Christmas Offer : Get Flat 35% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
“Where there is data smoke, there is business fire.”- Thomas Redman.
This analogy rightly describes the focus and the emphasis that the organizations are placing on Data analytics to continue their “business fire”. But what does this mean? This means that data is the fuel that can get a business on track or at least provide actionable information that can help strategize current campaigns, easily organize the launch of new products, or try out different experiments. But do you know how much data is created per day? Hold your breath because the figure will shock you.

Data is a life-saver, and data science is about dealing with raw or structured data. We are entering into a world of digitization where every component is driven by data. This has led to increasing demand for data science courses among the aspirants. Our online certification training programs let you master the basic and advanced concepts with real-life industry cases that will enhance your candidature in the job market.
So, let us start to navigate on data and the types of data through this blog. Just scroll down your eyes and enhance your intuition.

Since the inception of computers, people have referred to data as a piece of information that is either stored or transmitted. But does it end here? No. Data encompasses the systematic recording of numerical information derived from digital interactions as facts and figures. The continuous data flow has helped millions of organizations all over the world to attain growth. So, in simple terms, data is a huge record of information divided into various categories to get different types of data.
Information on the other hand is organized data that is used to make decisions and is of value to the user. When this data is of so much importance, it becomes inevitable to store this data properly and safely. We use data science to ease our work with data. Data science is defined as a field that combines mathematical knowledge, programming skills, expertise in the field, and knowledge from structured and unstructured data and then applied to a broad range of uses and domains.
Data helps in visualizing relationships in an organization. Data allows organizations to communicate effectively in different departments or systems. Let us see how data serves its importance in an organization-
For more updates, check our latest blogs at JanBask training and get yourself registered for free.
Data Science Training - Using R and Python

