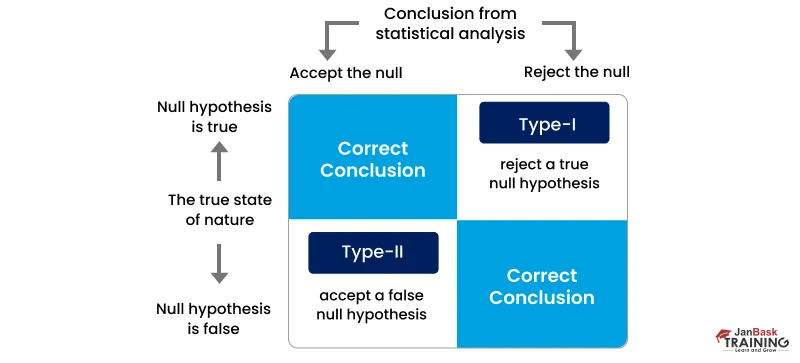
Ans: A control refers to the current version of a landing page or webpage being tested against. Sometimes we consider testing two versions of a page that did not exist previously. In such a case, we must select one variation and refer to it as the control. We need to select the version that resembles the currently designed web pages and utilize the other version as a treatment.
Ans: If the results are unreliable enough and have not considered any mistakes to the test’s validity, we can rerun the test. Treating it as a completely different test, we must observe if the outcome replicates. If it does, then we do have a set of reliable results.
Ans: Survey tools are required to gather qualitative feedback from the website. In regard to this, the returning visitors are asked a few survey questions. The survey focuses on asking simple questions and allows the visitors to submit their views or choose from pre-given options.This might get asked as one of your ab testing interview questions .
Ans: The following process after the completion of an experiment involves analysis of the results. A/b testing tool will display the data from the experiment and will point out the difference between the way various variations of the web page are done. It will further display a noticeable distinction between multiple variations through the utilization of mathematical methods and statistics.
Ans: You must select the ON button on the side panel to integrate Optimizely with Google Analytics. Then there must be a Custom to populate with Optimizely experiment data.
The Google Analytics tracking code should be placed at the bottom of the
section. However, Google Analytics integration will not work smoothly if the Optimizely snippet is not above the Analytics snippet.
Ans: Google Analytics comprises two data analysis options, Universal Analytics, and Classic Google Analytics. Universal Analytics allows the user to utilize 20 simultaneous a/b tests transferring data to Google Analytics, but Classic Google Analytics allows up to five a/b tests.
Ans: Multivariate testing depends on a mechanism similar to a/b testing, but it compares more variables and gives more insight into how the variables behave. a/b testing involves dividing the traffic of a web page between multiple versions of the design. Multivariate testing measures the efficiency of the design.
Ans: Testing different variables at a time includes properly identifying which of the variables has made the difference. You can state that a certain page has outperformed the other, but when there are three or four variables on each page, it can’t be assured why a particular variable is a drawback for the page. It’s also impossible to replicate the good elements of other pages. Do not miss this while prepping for a/b testing interview questions.
Ans: After the test begins and the results pour in, you are eager to find the winner. However, the initial stages should not be taken to interpret the results. You need to wait until the test reaches statistical significance and revisit the actual hypothesis. If the test disproves the hypothesis, you can draw a few conclusions. Staying disciplined about aligning the results to certain changes is important while interpreting the test.
Ans: A one-tailed hypothesis test is responsible to find the effect in one direction (B is better than A). A two-tailed test finds the effect in both direction (B is different from A).
A one-tailed test is used when there is a certain directional hypothesis, and a two-tailed test is implemented when you want to know the difference between the two entities. With these a/b test interview questions and answers you will future proof your career.
Ans: To ensure Valid Hypothesis Testing, the following measures can be taken:
Ans: It is among the important a/b testing questions. Addressing SRM in Hypothesis Testing involves the following steps:
Ans: Observing the real measurement of the p-value, we know that the standard is .05, which implies that 19 out of 20 times that the test is conducted, you will get the correct result that there's a distinction between the populations. But you need to see certain considerations regarding the test in the measurement method, which include: the sample size of the test, the time duration before the product manager measured the p-value, and the way the product manager measured it. Make sure you answer confidently by prepping with these helpful ab testing interview questions.
