 Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL

 Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL

Are you looking for the most asked Java advanced interview questions, Java viva questions, & most importantly Java interview questions for freshers? It can be quite tricky to match the expectations of a recruiter thereby you need to learn the latest Java viva questions & Java advanced interview questions and answers frequently asked!
A plethora of job opportunities are available for Java Developers and so the competition is stiff. Therefore our goal in providing these Java viva questions and Java interview questions for freshers is to help you gain a deeper understanding of the language and be better prepared for your Java job interviews.
In this blog, you will go through the top Java viva questions & Java interview questions for freshers that you will come across in Java interviews. Let us have a glance at a few of the important Java programming interview questions and Java advanced interview questions here:
Java Certification Training Online

Here is a list of some frequently asked advanced Java interview questions and answers for freshers. These Java advanced interview questions, Java interview questions for freshers, Java viva questions will also enhance your knowledge on Java.
Let’s check out the advanced java interview questions and Java interview questions and answers for freshers.
Let's begin with the first set of basic core Java technical interview questions, which are primarily relevant for freshers.
Ans: Java is an object programming language that was premeditated to be moveable across several platforms and operating structures. This language was developed by Sun Microsystems.
Java is exhibited after the C++ programming language and comprises special structures that make it perfect for programs on the Internet.
public class JanBask{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}
Ans: Here's a breakdown of their distinctions:
C++ lacks platform independence, adhering to the "write once, compile anywhere" principle. In contrast, Java generates platform-independent bytecode through its compiler, allowing Java programs to run on any machine, adhering to the "write once, run everywhere" mantra.
C++, originating from C, is highly compatible with other high-level languages. Java, however, is less compatible with most other languages, its compatibility primarily aligning with C and C++.
C++ permits direct access to native system libraries, making it suitable for system-level programming. In contrast, Java's native libraries do not support direct calls; you must use the Java Native Interface or alternative methods to access them.
C++ incorporates features from both procedural and object-oriented languages. Notably, Java's standout feature is automatic garbage collection, while it lacks support for destructors.
C++ treats primitive and object types with consistent semantics, while Java distinguishes between primitive types and object classes, offering differing semantics.
Java combines compilation and interpretation, generating platform-independent bytecode from the source code. Conversely, C++ is solely a compiled language, translating source code into object code for execution.
These are the most important Java interview questions and answers for freshers. Let’s check out!
Ans: Java is a programming language that was first developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems (which has since been acquired by Oracle) in the early 1990s. The language was designed with the goal of being "write once, run anywhere," meaning that code written in Java should be able to run on any platform without modification.
In 1995, Sun Microsystems released the first version of Java, called Java 1.0, which included the basic features of the language. This included the ability to create standalone programs as well as applets (small programs that run within a web page).
Over the years, Java has undergone several updates and improvements, with new versions being released regularly. Some of the most notable versions include Java 1.1 (1997), which added support for inner classes and JavaBeans, and Java 5.0 (2004), which introduced generics and annotations.
Ans: Static Variables:
Static Methods:
Static Classes:
In summary, while static methods and static variables are fundamental features of Java, static classes are not directly available. Instead, Java provides the concept of static nested classes for specific use cases.
Q6). Why is Java Perceived to be Platform-Independent?
Ans: This is because platform-independent is the term that means “write once run anywhere”. Java is referred to because of its bytecodes that have the capacity to run on any system or device whatsoever irrespective of the underlying operating system.
Ans: Java is a general-purpose, object-oriented programming language that is known for its features such as:

Ans: Java is not cent percent object-oriented because it utilizes eight types of primitive datatypes named boolean, byte, char, int, float, double, long, and short which are not objects.
Ans: Generics in Java offer compile-time type safety, which enables the detection of inappropriate types during compilation, preventing runtime errors. They allow developers to define a single method declaration, a group of related methods, or associated types through a class declaration.
Ans: In Java, a constructor is a special type of method that is used to initialize an object when it is created. It is called automatically when an object is created using the "new" keyword, and it is used to set up the initial state of the object.
A constructor has the same name as the class, and it does not have a return type (not even void). Constructors can be overloaded, which means that a class can have multiple constructors with different parameter lists.
Here is an example of a simple class called "Person" that has a constructor:
class Person {
String name;
int age;
// constructor
Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
To create an instance of the Person class and initialize it using the constructor, we would use the following code:
Person person1 = new Person("John", 30);
There’s a third one called Copy constructor. Similar to C++, Java does offer the concept of a copy constructor. However, unlike C++, Java doesn't automatically generate a default copy constructor if you don't explicitly define one.
Ans: A Copy Constructor in Java is a specialized type of constructor used for initializing an object by duplicating the values of another object belonging to the same class. This allows you to create a new instance with the same attributes and state as an existing object, making it a convenient way to replicate or clone objects within your Java program. Copy constructors are particularly useful for maintaining data integrity and ensuring that objects share similar properties and characteristics.
Ans: Constructors are responsible for initializing the object's state. They function similarly to methods, as both comprise a set of instructions executed when an object is created. However, methods are collections of statements designed to perform specific tasks and provide results to the caller. Unlike methods, a method can also execute without producing a return value.
Ans: Certainly, a class can have multiple constructors, and each constructor can call another constructor using the `this()` invocation. The first statement within the constructor should be either `this()` or `this(args)`. This concept is referred to as constructor overloading. Please note that this usage of `this()` is distinct from the `this` keyword.
Ans: Constructor overloading involves having multiple methods within a class with names identical to the class name, differing in the parameters they accept.
Ans: The 'this' keyword is a specific keyword with the purpose of serving as a reference keyword. It is employed to point to the properties of the current class, such as methods, instance variables, and constructors.
Ans: The 'super' keyword is a specific keyword used as a reference keyword. It is employed to refer to the object of the immediate parent class.
Ans: No, it's not permissible to use the "this" and "super" keywords in the same statement within a class constructor. In the provided code example, "super();" and "this();" are utilized in separate statements within the constructor, and this is the appropriate usage.
class Parent {
Parent() {
System.out.println("Parent constructor");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
Child() {
super(); // Calls the parent class constructor
System.out.println("Child constructor");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child child = new Child();
}
}
In this example, the "super()" keyword is used to call the constructor of the parent class (Parent), and the "this" keyword is not used within the constructor of Child. This demonstrates that the "super" and "this" keywords are used separately and appropriately within the constructors.
Ans: Fundamentally, the "super" keyword is utilized to reference the parent class. It comes into play when there exist identical fields in both the parent and child classes, enabling the use of the "super" keyword to access the data members of the parent class.
Ans: Singleton class is a class whose only instance can be created at any given time, in one JVM. A class can be made singleton by making its constructor private.
Ans: No, there is no provision to override a private or static method in Java. However, you can use the method hiding approach in extraordinary cases.
Ans: Association refers to a relationship where all the objects of the class have got their lifecycle and there is no owner as such. These relationships or associations as we call them can be one to one or one to many or many one or many to many.
Apart from these basic java interview questions for seasoned professionals, if you would like to be trained by experts in this technology, you can opt for JanBask Java Training.
Ans: Aggregation is a concept in JAVA for a specialized form of Association where all the objects have got their own lifecycle but there is ownership and the child object cannot belong to another parent object in any manner.
These were the java freshers' interview questions, now let’s move toward the questions asked by the seniors.
Ans: It is a subsystem of JVM that is used to load class files. When we run any Java program, it is loaded first by the classloader. There are three built-in classloaders in Java- Bootstrap ClassLoader, Extension ClassLoader, and System/ Application ClassLoader.
Ans: In Java, encapsulation is the technique of making the fields in a class private and providing access to the fields via public methods. It is one of the four fundamental principles of object-oriented programming (OOP) along with inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.
Data encapsulation in Java refers to the practice of hiding the implementation details of an object and exposing only the necessary information to the outside world. By making the fields of a class private and providing access to them through public methods, it ensures that the internal state of an object is protected from unauthorized access or modification. This allows for a more robust and secure design and also allows for greater flexibility in the implementation of the class.
Ans: Java design patterns are typically divided into three categories: creational, structural, and behavioral design patterns.
Could you highlight the distinction between the equals() method and the equality operator (==) in Java?
The equality operator (==) is employed to verify equality between two variables, whereas the equals() method is used to determine equality between two objects.
Ans: An infinite loop in Java can be declared using a ‘while’ loop by providing a condition that always evaluates to true. For example:
while (true) {
// Code to be executed repeatedly
}
This loop will continue running indefinitely because the condition ‘true’ is always true, creating an infinite loop.
Ans: Freeing the heap memory by destroying unreachable objects is the main purpose of garbage collection. In essence, Garbage Collection ensures that memory is used optimally, preventing memory leaks and allowing the program to run smoothly by automatically reclaiming memory occupied by objects that are no longer needed. This proactive memory management process not only enhances the program's performance but also simplifies memory management for developers, reducing the risk of memory-related bugs and making it a fundamental feature in many modern programming languages, like Java and C#.
Ans: Garbage collection operates in the Heap memory, where it reclaims memory utilized by objects lacking references. In the Heap space, every object enjoys accessibility throughout the entire application and can be referenced from any location.
Ans: Indeed, even with a garbage collector in operation, a program might still confront memory constraints. Garbage collection serves the purpose of identifying and eliminating program objects that are no longer in use, thereby releasing the resources they occupy. It executes garbage collection on objects that can no longer be accessed within the program. However, if the available memory is insufficient to accommodate new object creation, the garbage collector strives to free up space for items that have been removed from scope. When the reclaimed memory isn't adequate for generating new objects, the program surpasses its memory limit.
Ans: When you download Java, you receive two key elements within the package, JDK and JRE. The following are its differences:
|
JDK - Java Development Kit |
JRE - Java Runtime Environment |
|
Specifically designed for software development |
Primarily intended for executing Java programs |
|
Platform-dependent, just like the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) |
Also platform-dependent, similar to the JVM |
|
Comprises a comprehensive set of tools for debugging and development |
Contains essential files and libraries required for a runtime environment |
|
JDK package typically includes an installer for ease of setup |
Unlike the JDK, the JRE package does not include an installer; it provides only the runtime environment components. |