While dealing with datasets, categories of data play a vital role. It determines which strategy should work best for a particular set to bear effective results or which type of analysis should be done for better output. Let’s quickly discover what are the types of data-
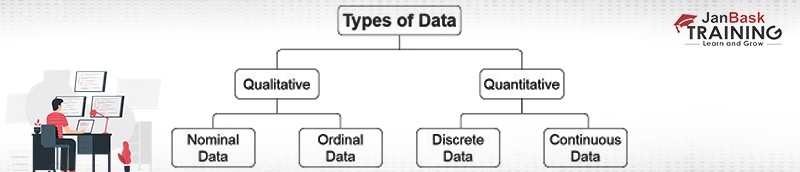
Qualitative data is also known as categorical data which means that these types of data cannot be counted or measured using numbers and therefore, divided into categories of Data. Some examples of Qualitative data include- Case studies, Photographs, Diary Writing, Documents, etc. These types of data answer “why” or “how” after an analysis. It is important to determine traits or characteristics and their frequency. Understanding your data can help you to understand your customers better, which will make you happier in the long run. Qualitative data ensures what problems users face and how they can be addressed or improved.
Some characteristics of Qualitative data include-
This kind of data has both benefits and drawbacks.
Pros of Qualitative data-
Cons of Qualitative Data-
i) Interviews- Personal interviews are one of the most commonly used qualitative data collection methods for qualitative research, because of their personal approach. The interview is often conversational in nature and the interviewer or the researcher collects data directly.
ii) Group Discussions- Group discussions are held with 6 to 10 people where the moderator assigns a particular topic to be discussed. Depending on the qualitative data that is needed, the members of the group may have something in common.
iii) Observation- Observation is a lengthy qualitative data collection method where the researcher simply observes behaviors in a participant. They keep a close eye on the participants and take transcription notes to find innate answers and reactions without inducement.
Qualitative Data collection tools-
Every data collection is incomplete without the right set of tools. Here are some of them-
There are two sub-categories of Qualitative data- Nominal Data & Ordinal Data.
Nominal Data- Nominal data, also called “Labeled” or “Named” data, are the types of data that are used to label or name something without the use of numerical. Data analysts use nominal data to identify the differences among datasets. These types of data are useful while conducting research when there is freedom of opinion. A multiple-choice test of a candidate can be identified as nominal data.
Ordinal Data- Ordinal data is a category of qualitative data which has a natural order while maintaining a class of values. When researchers use ordinal data, the order of the data matters more than the differences. Data analysts might use these types of data while preparing charts or to classify groups. These data help in deciding which coding strategy will work the best for the particular data.
For deeper insight into the Data Science course, read our tutorial on Data Science for beginners
These types of data quantify things by the use of numbers that make them countable in nature. This means you can gather percentages and statistics and analyze your results using graphs and charts. Most of the data found by quantitative methods are less prone to bias and can often accommodate a larger sample size than the data collected. Quantitative data is used when a researcher needs to solve a problem, and answers questions like “what,” “how many,” and “how often.” These types of data are frequently used in math calculations, algorithms, or statistical analysis. Some examples of this category include- Experiment results, time in days or weeks, age in months or years, distance in km/m, etc.
Some characteristics of Quantitative data include-
There are both benefits and drawbacks of this kind of data.
Pros of Quantitative data-
Cons of Quantitative Data-
i) Questionnaires and Surveys- Surveys and questionnaires are commonly used in quantitative research because they are useful for gathering in-depth feedback from users and customers, particularly for finding out how people feel about a certain product, service, or experience. With a wide range of simple-to-use tools, conducting online surveys is a fast and practical search method.
ii) Experiments- An experiment is another common type of quantitative data collection method which includes a control and an experimental group. The data collected is extensive as it pertains to a set of records involved in the experiment.
iii) Sampling- Sampling is the process of selecting a sample of data, which can save both time and resources. There are two ways of this process- Random sampling and Non-random sampling.
There are a variety of tools that are used by data analysts and researchers for these types of data collection. Some of them are-
Read our blog on R programming for Data Science tutorial guide for beginners.
There are two subcategories of Quantitative data. ThContinuous Data– ey are- Discrete Data and Continuous Data.
Discrete Data- These types of data include numerical data that are integers or whole numbers. These data types used in statistics cannot be measured, they can only be counted as objects that have a fixed value. Some examples of this type of data include- the number of players in a team, the number of employees in a company, etc. Discrete data can usually be displayed by pie charts or bar graphs.
Continuous data can take any numerical and can vary. Unlike discrete data, continuous data can be broken into smaller pieces like fractions and can take any value. Examples of these types of data include- web traffic, wind speed, the temperature of the water, etc. Since continuous data changes over time, they are best represented through graphs or grouped into categories. Continuous data can be subdivided into Interval data and Ratio data. Interval data is always measured in numbers where the distance between two points is equal. Ratio data can be measured on a continuous scale but has a true zero.
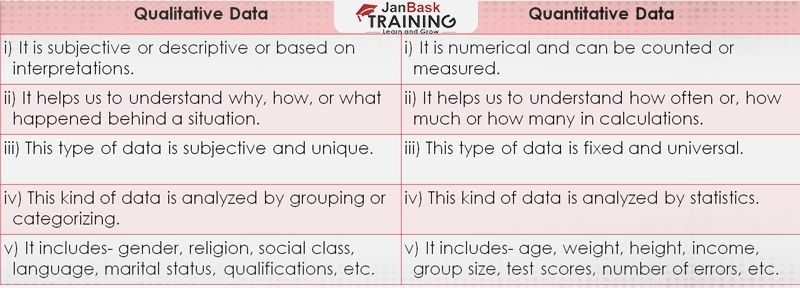
After getting deep insights into different kinds of data, it’s time to understand the key differences between these two types of data.
Before plunging into the job market, take this free quiz on Data Science to know your subject expertise and your areas of concern.
Data Science Training - Using R and Python

Today, almost all organizations and businesses of all sizes and kinds, are spending large amounts of time collecting data. Different types of data are used for different sets of activities. According to LinkedIn, there is a rising demand for professionals who can analyze and interpret data. But, what exactly does a Data Scientist do?
They are Data Scientists who decipher data and analyze them especially, in complex databases. LinkedIn’s Emerging Jobs Report ranked data science as the fastest-growing career that has grown by over 650% since 2012. The market for data science is projected to grow from $37.9 billion in 2019 to $230.80 billion by 2026.
Skills required to become a Data Scientist- If you want to make a career in data science, you need to develop skills like machine learning, analysis, mathematics, and programming along with soft skills like communication and critical thinking. You can also become adept at data science with our Data Science certification and training program that makes you ready for a lucrative career in the market.