Ans: A holdback experiment offers a certain feature to a huge range of users but also holds back or detains the remaining percent of users from observing their behavioral changes over a certain time span. This further helps the analysts to quantify the lift of a transformation over a longer time span.
A/b testing in marketing has several benefits according to the test you want to do. A few elements you can test in the business areas include subject lines, CTAs, headers, titles, fonts and colors, images, graphics, body, and navigation. There are various options, and the tests are necessary for the business owing to their cheap rate and high reward. Let’s understand through an example. Suppose you hire a content creator with a $50,000/year salary. He publishes five blogs weekly, accounting for 260 articles every year.
If the average post on the blog gets ten leads, it costs more than $192 to get ten leads. Now, that’s a significant change. Then if you ask the creator to work for two days creating an a/b test on an article, you can spend $192 because you publish fewer articles.
However, if the a/b test finds that the conversion rate can be raised to 20 leads, you burn $192 to double the customers' count. If the test fails, $192 is wasted, but you can improve the next a/b test. And if it succeeds, then You spend $384 to raise the revenue. So the final success will counterbalance the rate of performing the test irrespective of the number of times the a/b test fails.
QA Software Testing Training

A/B Testing is a great tool that helps uncover the power of the website. Optimizing the elements helps refine the user experience and raise customer engagement. A/B testing comprises making data-driven decisions to guarantee that you provide the best customer experience. You can also visit to get a detailed insight on ab testing.
Ace your interviews with flying colors with help of these a/b testing interview questions and answers we have curated for you. If you have any doubts regarding the concept, then Janbask Training is the right platform to help you grasp better knowledge.
Q1. What is data sampling in a/b testing?
Ans: The sample count varies according to the number of experiments done. The number of conversion rates is referred to as a sample, and the method to gather these samples is called data sampling.
Q2. What are Alpha and Beta in a/b testing data science?
Ans: Alpha signifies the probability of type I error, also known as the significance level. Beta refers to the chance of type II error.
Q3. What is a p-value?
Ans: P-value refers to the number that shows the probability of someone finding a certain set of observations in case the null hypothesis is true.
Q4. What is the main difference between one-tailed and two-tailed tests?
Ans: One-tailed tests consist of one complex area, and two-tailed tests have two complex areas. One-tailed tests indicate the chance of an effect in a single way, and two-tailed tests do the same in both positive and negative directions.
Q5. When is the right time to run a split test?
Ans: a/b test or split test is done to assess the success of a newly launched feature of a product. It raises user engagement and conversion rate and decreases bounce rate. a/b testing is further important in data science because it is the most suitable way to quantify product or marketing strategy transformation.
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Interviews
Kairo Gray
Hi! This is a very informative blog. It emphasizes on the role of ab testing data science and also provides a range of a/b testing interview questions to help ace the interview at one go.
JanbaskTraining
Thank you for your kind words. Keep reading and learning!
Bill
Most questions covered. Good work.
JanbaskTraining
Thank you for reaching out to us. So, if your number of visitors is high enough, this is a valuable way to test changes for specific sets of visitors. A common segment used for A/B testing is splitting out new visitors versus return visitors. This allows you to test changes to elements that only apply to new visitors, like signup forms.
Manny
What is a summary of AB testing? Could you help me out a bit.
JanbaskTraining
Thank you so much for your appreciation. Keep reading!
Phil
Good questions and answers on ab testing interviews
JanbaskTraining
Thank you for your valuable feedback. Keep reading!
Lewis
I was searching for the important interview questions. Fount it.
JanbaskTraining
Thank you for reaching out to us. Be concrete. Provide the percentage lift or loss, compared to the original, conversion rates by variation, and the statistical significance or difference interval. Lessons Learned: This is your chance to share your interpretation of what the numbers mean and key insights generated from the data.
Gloria
How do I share my ab test results?
JanbaskTraining
Thank you for your kind words. Keep reading and learning!