Ans: Objects can be marked for garbage collection when their reference variables are no longer accessible within the program during runtime. These objects are sometimes referred to as "inaccessible objects." The new operator dynamically allocates memory for an object and then returns a reference to it.
Ans: Constructor injection is the recommended method for dependency injection. In this scenario, a class requests its dependencies through its constructor. This approach ensures that the client is always in a valid state because it cannot be instantiated without the necessary dependencies.
Ans: Handling pattern-based programs in Java typically involves using nested loops and conditional statements to print the desired pattern. Understanding the structure of the pattern is crucial. It requires iterating through rows and columns using loops, and applying logic to achieve the pattern's design. Control structures like for loops and if statements are used to control the formation of the pattern. Variables might be employed to track positions and make adjustments based on pattern requirements. Proficiency in this area is gained through practice and experimentation with various patterns.
Ans: JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine. It is an abstract computing machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled into Java bytecode. The JVM is responsible for converting the bytecode, which is platform-independent, into machine code, which is platform-specific.
It also provides the runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed. It is responsible for memory management, secure execution of code, and implementing the various features of the Java language, such as object-oriented features and exception handling.
In summary, JVM is a crucial component of the Java ecosystem that enables Java programs to run on different platforms without modification, by providing a standard runtime environment for executing Java bytecode.
Ans: JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment. It is a software package that contains the necessary components to run Java programs on a particular platform. It includes the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), the Java class libraries, and the Java application launcher.
The JRE provides the runtime environment for executing Java bytecode, which is the intermediate form of a Java program after it has been compiled. The JVM, which is a part of the JRE, interprets the bytecode and executes the program.
Ans: The JDK stands for Java Development Kit. It is a software development environment used for developing Java applications and applets. It contains the necessary tools and libraries to develop, compile, and run Java programs.
The JDK includes the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), which provides the runtime environment for executing Java bytecode, the Java compiler, which is used to convert the source code into bytecode, and various other tools and utilities.
Ans: An applet's life cycle comprises the following stages:
This summarizes the key phases in the applet's life cycle.
Ans: Following are the difference between JVM, JRE, and JDK:
Ans: A package in Java is a grouped collection of classes, interfaces, as well as the essential libraries and JAR files. Packages play a crucial role in enhancing code reusability by organizing related components and allowing for their efficient management.
Ans: Packages in Java provide several advantages, including:
Ans: It is entirely possible to import the same class or package multiple times, and neither the compiler nor the JVM will raise any issues. Even if you import the same class multiple times, the JVM will only load it once internally.
Ans: Importing the main package will not automatically include its sub-packages. When you import a package, it encompasses all its classes and interfaces, but it does not extend to classes and interfaces within its sub-packages.
Ans: The externalizable interface helps to control the serialization process. Just like the serializable interface, it is a class that implements the Externalizable interface and is marked to be persisted.
Ans: JIT (Just-In-Time) compiler is a component of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that is responsible for improving the performance of Java applications at runtime. The JIT compiler works by converting the Java bytecode, which is platform-independent, into native machine code, which is specific to the host platform.
The JIT compiler analyzes the code as it is being executed, and dynamically compiles the most frequently executed sections of code into native machine code. This can significantly improve the performance of the application, as the compiled code can be executed much faster than the interpreted bytecode.
Ans: In Java, a class is a blueprint or template for creating objects. It defines the properties and methods that an object of that class will have. A class can be thought of as a container for data (fields/variables) and functionality (methods) that are related to each other.
A class definition typically includes:
For example, a class called "Car" might have fields like "year", "make", "model", "color", "speed", and methods like "start()", "stop()", "accelerate()", "brake()". An object of the class "Car" would be an instance of that class, with its own set of data and functionality.
These are the very basic java developer interview questions. Let's see some intermediate-level interview questions for java developers.
Ans: In Java, an object is an instance of a class. It is a real-world entity that has a state (data) and behavior (methods). An object is created from a class, and it has its own unique identity, state, and behavior.
Ans: As a default, numerical values are set to 0, boolean values are set to false, and objects are initialized as NULL.
Ans: Pointers are not used in Java because they are a major source of security vulnerabilities and stability issues. Pointers allow direct memory manipulation, which can lead to memory leaks and buffer overflows. These types of bugs can allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or take control of a program.
Ans: Typecasting in Java refers to the process of converting one data type to another. This is also known as type conversion or type coercion.
There are two types of typecasting in Java:
An example of implicit typecasting:
int x = 10; double y = x; // int is implicitly typecasted to double An example of explicit typecasting: double x = 10.5; int y = (int) x; // double is explicitly typecasted to int
Ans: In Java, access modifiers are keywords that are used to set the level of access for classes, methods, and variables. The four main access modifiers in Java are:
Ans: Double brace initialization is a technique used to initialize an anonymous inner class, typically used for creating anonymous instances of a class or an interface. It uses two sets of curly braces, one for the anonymous inner class and another for the instance initialization block.
An example of Double brace initialization for creating an anonymous HashSet:
Set set = new HashSet() {{
add("item1");
add("item2");
}};
Ans: Unicode is a standardized character encoding system that assigns unique numerical codes to each character in a wide range of scripts and languages. In Java, Unicode is used to represent characters and strings and is the default character encoding used in the Java platform.
Java uses the Unicode character set, which includes most of the characters used in the world's written languages, as well as many symbols and special characters. Each character is represented by a unique code point, which is a number between 0 and 65535. For example, the code point for the letter "A" is 65, and the code point for the euro symbol (€) is 8364.
If you face difficulties with these technical java interview questions, you can comment your queries in our comment section. Our team will revert back to you. In addition to this blog, if you want expert training on this technology, you can opt for JanBask Online Java Training.
Ans: Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data and methods that operate on that data. Java is an object-oriented programming language, which means that it follows the principles of OOP.
Ans: Wrapper classes in Java serve the purpose of transforming primitive data types into object-oriented, reference types. These classes are responsible for encapsulating primitive values within objects, allowing for the utilization of primitive data in object-oriented contexts. Wrapper classes in Java are also sometimes referred to as "boxed types" or "boxing classes."
Ans: The main concepts of OOP in Java are:
Ans: Composition enhances a class's testability when compared to inheritance. If a class is constructed by incorporating another class, it becomes straightforward to generate a mock object to simulate the composed class, which is immensely useful for testing purposes. This flexibility is not afforded by inheritance. While both composition and inheritance provide mechanisms for code reuse, inheritance carries the disadvantage of potentially breaking encapsulation. When the behavior of a subclass is contingent on the actions of its superclass, it becomes susceptible to sudden disruptions. Changes in the superclass's behavior can unintentionally disrupt the functionality of the subclass without any modifications made to the superclass.
Ans: Polymorphism in Java is the ability of an object to take on many forms. It is one of the four fundamental principles of object-oriented programming (OOP) along with encapsulation, inheritance, and abstraction.
There are two types of polymorphism in Java:

Ans: In Java, abstraction is a process of hiding the implementation details and showing only the functionality to the user. It is one of the four fundamental principles of object-oriented programming (OOP) along with encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
Abstract classes and interfaces are used to achieve abstraction in Java. An abstract class is a class that cannot be instantiated and is typically used as a base class for other classes. An interface is a collection of abstract methods (methods without a body) that a class can implement.
For example, consider a class called "Car" which has methods such as startEngine(), stopEngine(), and changeGear(). Instead of showing how these methods are implemented, we can simply show that the class has these methods and what they do. This way, the user of the class can use these methods without worrying about how they are implemented.
Ans: In Java, an interface is a blueprint for a class. It defines a set of methods that a class must implement, but does not provide an implementation for those methods. Interfaces are used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java.
An interface is defined using the keyword "interface" and it can contain only abstract methods (methods without a body) and constants. A class that implements an interface must provide an implementation for all the methods defined in the interface. A class can implement multiple interfaces.
For example, consider an interface called "Movable" which has methods such as moveUp(), moveDown(), moveLeft() and moveRight(). Any class that implements this interface must have these methods and provide an implementation for them.
Ans: Inheritance is referred to one class that can extend to another. So that the codes can be used again from one to another class. The existing class is referred to as the Superclass whereas the derived class is known as a subclass.
Ans: In Java, there are four types of inheritance:
Ans: Java does not support multiple inheritances, which means that a class cannot inherit from more than one superclass. This is because of the diamond problem, which can occur when multiple classes inherit from a common superclass.
In traditional multiple inheritance, a subclass can inherit conflicting implementations of the same method from its multiple superclasses. This creates an ambiguity about which method should be invoked when the method is called on an instance of the subclass.
For e.g.
class JanBask1
{
void test()
{
system.out.println("test() method");
}
}class JanBask2
{
void test()
{
system.out.println("test() method");
}
}Multiple inheritance
class C extends JanBask1, JanBask2
{
/* Code */
}
Ans: In Java, method overloading and method overriding are two concepts related to polymorphism.
Method overloading is the ability of a class to have multiple methods with the same name but different parameters. This allows methods with the same name to be called with different arguments, and the appropriate method will be executed based on the number and type of arguments.
Method overriding is the ability of a subclass to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by its superclass. The subclass can override a method by providing a new implementation for the method with the same name, return type, and parameters as the method in the superclass. The overriding method must use the same method signature as the method it is overriding.
For example, consider a class called "Shape" with a method called "draw()". If a subclass called "Circle" wants to provide a different implementation of the "draw()" method, it can override the "draw()" method in the superclass with its own implementation.
Ans: The purpose of encapsulation in Java is to hide the implementation details of a class and provide controlled access to its properties and methods. It is one of the four fundamental principles of object-oriented programming (OOP) along with inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.
Encapsulation is achieved through the use of access modifiers such as "private", "protected", and "public". A class can use these modifiers to control access to its properties and methods. For example, a class can use the "private" modifier to make a property or method accessible only within the class, and the "public" modifier to make a property or method accessible to any other class.
Encapsulation provides several benefits, including:
Ans: The "final" keyword in Java is used to indicate that a variable, method, or class cannot be modified.
The final keyword also can be used to improve the performance of a program by telling the compiler that the value of a final variable will not change, and the JIT compiler can optimize the code accordingly.
Ans: In Java, the "final" keyword can be employed with variables, methods, and classes. When used with a variable, it transforms the variable into a constant. When used with a method, it prevents inheritance, and when applied to a class, it disallows overriding.
Ans: No, an empty .java file name is not a valid source file name in Java. In Java, a source file must have a valid name and it should follow the naming conventions. According to the Java Language Specification, the source file name should have a .java extension and it should contain a top-level class or interface declaration.
Apart from these basic java interview questions for seasoned professionals, if you would like to be trained by experts in this technology, you can opt for JanBask Java Training.
Ans: Object cloning in Java refers to the process of creating a copy of an existing object. The clone method in the Object class can be used to create a copy of an object, but it is a protected method and should be overridden in order to be used.
In order to create a new object that is an exact copy of an existing object, the class of the object must implement the Cloneable interface. This interface is a marker interface, which means that it doesn't contain any methods, it only serves as a flag to indicate that a class allows objects of its type to be cloned.
When an object is cloned, a new object is created with the same state as the original object, but the new object has a different memory address. This means that changes made to the new object will not affect the original object and vice versa.
Ans: Java strings are immutable in nature because strings are commonly used as keys in hash tables, such as those used in HashMap and Hashtable classes. If strings are mutable, their values could change after they were used as keys in a hash table, which would make it difficult or impossible to retrieve the corresponding value.
In addition to this blog, if you want expert training on this technology, you can opt for JanBask Online Java Training.
Ans: Immutability is imposed on strings in Java for several reasons, including security, synchronization, concurrency, caching, and class loading. Declaring strings as final helps preserve their immutability and prevents attempts to extend them. String objects are cached in the String pool, contributing to their immutability.
Ans: Because the Java String class internally employs a char[] array, the length variable cannot be made publicly accessible.
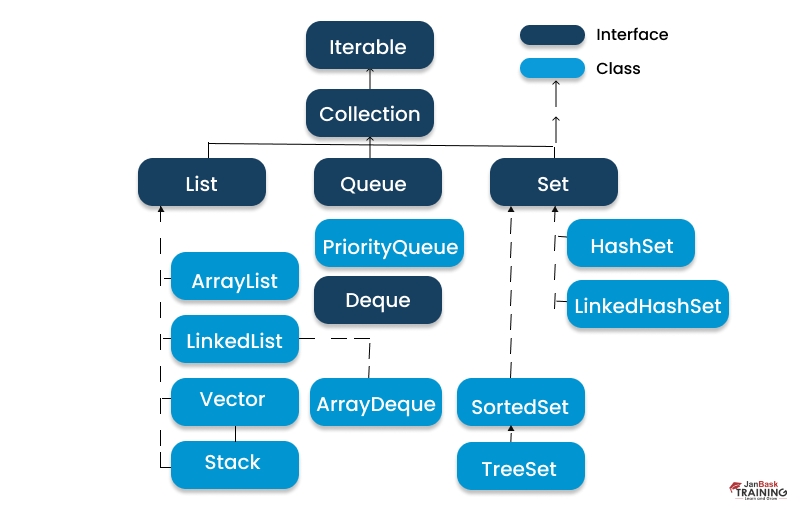
Ans: A collection class in Java is a class that is used to store and manage a group of objects. The Java collections framework is a set of classes and interfaces that provides a unified architecture for storing and manipulating collections of objects.
The core interfaces of the Java collections framework are:
Ans: Within the List interface of the Java Collections Framework, the pivotal methods are add() and addAll(). These methods serve to augment a list with elements. Here's an overview of the available overloaded add() and addAll() methods:
The add() method, which is used to append a single element to the list, comes in two forms:
Ans: It is a process to execute different threads simultaneously. Multithreading is generally used for multitasking. It consumes less memory and provides fast and effective performance.
Apart from this blog, if you want to become a certified Java Developer in 2023 then you should definitely check out this JanBask course.
Ans: Java String Pool, also known as String Intern Pool, is a storage area in Java heap where string literals are stored.
Ans: It's generally recommended to use StringBuilder when extensive updates are needed because of its superior performance compared to StringBuffer. Nevertheless, if the situation necessitates thread safety, then StringBuffer objects remain the preferred choice.
Ans: When you create a String object using the `new()` operator, it invariably generates a new object in the heap memory. In contrast, if you create an object using the String literal syntax, like "Baeldung," the String pool may provide an existing object instead.
Ans: It is an interface of Util packages that maps unique keys to values. Map interface is not just a subset of the primary collection interface and hence it works in a different way.
Ans: In JAVA atmosphere a Java Servlet is a server-side technology used to extend the capability of the web servers by providing support for dynamic response and data persistence.
Ans: The Java Persistence API (JPA) empowers the creation of the persistence layer for both desktop and web applications. JPA encompasses the following aspects:
This summarizes the key components and functionalities associated with JPA in Java.

