Introduction
Artificial Intelligence is becoming extremely relevant and increasingly prevalent in our lives. From healthcare to finance, transportation to entertainment, it is revolutionizing how we live and work.
As we enter this era of unprecedented technological advancements, understanding AI, how it works and its implications does not seem optional anymore. Whether you are a student, a professional, or an entrepreneur, acquiring AI skills opens up boundless opportunities, and positions you at the forefront of innovation.
By delving into AI, you can equip yourself with the knowledge and tools to harness immense potential , drive meaningful change, and shape the future of industries worldwide. However, it is important that you gain the right perspective and knowledge on this topic by enrolling yourself to an online artificial intelligence course to leverage the new opportunities that AI brings along.
In this article, we will delve into the various types of Artificial Intelligence, shedding light on its meaning, applicability and more! Are you ready to take this journey into the realm of AI?
What Is Artificial Intelligence? And What Are Its Goals In The Industry?
The field of AI is incredibly diverse, encompassing multiple technologies, approaches, and methodologies. In simple terms, it is the creation of intelligent systems with human-like ability to solve problems. It involves machines imitating cognitive abilities of humans to process data, analyze it, extract meaningful insights, and leverage that to make informed decisions and take specific action. Ultimately, the goal is to create types of AI-based systems that can exhibit human-like behavior, adapt to new situations, and perform tasks autonomously with minimal human intervention.
Numerous different types of AI have emerged within this expansive field, and each type has specific characteristics and applications. So while a generic understanding of the topic is a given, it is also crucial to know the types of AI, their unique capabilities and actual implications. Have you ever wondered what Machine Learning (ML) is, and how it is different from natural language processing (NLP)? Let’s find out!

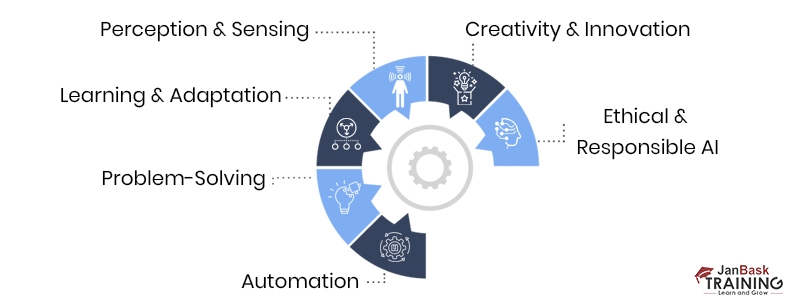
The goals of AI can vary depending on the application and the specific approach taken. However, some standard plans in the field of AI include the following:
1. Automation: AI aims to automate tasks currently performed by humans, thereby increasing efficiency and productivity. This includes automating repetitive or mundane tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex and creative endeavors.
2. Problem-Solving: AI seeks to develop systems that can analyze complex problems and provide effective solutions. This involves building intelligent algorithms and models to reason, infer, and make decisions based on available data.
3. Learning and Adaptation: AI aims to create systems that can learn from experience and improve performance over time. Machine Learning (ML) techniques enable AI systems to automatically remember from data, recognize patterns, and make predictions or decisions based on that learning.
4. Perception and Sensing: AI aims to develop systems that can perceive and understand the world through various sensors and inputs. This includes computer vision, which enables machines to interpret and analyze visual information and other sensing modalities like audio, touch, and motion.
5. Creativity and Innovation: AI explores the boundaries of human creativity by developing systems that can generate new ideas, artworks, music, and designs. This field, known as computational creativity, aims to harness AI's capabilities to enhance and augment human creativity.
6. Ethical and Responsible AI: As AI becomes more pervasive, ensuring its ethical and responsible development and deployment is a crucial goal. This includes addressing issues like bias, fairness, transparency, accountability, and privacy in AI systems.
It's important to note that these goals are not mutually exclusive, and AI research and applications often combine multiple objectives to achieve more comprehensive and advanced intelligent systems.
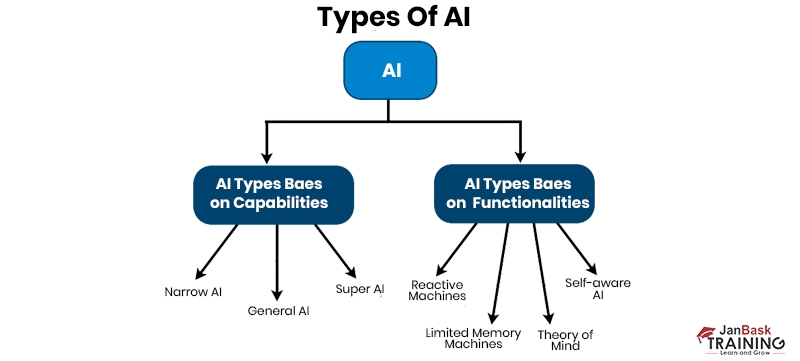
Types Of Artificial Intelligence Based On Capabilities And Scope
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be classified based on its capabilities and scope, offering various categories that capture the diverse types of AI. From narrow AI, which specializes in specific tasks, to general AI, which possesses human-like intelligence across a wide range of domains, the classification considers the level of autonomy, problem-solving ability, and adaptability of AI systems. This categorization helps understand the different levels of AI advancement and its potential impact in various fields.
1. Narrow AI (also known as Weak AI) refers to AI systems designed to perform specific tasks or solve problems within a limited domain. These systems excel at their designated tasks but cannot generalize their knowledge to other areas. Examples of narrow AI include voice assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa), recommendation systems, image recognition software, and autonomous vehicles.
2. General AI (also known as Strong AI or Human-Level AI) refers to AI systems that can understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks similar to human intelligence. These systems can reason, understand natural language, perceive their environment, and learn from experiences. General AI is still largely hypothetical and is yet to realize fully.
3. Strong AI (also known as Artificial General Intelligence or AGI): Strong AI represents an even more advanced form of AI that possesses human-level intelligence and surpasses human capabilities in various cognitive tasks. Strong AI is a construct and aims for AI to exhibit consciousness, self-awareness, and the ability to understand and experience emotions. Strong AI remains speculative and is an active area of research and debate.
It's important to note that while narrow AI is the most prevalent form of AI today, the development of general AI and strong AI remains an ongoing pursuit. Achieving general AI and strong AI is considered a significant scientific and technological challenge with profound implications for society.