Job roles you can fit in- You can build your career by exploring any of these job titles.
How much can you earn?- Over the past years, there has been a tremendous shift in Data Scientists’ roles which leads to a perk in salary. According to The Bureau of Labor Statistics, data scientists’ jobs will experience a 14% hike by 2028. The salary of a Data Scientist depends on various factors like- experience, location and skills. According to Ambitionbox.com, in India, an entry-level Data Scientist can earn approximately ⏯4,50,000 per year, whereas an experienced candidate with nearly 5 years of experience can earn approximately ⏯11,00,000 per year. In the USA, according to Glassdoor.com, an entry-level Data Scientist earns approximately $93, 167/yr, while those with experience earn $142,258/yr on an approx.
Read- Data Science career Path that will explicitly describe the career, skills and salary of a Data Scientist.

Data Scientist future market- With millions of job openings all over the world, the demand for data scientists has become the talk of the world. According to LinkedIn, there are 856k+ job openings for data scientists worldwide. Data scientists are considered to be one of the most rising careers and were second in the top 50 jobs in the USA in 2021. So, what are you waiting for? Prepare yourself for the upcoming Data Scientist interview with our blog on Data Science interview questions and answers because who knows, you might be the lucky one! Also, make sure that your Data Scientist resume gives you an interview call.
Hey, it’s time for wrapping up. In this blog, we have discussed data, types of data and how you can utilize data by becoming a certified data scientist. These different types of data are arranged according to your needs. You just need to pick the right one for you. Explore the trending questions in data science by joining our Data Science community and forum.
Data Science is in the lead. If you want to venture into the world of data science, be ready to take up challenges. We can make it simpler by guiding you through our online certification courses on Data Science that will make you more career-focussed and allow you to gain an in-depth knowledge of the skills and concepts covered in the course.
“We are surrounded by data, but starved for insights” and this is just exactly our focus.
Hope you find it useful.
Data Science Training - Using R and Python

Q1. Is there any difference between data science and data analytics?
Ans- Data science focuses on broader insights into data sets. Data Analytics is a part of data science that answers specific questions brought by data science. Data science brings innovations to businesses in unique ways, while data analytics provides solutions to these questions.
Q2. What are the responsibilities of a data scientist?
Ans- A data scientist is mainly involved in gathering, and analyzing data, using various types of tools to analyze data, and detect trends and reports. He is also responsible for building models to address business problems and develop statistical reports on them.
Q3. Can I become a data scientist after class 12?
Ans- In order to become a data scientist, you need to possess a bachelor’s degree in computer science or software engineering with a sound knowledge of mathematics. However, you can become a data scientist after your class 12th by doing professional courses on Data Science which are available at our JanBask training.
Q4. What will I be learning in this course?
Ans- In the Data Scientist course, you will learn R programming, Python, machine learning, deep learning, regression analysis, data architecture, visualization techniques, risk analysis, process improvement, systems engineering, and many more concepts that are important for the Data Scientists certifications exam and to be an industry-ready professional.
Q5. Which data certifications are in demand?
Ans- Here are the few in-demand Data Science Certifications-
Q6. What are the steps for qualitative data?
Ans- Here are some steps for qualitative data-
Q7. Is qualitative data better than quantitative data?
Ans- It is not possible to say which is better. Rather, they work together to produce the best data results. Understand the importance of both types of data and utilize them accordingly for the most productive outcomes.
Q8. Which are the fields where Quantitative data are used?
Ans- Quantitative data is used in many fields of study like psychology, economics, demography, marketing, sociology, political science and human development. They are less commonly used in fields like history and anthropology.
Q9. Why are Data science courses necessary?
Ans- Data Science certifications are important to have as they improve & validate your skills for the real-time job market, give an edge in your resume/portfolio, increase your probability of getting hired over non-certified professionals, help during salary discussions and brins great confidence while commencing any job or taking up any project.
Q10. What can I expect after this course?
Ans- After completing our Data Science Certification training, you will end up having competent skills & knowledge. It imparts intellectual ways to penetrate in the in-demand job roles. A Data Scientist Training Certificate by a highly acclaimed name in the e-learning world “JanBask Training” - marking as proof of the successful completion of your learning-filled training journey. Our training completion certification will give you great recognition during the hiring process.
Abhijeet Padhy is a content marketing professional at JanBask Training, an inbound web development and training platform that helps companies attract visitors, convert leads, and close customers. He has been honored with numerous accreditations for technical & creative writing. Also, popularly known as “Abhikavi” in the creative arena, his articles emphasize the balance between informative needs and SEO skills, but never at the expense of entertaining reading.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Interviews