Ans: The request Dispatcher interface in JAVA is used to forward the request to another resource which can be HTML, JSP or any other servlet within the same application.
There are two methods defined in this interface:
Java Certification Training Online

Let’s discuss Java interview questions for experienced
Ans: Cookies are small text files that a server can store on a client's computer. In a Servlet, you can use the javax.servlet.http.Cookie class to create and retrieve cookies.
To set a cookie, you can create a new Cookie object, set its name, value, and other properties, and then add it to the response using the HttpServletResponse.addCookie() method.
To retrieve a cookie, you can use the HttpServletRequest.getCookies() method to get an array of all cookies associated with the current request, and then iterate through the array to find the cookie you're looking for.
Once you have a cookie, you can read its properties, like its name and value, and use that information to personalize the user's experience.
Ans: Java Servlets offer multiple authentication options, including four distinct approaches:
These options cater to a range of authentication requirements in Java Servlets.
Ans: Late binding, also known as dynamic method dispatch, is a feature in Java that allows a program to determine the method to be invoked at runtime rather than at compile time. This is achieved through the use of polymorphism, which allows objects of different classes to be treated as objects of a common superclass or interface.
In Java, late binding is implemented through the use of virtual method tables (VMTs) and virtual method pointers (VMPs). When a method is called on an object, the JVM looks up the method to be invoked in the object's VMT, which is a table that contains a list of all the methods that can be invoked on the object. The VMT also contains the memory address of the method implementation, which is called the VMP. The JVM uses the VMP to invoke the correct method at runtime.
Ans: Yes, you can generate an array volatile in Java but then again only the situation is directed to an array, not the entire array. This means that, if one thread deviates the reference variable to direct to the extra array, that will offer a volatile assurance, but if multiple threads are altering separate array elements they won’t be having ensues before assurance offered by the volatile modifier.
Also read: Java Developer Role & Responsibilities
Ans: The indexing in a Java array begins at 0 because the initial element is positioned right at the start of the array. As a result, the offset or distance from the array's beginning is zero.
Ans: Interfaces are gentler in performance as compared to abstract classes as additional indirections are compulsory for interfaces. An additional key factor for designers to take into deliberation is that any class can spread only one abstract class through a class that can implement numerous interfaces. The use of lines also places an additional burden on the developers at any time an interface is executed in a class; the developer is required to contrivance each and every technique of interface.
Ans: One of the real-world uses of the volatile variable is to generate interpretation double and long atomic. Equally double and long are 64-bit extensive and they are recited in two parts, primary 32-bit first time and following 32-bit another time, which is non-atomic but then again volatile double in addition long read is atomic in Java. Additional use of the volatile variable is to deliver a recall barrier, just like it is cast off in the Disruptor framework. Fundamentally, the Java Memory model pull-outs a write barrier. Subsequently, you write to a volatile variable besides a read barrier beforehand you read it. That means, if you inscribe to the volatile field then it’s definite that any thread retrieving that variable will see the worth you wrote and everything you did beforehand doing that correct into the thread is certain to have occurred and any rationalized data values will also be noticeable to all threads since the memory barrier flushed all additional writes to the cache.
Ans: Static loading and dynamic loading are two different ways to load class files into a Java program at runtime.
Static loading, also known as early binding, occurs when the class files are loaded into the program at compile time. This means that the JVM loads all the required class files into memory when the program is compiled, and the classes are available to the program when it starts.
On the other hand, dynamic loading, also known as late binding, occurs when the class files are loaded into the program at runtime. This means that the JVM does not load the class files into memory until they are actually needed by the program. This can be done using the Class.forName() method or the ClassLoader.loadClass() method.
|
Feature |
Static Loading |
Dynamic Loading |
|
Loading Time |
Compile Time |
Run Time |
|
Memory Usage |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Flexibility |
Less |
More |
|
Class Availability |
Available at program start |
Available when needed |
|
Method Overriding |
Can't handle overridden methods |
Can handle overridden methods |
|
Performance |
Slower |
Faster |
Ans: Java is considered dynamic because it is designed to be flexible and adapt to changing environments. Java programs contain a significant amount of runtime information, allowing them to dynamically resolve access to objects in real-time.
Ans: JAXP (Java API for XML Processing) is a Java API that provides a set of standard interfaces for processing XML documents. JAXP allows developers to parse, transform, and validate XML documents using a common set of interfaces regardless of the underlying XML parser implementation. JAXP provides a pluggable architecture, which means that developers can switch between different XML parsers, such as SAX and DOM, without changing the code that uses JAXP.
JAXB (Java Architecture for XML Binding) is a Java API that provides a way to map Java classes to XML documents and vice versa. JAXB allows developers to marshal Java objects to XML and unmarshal XML to Java objects, using annotations or XML schema to define the mapping between the Java classes and the XML documents. JAXB also provides a way to validate XML documents against a schema and perform other operations such as filtering and transforming the XML.
Ans: Thread-local variables are variables limited to a thread, it’s like a thread's individual copy which is not public between numerous threads. Java offers a Thread Local class to care for thread-local variables. It’s one of the numerous ways to attain thread safety. Though be cautious while using thread locally adjustable in managed environments e.g. with network servers where operative thread outlives somewhat application variables. A somewhat thread-local variable that is not detached once its work is done can possibly reason a memory leak in a Java application.
Ans: A Memory Leak refers to the gradual deterioration of system performance due to the fragmentation of a computer's RAM. It typically occurs as a result of suboptimal application design or programming practices that neglect to release memory resources when they are no longer needed. Memory leaks often stem from issues such as an accumulation of session items, failure to remove items from Collection objects, excessive caching, and frequent switching between operating system pages, unused listener methods, and poorly crafted custom data structures.
Ans: A platform is the hardware or software setting in which a program executes. Maximum platforms in JAVA can be defined as a grouping of the operating system and hardware, Windows 2000/XP, Linux, Windows 2000/XP, macOS, and Solaris.
In addition to this blog, if you want expert training on this technology, you can opt for JanBask Online Java Training.
Ans: The main difference between an abstract class and an interface is that a boundary can only own assertion of public static approaches with no existing application while an abstract class can have associated with any admittance specified (i.e. public, private, etc.) with or without real implementation. Additional key variance in the usage of abstract classes and lines is that a class that gears an interface must contrivance all the approaches of the interface while a class that receives from an abstract class doesn’t need the execution of all the methods of its superclass. A class can instrument numerous interfaces but it can spread only one abstract class.
Ans: No, these terms are not recognized as keywords in the Java language. "Delete" and "next" are operations performed in Java programs, "main" is a predefined method, "exit" is a command to terminate a program, and "null" represents the default value for the String type.
Ans: In linked lists, the delete operation involves a relatively straightforward update to the pointer value, enabling the affected node to point to its next successor in the list. This process is more efficient compared to the array's deletion, which necessitates shifting elements and can be a more time-consuming task.
Ans: An enumeration, also known as an enum, is a special type of data type in Java that defines a fixed set of named values. Enumerations are used to represent a fixed set of predefined values, such as days of the week, months of the year, or error codes.
An enumeration is defined using the enum keyword, followed by the name of the enumeration and a list of enumeration constants enclosed in curly braces. Each enumeration constant is separated by a comma, and the list of enumeration constants is terminated with a semicolon.
Here is an example of an enumeration that defines a set of possible status codes for a customer:
public enum Status {
ACTIVE, INACTIVE, PENDING, SUSPENDED;
}
Ans: Vector classes, such as java.util.Vector, are used in Java to provide a dynamic array data structure. They are similar to arrays but can grow or shrink in size as needed, which makes them more flexible and efficient than arrays in certain situations.
Here are some reasons why you might use vector classes:
Ans: In arrays, you'll typically find primitive data types such as int and float. In this case, arrays directly store these elements in contiguous memory regions. In contrast, ArrayLists don't contain primitive data types; instead, they hold references to objects located in various memory locations. As a result, the objects are not stored in contiguous memory regions within an ArrayList.
Ans: In a LinkedList, removal, addition, and insertion operations are faster because there's no need for resizing the underlying data structure like in an array. When you add a new item in the middle of the list, only the references in the adjacent items need to be updated, which contributes to the faster performance of the remove method in a LinkedList.
Ans: ArrayList in Java is a type of resizable array. It enables the addition of new elements at any point. The internal data structure of an ArrayList comprises an array of the Object class. ArrayList in Java offers three constructors and features specific readObject and writeObject methods. It's important to note that the Object Array within an ArrayList is temporary. Additionally, there are versions of RandomAccess, Cloneable, and java.io (which are Marker Interfaces in Java) implemented and compatible with Serialization.
Ans: FailFast and FailSafe iterators are techniques employed in Java Collections.
FailFast iterators prohibit alterations to the Java Collections. Consequently, they fail when an attempt is made to add a new element to the collection or remove an existing one. These iterators tend to fail and raise an exception known as ConcurrentModificationException. For instance, ArrayList, HashMap.
Conversely, FailSafe iterators permit modifications to Java Collections. This is achievable because FailSafe iterators typically operate on a cloned copy of the collection. As a result, they do not generate any specific exceptions. For instance, CopyOnWriteArrayList.
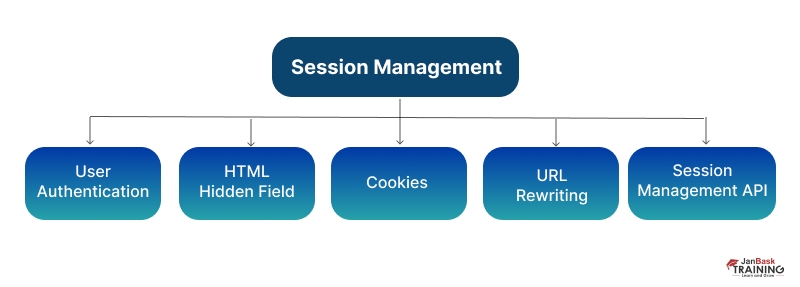
Ans: Session management in Java refers to the process of tracking and maintaining the state of a user's interactions with a web application over a period of time. It allows the web application to remember information about a user's interactions and preferences, even if the user closes the browser or navigates to a different page.
There are several ways to implement session management in Java, but the most common method is to use the HttpSession interface provided by the Servlet API. The HttpSession interface allows you to create, retrieve, and invalidate a session, as well as set and get attributes associated with a session.
Here is an example of how you might use the HttpSession interface to create and retrieve a session:
// Creating a session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
// Setting an attribute
session.setAttribute("user", "John Doe");
// Retrieving an attribute
String user = (String) session.getAttribute("user");
Ans: In Java, a transient variable is a variable that will not be serialized (saved as part of the object's state) when the object is persisted to storage. This means that when an object containing a transient variable is serialized and then deserialized, the value of the transient variable will not be retained.
A volatile variable, on the other hand, is a variable that is guaranteed to be visible to all threads. When a thread reads a volatile variable, it will see the most recent value written to that variable by any other thread, even if the other thread wrote to it from a different core or processor. This can be useful for ensuring that threads see the most up-to-date value of a variable, particularly in multi-threaded code.
Ans: An Inner class is a class that is copied up to the additional class. An Inner class has admit privileges for the class which is nesting it and it can contact all variables and systems well-defined in the outer class, whereas a sub-class is a class that receives from another class named Superclass. Sub-class can contact all public and protected approaches and fields of its superclass.
Ans: Yes, we can generate an abstract class via abstract keyword beforehand class name even if it doesn’t have any abstract method. Though, if a class has even one abstract technique, it must be acknowledged as abstract or else it will give an error.
Ans: This additional good question I prefer to ask on volatile, typically as a follow-up of the preceding question. This query is also not simple to respond since volatile is not about atomicity, but there are situations where you can practice volatile flexibility to make the operation atomic. One instance I have seen is having a long arena in your class. If you distinguish that a long field is retrieved by extra than one thread e.g. an application, a value field or everything, you will make it volatile. Why? Since reading to an extended variable is not atomic in Java and done in double steps, if one thread is lettering or apprising long value, it’s probably for the additional thread to see half value (fist 32-bit). While interpretation/writing a volatile long or dual (64 bit) is atomic.
Ans: In Java, the HTTP GET method is used to retrieve data from a server, while the HTTP POST method is used to send data to a server for processing.
The main difference between the two methods is that GET requests include data as part of the URL, while POST requests include data in the body of the request. Additionally, GET requests are idempotent, meaning that multiple identical requests will return the same response, while POST requests may have side effects and may not be idempotent.
Due to these differences, GET requests are typically used for simple queries or data retrieval, while POST requests are used for more complex operations such as updates or data creation.
Ans: In Java, the forward() method and the sendRedirect() method are used to navigate between different pages or resources within a web application.
The forward() method, which is part of the ServletRequest interface, is used to forward a request from one servlet to another resource, such as a JSP page or another servlet.
The sendRedirect() method, which is part of the HttpServletResponse interface, is used to redirect the client's browser to a different URL.
Java Certification Training Online

Q112). Explain the wait-notify code for the producer-consumer situation?
Ans: Please understand the response for a code example. Just recollect to call wait () and inform () technique from the coordinated block and test waiting for ailment on the loop as an alternative of if block.
Ans: Please understand the answer for a code instance and stage-by-stage guide to generating thread-safe singleton code in Java. As soon as we say thread-safe, which means Singleton should continue singleton even if low-level formatting occurs in the case of numerous threads. Using Java enum as Singleton class is one of the simplest ways to generate a thread-safe singleton in Java.
Ans: Interfaces are gentler in performance as compared to abstract classes as additional indirections are compulsory for interfaces. Additional key factor for designers to take into deliberation is that any class can spread only one abstract class through a class that can implement numerous interfaces. Use of lines also places an additional burden on the developers at any time an interface is executed in a class; the developer is required to contrivance each and every technique of interface.
Ans: JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is a Java API that allows Java programs to interact with a database. In order to use JDBC, a JDBC driver is required. A JDBC driver is a software component that enables a Java application to interact with a database by providing a standardized API for database access.
There are four types of JDBC drivers:

Ans: The JDBC API (Java Database Connectivity API) is a collection of classes and interfaces that provide a standard way for Java programs to interact with databases.
Ans: Here are the general steps to connect to a database in Java using JDBC:
Ans: Public static ultimate variables are also recognized as a compile-time endless, the public is non-compulsory there. They are swapped with definite values at compile time since the compiler distinguishes their value up-front and also distinguishes that it cannot be changed throughout run-time. One of the problems with this is that if you used a public stationary final variable from some in-house or third-party library and their worth changed, then your client will still be using the old value even after you organize a new version of JARs. To evade that, make certain you compile your program when your elevation dependence JAR files.
Ans: Java development team hit to make Java as
Ans: This method allows you to specify the type of a running thread as either a user thread or a daemon thread. For example, setting tU.setDaemon(true) transforms a user thread named tU into a daemon thread, while executing tD.setDaemon(false) converts a daemon thread, tD, into a user thread.
A Daemon thread can be described as a thread assigned with the lowest priority. It is intended to operate in the background, particularly during Java's Garbage Collection process. A Daemon thread in Java is established using the setDaemon() method.
Ans: Observer is any object that wants to get notified when the stage of another object changes. While observable is any object whose stage might be interested, and in whom another object may get its interest listed.
In addition to this blog, if you want expert training on this technology, you can opt for JanBask Online Java Training.
Ans: There are mainly two ways to handle exception:
Check Java Developer Resume Guide.
Ans: It's not mandatory for every try block to be directly followed by a catch block. Instead, either a catch block or a final block should follow it. Additionally, any anticipated exceptions that might be thrown must be declared in the method's throws clause.
Ans: The system is set up as the final operation to run, ensuring that nothing else occurs afterward, rendering both the catch and finally blocks effectively inactive.
Ans: The JDBC DriverManager class is a central point of the JDBC API that is responsible for managing a list of JDBC drivers and for establishing a connection to a database. The main role of the DriverManager class is to:
Ans: Converting any file into a byte stream is referred to as Serialization. The objects of the field are converted into bytes for security reasons.
If you face difficulties with these java core interview questions and Java interview questions and answers for freshers, please comment down your queries.
Ans: One way to prevent the serialization of a class's attributes in Java is to utilize the writeObject() and readObject() methods within the subclass and raise a non-Serializable exception.
Ans: No, there are return value statements in the constructor.
Ans: JIT stands for Just-in-Time compiler, it is basically a program to convert the Java bytecode into instructions, sent directly to the processor. JIT compiler is enabled by default in Java, it is activated when a Java method is invoked.
Ans: The memory allocations are available in three parts, namely Code, Stack, Heap, and Static.
In Java, there are five primary categories of memory allocations:
Ans: A conversational stage between the client and server, sessions can consist of numerous requests from client and server. Since HTTP and Web Server are stateless, the only way to maintain a session is when some unique info is passed through the client and server in every response.
Ans: In JSP (JavaServer Pages), directives are used to provide additional information to the JSP container about how a page should be handled and processed.
The following are the main types of directives in JSP:
Ans: In Java, the hashCode() method is a method that is defined in the Object class, which is the parent class of all objects in Java. The hashCode() method returns an integer value that represents the hash code of an object.
The hash code is a unique integer value that is associated with an object, it's typically used to identify the object in a hash-based data structure, such as a HashMap or HashSet. The hash code is calculated based on the object's internal state, such as its field values.

Ans: In Java, Stack and Heap are two different types of memory that are used for different purposes.
Stack memory:
The Stack is a memory space that is used to store method call frames and local variables. Each thread in a Java program has its stack, and each time a method is called, a new frame is pushed onto the stack. The frame contains information about the method call, such as the method arguments and local variables. When the method returns, the frame is popped off the stack, and the memory is reclaimed. Because the stack is used to store method call frames and local variables, the size of the stack is typically much smaller than the size of the heap.
Heap memory:
On the other hand, Heap memory is the memory space where the objects and class instances are stored. The heap is a global memory space that is shared by all threads in a Java program. When an object is created, it is allocated memory on the heap, and when the object is no longer needed, the memory is reclaimed by the garbage collector. Because the heap is used to store objects and class instances, the size of the heap is typically much larger than the size of the stack.
Ans: If the main method is not defined as static, the program can be successfully compiled, but it will encounter a significant ambiguity issue during runtime, resulting in a "NoSuchMethodError" being thrown.
Ans: Java's main() method is inherently static, enabling the compiler to invoke it without the need to create an instance of the class. This static nature of main() is essential because it serves as the entry point for program execution in Java. As a result, the main() method must be callable directly by the compiler. If it were allowed to be non-static, the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) would need to instantiate the class before invoking the method, introducing unnecessary complexity.
Ans: In Java, the main method is invoked by the JVM before any objects are instantiated. Therefore, if the code compiles without errors but lacks the static modifier, a runtime error will still arise.
Ans: There isn't a restriction on the quantity of main methods you can employ. It's possible to use method overloading to have main methods with signatures differing from the standard main(String[]), and the JVM will simply ignore those alternate main methods.
Ans: Yes, you can execute code before the main method by using a static block of code. This code block is executed when the class is loaded, and any statements within it are executed prior to forming objects in the main method.
Ans: Yes, it is permissible to overload the main method multiple times. However, it's essential to note that the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) typically invokes the main method using its predefined calling mechanism.
For example, you can have overloaded versions of the main method, like in the following code:
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Main Method");
}
public static void main(int[] args){
System.out.println("Overloaded Integer array Main Method");
}
public static void main(char[] args){
System.println.out.println("Overloaded Character array Main Method");
}
public static int main(double[] args){
System.out.println("Overloaded Double array Main Method");
}
public static void main(float args){
System.out.println("Overloaded float Main Method");
}
}
Ans: Hibernate Framework is the programming technique that maps application domain model objects to the relational database tables. The Hibernate Framework provides the option to map plain old java objects to traditional database tablets with JPA annotations and XML configuration.
Ans: Here is the list of major benefits of using Hibernate Framework:
Ans: Spring is an application framework for Java known for its inversion of control containers. It is used to develop Java enterprise applications, and it's worth noting that the core features of the Spring Framework are applicable to a wide range of Java applications.
Ans: Java Cryptography Architecture is a framework that offers a platform and a set of architectural guidelines and APIs for performing encryption and decryption operations.
Developers employ Java Cryptography Architecture to integrate their applications with security features, facilitating compliance with third-party security regulations and standards.
Java Cryptography Architecture leverages various cryptographic components such as hash tables and encryption message digests to enhance security implementation.
Ans: An error is an irrecoverable condition that occurs at the runtime. Exceptions are conditions, occurring because of bad input or human error.
|
Error |
Exception |
|
Represent serious problem |
Represent a problem that can be handled by the program |
|
Beyond the control of the program |
Can be handled and recovered from |
|
Example: OutOfMemoryError, StackOverflowError |
Example: FileNotFoundException, IllegalArgumentException |
|
Should not be caught but logged and recorded |
Can be caught and handled using a try-catch block |
|
Can crash the application |
Can be handled and the application can continue to run |
|
Extends the Error class |
Extends the Exception class |
Ans: Indeed, there are situations in which the 'finally' block may not be executed. Here are some instances in which this can occur:
Ans: The finalize method is called by the Garbage Collector. It is important to note that the Garbage Collector invokes the finalize() method only once for each object.
Ans: A local variable in Java is mainly used in a method, constructor, or block and has a local scope. While an instance variable is a variable that is bound to its object itself.
Ans: Local variables, as well as primitive and object references, do not come with any predefined default values.
Ans: In Java, there are two main types of exceptions: checked exceptions and unchecked exceptions.
Ans: When an exception is unhandled, it begins by being thrown from the top of the call stack and then descends through the call stack to the previous method. The runtime system seeks a means to handle an exception raised by a method. The succession of methods called leading to the method encountering the error represents the pool of potential "candidates" available for managing the exception. This sequence of methods is known as the call stack, and the process of exception propagation encompasses the search process.
Ans: Failing to address an exception when it arises will result in the program terminating abruptly, and any code following the line where the exception occurred will not be executed.
Ans: Both the 'new' operator and the 'newInstance()' method serve the purpose of object creation in Java. When we are aware of the specific object type to create, the 'new' operator is employed. Conversely, if we receive the object's type dynamically at runtime, we rely on the 'newInstance()' method for object instantiation.
Ans: Java follows the "pass by value" concept since "pass by reference" relies on the presence of pointers, which are not used in Java.
Ans: In Java, the throw and throws keywords are used to handle exceptions, but they have different purposes and are used in different contexts.
The throw keyword is used to throw an exception explicitly from a method or a block of code. It is used to signal that an exceptional condition has occurred and that the normal flow of control cannot be resumed. The throw keyword is followed by an instance of the exception class that is to be thrown.
For example:
if (age < 18>
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Age must be 18 or older");
}
The throws keyword is used to declare that a method or a constructor may throw one or more exceptions. When a method or a constructor declares that it throws an exception, it is indicating that the caller of the method or constructor should be prepared to catch and handle the exception. The throws keyword is followed by a list of exception classes that the method or constructor may throw.
For example:
public void readFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
// code to read file
}
Ans: In JSP (JavaServer Pages), the expression language (EL) is a simple language that is used to access data and perform operations on it. The EL allows a JSP page to access data stored in JavaBeans, request attributes, session attributes, and application-scope attributes. It also allows a JSP page to perform basic operations such as arithmetic, logical, and comparison operations.
The EL expressions are enclosed in ${ } and can be used in various parts of a JSP page, such as in scriptlets, JSP tags, and attributes of JSP tags.
If you face difficulties with these java core interview questions, please comment on your problem in the next section. Apart from this blog, if you want to become a certified Java Developer in 2023 then you should definitely check out this JanBask course.
Ans: In Spring MVC, the DispatcherServlet and the ContextLoaderListener are two important components that are responsible for the overall request handling and initialization of the Spring context, respectively.
1. DispatcherServlet: DispatcherServlet is the front controller of the Spring MVC framework. It acts as a single entry point for all incoming web requests to the application. It is responsible for mapping requests to appropriate controllers, handling the request flow, and returning the appropriate response. The DispatcherServlet is configured in the web.xml file and it maps to specific URL patterns. It is responsible for handling all incoming requests and dispatching them to appropriate controllers for further processing.
2. ContextLoaderListener: The ContextLoaderListener is an implementation of the ServletContextListener interface that is responsible for initializing the Spring context for the application. It creates an instance of the ApplicationContext, which is the root container for the application's beans. The ContextLoaderListener is also configured in the web.xml file. It's responsible for loading the application context and making it available to all the components of the application. The listener is responsible for loading the root application context as well as any additional contexts that are configured through the contextConfigLocation parameter.

Ans: Spring MVC provides two methods for handling exceptions:
Ans: In JSP (JavaServer Pages), the life-cycle of a JSP page consists of the following methods:
Ans: The Spring framework provides four methods for specifying the scope of a bean: singleton, prototype, request, and session.
The request scope produces a new bean instance for every HTTP request, while the session scope maintains a single instance of a bean shared by all objects within a single HTTP session.
Ans: In Java, a thread has a specific lifecycle that it goes through, from its creation to its termination. The following are the main stages of the thread lifecycle:

Ans: In multi-threaded software, the simultaneous access of shared resources by multiple threads often leads to unexpected and erroneous outcomes. To maintain order and reliability, it becomes crucial to guarantee that only one thread can access a particular resource at any given moment. Java provides a mechanism for managing threads and synchronizing their activities through synchronized blocks.
In Java, synchronized blocks are identified by the synchronized keyword and are associated with a specific object. Such blocks ensure that only one thread can execute within them at a time, as they are all synchronized on the same object. When one thread is inside a synchronized block, any other threads attempting to enter the same block are held in a waiting state until the first thread exits the block. This synchronization mechanism prevents potential conflicts and race conditions, ensuring the orderly execution of critical sections of code.
Ans: There are two primary methods for defining and implementing threads in Java: by extending the Thread class and by implementing the Runnable interface.
1. Extending the Thread class:
class InterviewBitThreadExample extends Thread {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread runs...");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
InterviewBitThreadExample ib = new InterviewBitThreadExample();
ib.start();
}
}
2. Implementing the Runnable interface:
class InterviewBitThreadExample implements Runnable {
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread runs...");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Thread ib = new Thread(new InterviewBitThreadExample());
ib.start();
}
}
Utilizing the Runnable interface to implement a thread is generally preferred and advantageous because Java lacks support for multiple class inheritances.
The start() method is employed to create a separate call stack for thread execution. Once the call stack is established, the JVM calls the run() method to execute the thread within that call stack.
Q166). What do shallow copy and deep copy mean in Java?
Ans: Shallow copying involves duplicating primitive data types, while deep copying entails replicating not only primitive data types but also the object references.
Ans: In Java, an OutOfMemoryError is a type of error that occurs when the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is unable to allocate memory for a new object or array. This can happen when the heap space, which is the area of memory where objects are stored, runs out of free memory.
An OutOfMemoryError can occur for several reasons, such as:
Ans: Absolutely, the program will execute without any issues. This is because Java doesn't enforce strict rules regarding the order of specifiers.
Ans:
public class PalindromeChecker {
public static boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
if (s.length() == 0 || s.length() == 1) {
return true;
}
if (s.charAt(0) == s.charAt(s.length() - 1)) {
return isPalindrome(s.substring(1, s.length() - 1));
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "racecar";
if(isPalindrome(input))
System.out.println(input + " is a palindrome.");
else
System.out.println(input + " is not a palindrome.");
}
}
Ans:
public class Fibonacci {
static int n1=0,n2=1,n3=0;
static void printFibonacci(int count){
if(count>0){
n3 = n1 + n2;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
System.out.print(" "+n3);
printFibonacci(count-1);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int count=10;
System.out.print(n1+" "+n2);
printFibonacci(count-2);
}
}
Ans:
public class AnagramChecker {
public static boolean isAnagram(String s1, String s2) {
char[] c1 = s1.toCharArray();
char[] c2 = s2.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(c1);
Arrays.sort(c2);
return Arrays.equals(c1, c2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "listen";
String s2 = "silent";
if (isAnagram(s1, s2))
System.out.println(s1 + " and " + s2 + " are anagrams.");
else
System.out.println(s1 + " and " + s2 + " are not anagrams.");
}
}
Ans:
public class Factorial {
public static int findFactorial(int number) {
int factorial = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
factorial *= i;
}
return factorial;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 5;
System.out.println("Factorial of " + number + " is " + findFactorial(number));
}
}
Ans:
public class MissingNumber {
public static int findMissingNumber(int[] nums) {
int expectedSum = nums.length * (nums.length + 1) / 2;
int actualSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums>
actualSum += nums[i];
}
return expectedSum - actualSum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 2, 4, 5, 6};
System.out.println("The missing number is: " + findMissingNumber(nums));
}
}
Ans:
class MyException extends Exception {
public MyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
public class CustomExceptionExample {
public static void validateAge(int age) throws MyException {
if (age < 18>
throw new MyException("Age must be greater than 18");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
validateAge(16);
} catch (MyException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Ans:
class Java
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println(10 * 50 + "JanBask");
System.out.println("JanBask" + 10 * 50);
}
}
Output:
500JanBask
JanBask500
Ans:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MatrixRotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number of rows in the matrix: ");
int rows = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the number of columns in the matrix: ");
int cols = sc.nextInt();
int[][] matrix = new int[rows][cols];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the matrix:");
for (int i = 0; i < rows>
for (int j = 0; j < cols>
matrix[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
sc.close();
System.out.println("Original matrix:");
for (int i = 0; i < rows>
for (int j = 0; j < cols>
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Matrix after 90 degree clockwise rotation:");
for (int j = 0; j < cols>
for (int i = rows - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Ans: In Java, System.out.println() is used to display the supplied argument. The println() method outputs the results to the monitor, and it's commonly called using an object name.
Ans: System.out and System.err both serve as representations of the default output monitor and can be utilized to direct data or messages to the screen. System.out is typically employed for displaying regular messages and results, while System.err is utilized for presenting error messages. On the other hand, System.in represents an InputStream object, which defaults to representing the standard input device, i.e., the keyboard.
Ans:
public class MagicNumber {
public static boolean isMagicNumber(int number) {
while (number > 9) {
int sum = 0;
while (number > 0) {
sum += number ;
number /= 10;
}
number = sum;
}
return number == 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 28;
if (isMagicNumber(number)) {
System.out.println(number + " is a magic number.");
} else {
System.out.println(number + " is not a magic number.");
}
}
}
Ans: Here's a simple Java program to find the square root of a number:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SquareRootFinder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
double number = scanner.nextDouble();
if (number < 0 xss=removed>
This program first takes an input number from the user, checks if it's negative (square root is undefined for negative numbers), and then computes and displays the square root for non-negative numbers.
Q181). Could you offer examples of implementing a Dictionary with a substantial number of words?
Ans: A straightforward implementation involves using a List to store words in order, allowing for binary search. Alternatively, for improved search performance, a HashMap can be used, where the key represents the first character of the word, and the value is a LinkedList.
At a more advanced level, you can create nested HashMaps like:
hashmap {
a (key) -> hashmap (key-aa , value (hashmap(key-aaa,value))
b (key) -> hashmap (key-ba , value (hashmap(key-baa,value))
z (key) -> hashmap (key-za , value (hashmap(key-zaa,value))
}
This hierarchy can extend to n levels, with n representing the average word length in the dictionary.
Q182). Develop a program that identifies duplicate characters within a given string.
Ans: Here's a Java program that detects duplicate characters in a string:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class DuplicateCharacterDetector {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "programming";
findDuplicateCharacters(input);
}
public static void findDuplicateCharacters(String str) {
char[] characters = str.toCharArray();
Map charCountMap = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : characters) {
if (charCountMap.containsKey(c)) {
charCountMap.put(c, charCountMap.get(c) + 1);
} else {
charCountMap.put(c, 1);
}
}
System.out.println("Duplicate characters in the string: " + str);
for (Map.Entry entry : charCountMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() > 1) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " - " + entry.getValue() + " times");
}
}
}
}
This program takes a string as input and uses a Map to count the occurrences of each character. It then prints the duplicate characters along with their frequencies.
Q183). Create a program that eliminates duplicate elements from an ArrayList.
Ans: Here's a simple Java program to remove duplicates from an ArrayList:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.List;
public class RemoveDuplicates {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List listWithDuplicates = new ArrayList<>();
listWithDuplicates.add("apple");
listWithDuplicates.add("banana");
listWithDuplicates.add("apple");
listWithDuplicates.add("cherry");
listWithDuplicates.add("banana");
listWithDuplicates.add("date");
System.out.println("List with duplicates: " + listWithDuplicates);
List listWithoutDuplicates = new ArrayList<>(new LinkedHashSet<>(listWithDuplicates));
System.out.println("List without duplicates: " + listWithoutDuplicates);
}
}
This program creates an ArrayList ‘listWithDuplicates’ that contains duplicate elements. It then uses a ‘LinkedHashSet’ to remove duplicates and store the unique elements in a new ArrayList called ‘listWithoutDuplicates’.
Q184). Write a Java program to reverse a string.
Ans:
public class StringReverser {
public static String reverseString(String input) {
char[] inputArray = input.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < inputArray>
char temp = inputArray[i];
inputArray[i] = inputArray[inputArray.length - i - 1];
inputArray[inputArray.length - i - 1] = temp;
}
return new String(inputArray);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "Hello, World!";
System.out.println("Original string: " + input);
System.out.println("Reversed string: " + reverseString(input));
}
}
Q185). Develop a Java program to determine if a given input number can be expressed as the sum of two prime numbers.
Ans:
public class SumOfPrimes {
public static boolean isPrime(int number) {
if (number < 2>
return false;
}
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(number); i++) {
if (number % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static boolean isSumOfTwoPrimes(int number) {
for (int i = 2; i <= number / 2; i++) {
if (isPrime(i) && isPrime(number - i)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 20;
if (isSumOfTwoPrimes(number)) {
System.out.println(number + " is the sum of two prime numbers.");
} else {
System.out.println(number + " is not the sum of two prime numbers.");
}
}
}
Q186). Compose a Java program to solve the Tower of Hanoi Problem.
Ans:
public class TowerOfHanoi {
public static void solveTowerOfHanoi(int n, String from, String to, String aux) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("Move disk 1 from " + from + " to " + to);
return;
}
solveTowerOfHanoi(n - 1, from, aux, to);
System.out.println("Move disk " + n + " from " + from + " to " + to);
solveTowerOfHanoi(n - 1, aux, to, from);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 3;
solveTowerOfHanoi(n, "A", "C", "B");
}
}
Q187). Apply Binary Search in Java with the help of recursion.
Ans:
public class BinarySearch {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int start, int end, int target) {
if (end >= start) {
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
if (arr[mid] > target) {
return binarySearch(arr, start, mid - 1, target);
}
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, end, target);
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 3, 4, 10, 40};
int target = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, target);
if (result == -1) {
System.out.println("Element not present");
} else {
System.out.println("Element found at index " + result);
}
}
}
Q188). Determine the count of words within a string utilizing the HashMap Collection.
Ans: Here's a Java program that finds the word count in a string using a HashMap:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String text = "This is a sample text. This text contains some sample words.";
String[] words = text.split("\\s+"); // Split the text into words
Map wordCountMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : words) {
word = word.toLowerCase(); // Convert to lowercase to make it case-insensitive
if (wordCountMap.containsKey(word)) {
wordCountMap.put(word, wordCountMap.get(word) + 1);
} else {
wordCountMap.put(word, 1);
}
}
// Display word counts
for (Map.Entry entry : wordCountMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
This program takes a string, splits it into words, and uses a HashMap to count the occurrences of each word, case-insensitive. It then prints the word counts.
Q189). Create a program to determine the second highest number within an ArrayList.
Ans: Here's a Java program to find the second-highest number in an ArrayList:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class SecondHighestNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList numbers = new ArrayList<>();
numbers.add(12);
numbers.add(5);
numbers.add(30);
numbers.add(15);
numbers.add(8);
int secondHighest = findSecondHighest(numbers);
System.out.println("The second highest number is: " + secondHighest);
}
public static int findSecondHighest(ArrayList list) {
if (list.size() < 2>
This program takes an ArrayList of integers, sorts it in descending order, and returns the second-highest number from the list.
Q190). How to write multiple catch statements under a single try block?
Ans: In Java, it is possible to have multiple catch statements under a single try block to handle different types of exceptions. This is useful when you want to handle different types of exceptions in different ways. Here is an example of how to write multiple catch statements under a single try block:
try {
// code that might throw an exception
int a = 1 / 0;
int[] arr = new int[5];
arr[10] = 5;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Arithmetic exception occurred: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Array index out of bounds exception occurred: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("An exception occurred: " + e.getMessage());
}
Check Core Java Interview Questions if you are looking to do a job in core Java.
Q191) Which of the following scenarios results in a compile-time error, and what is the underlying reason for this error?
Ans:
int[] n1 = new int[0];
boolean[] n2 = new boolean[-200];
double[] n3 = new double[2241423798];
char[] ch = new char[20];
A compile-time error occurs in line 3 due to an excessively large integer value. This error is a consequence of the requirement that the array size must be specified as an integer, with an integer typically occupying 4 bytes in memory. The number 2241423798 exceeds the maximum capacity of a 32-bit integer, which is 2147483647.
Since the array size must be an integer, lines 1, 2, and 4 do not trigger a compile-time error, and the program compiles without issue. However, a runtime exception arises in line 2, specifically a "NegativeArraySizeException." During runtime, when the JVM allocates the necessary memory, it detects that the specified size is negative, which is not permissible for an array. Consequently, the JVM throws this exception.
Q192). How can you distinguish between a String, StringBuffer, and StringBuilder?
Ans: They can be distinguished by the following attributes:
Both StringBuffer and StringBuilder use heap memory for storage, and they do not employ the string pool mechanism. This makes them suitable for situations where frequent string modifications are required.
In summary, the key distinctions lie in mutability, thread-safety, and memory storage strategy between String, StringBuffer, and StringBuilder.
Ans: In Java, a Comparator is an interface employed for the purpose of arranging or sorting objects.
Ans: In Java, it is indeed possible to override both private and static methods. This can be achieved by defining a method with the same return type and method arguments in a child class, which effectively hides the corresponding method in the superclass, a concept referred to as "method hiding."
However, it's important to note that private methods cannot be overridden in a subclass because they are not accessible from the subclass due to their visibility restrictions.
Ans: A HashSet stores elements without any specific order and typically operates more efficiently than a TreeSet. It is typically implemented using a hash table structure.
Let’s begin with the Java interview questions for freshers and advanced professionals!
Java is a very popular programming language that can be found in the technology stack of every company. No matter if you are heading for the Java developer interview or full-stack developer interview, knowing Java viva questions, Java interview questions for freshers, java interview questions and answers for freshers is important for you to give your best and get hired in your dream company.
All of the above Java interview questions for freshers and advanced professionals are frequently asked on interviews. So prepare for them and give your best shot in your upcoming Java interview.
Q1. What are the basic Java questions asked in the Interview?
Ans: Following are the basic Java questions:
Q2. How to prepare for a Java Interview?
Ans: Following are the topics you should prepare:
The best way to prepare yourself and become a successful Java Developer then your JanBask course is through the best course.
Q3. What are the Java interview questions for 2 years of experience?
Ans: Following are the questions for 2 years of experience:

Core Java Interview Questions and Answers

React JS Interview Questions - Ace Your React Interviews

Spring MVC Interview Questions and Answers

Top 20 Microservices Interview Questions & Answers For 2024

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Download Syllabus
Get Complete Course Syllabus
Enroll For Demo Class
It will take less than a minute
Tutorials
Interviews
You must be logged in to post a comment