Types Of Artificial Intelligence Based On Functionality And Cognitive Abilities
Discover the fascinating world of AI as we explore the various types of Artificial Intelligence systems based on their functionality and cognitive abilities. From narrow AI focused on specific tasks to general AI with human-like intelligence, delve into the diverse landscape of AI capabilities.
1. Reactive Machines: Reactive machines are the types of Artificial IntelligenceI systems that operate based on a specific input and produce output without memory or past experiences. They can't form memories or use past information to influence their current decisions. These systems can only react to the immediate present and are incapable of learning or reasoning. Computers that can play chess and analyze an ongoing game to make the best move without considering past games or strategies, can be an apt example of how a reactive machine would function.
2. Limited Memory: Types of AI systems with limited memory can utilize past experiences or information to enhance their decision-making process. These systems can learn from historical data and use that knowledge to improve their performance. However, their memory must still encompass a comprehensive understanding of the world. Self-driving cars that use past data to improve navigation and avoid accidents are an example of AI with limited memory.
3. Theory of Mind: AI systems with a theory of mind can understand and interpret the mental states of others, including beliefs, desires, intentions, and emotions. They can model the behavior of others and make predictions about their actions based on their understanding of mental states. Still, in its early stages of development, the concept is more rooted in theory.
4. Self-Awareness: Self-aware AI systems possess an understanding of the mental states of others and an awareness of their own existence and mental states. They have a sense of self and can recognize their thoughts, emotions, and consciousness. The concept of self-aware AI is still speculative and has yet to be fully realized.
Major Branches of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses various branches, each focusing on specific aspects of intelligent systems. From machine learning and natural language processing to computer vision and robotics, these major branches of AI contribute to the development of advanced technologies that mimic human intelligence and revolutionize various industries.

1. Machine Learning: A fascinating field that allows computers to learn and adapt by drawing from experience. By recognizing patterns and analyzing data with the help of machine learning algorithms the machine can decide and act, independently, without the need for explicit programming language. Image recognition can be one such instance, where a machine can differentiate between distinct images with the help of an algorithm with numerous labeled images.
2. Deep Learning: Deep Learning is a specialized area within the field of Machine Learning that concentrates on the development and implementation of artificial neural networks featuring numerous layers. Deep neural networks possess the ability to acquire hierarchical data representations autonomously, thereby enabling sophisticated functionalities in image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and other intricate undertakings.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP focuses on enabling AI systems to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It involves text analysis, sentiment analysis, language translation, question answering, and chatbots. NLP is crucial in applications like virtual assistants, language understanding, and content generation.
4. Robotics: Robotics combines AI, sensors, and mechanical engineering to design and develop intelligent machines that can perform physical tasks independently without any human intervention. AI techniques are used in robotics for perception, planning, control, and decision-making, enabling robots to interact with the environment and execute tasks.
5. Expert Systems: Expert Systems are AI systems designed to emulate human experts' decision-making and problem-solving capabilities in specific domains. They utilize knowledge bases, rule-based reasoning, and inference engines to provide expert-level advice and guidance in medicine, finance, and engineering.
6. Fuzzy Logic: Fuzzy Logic is a mathematical framework dealing with uncertainty and decision-making imprecision. It enables AI systems to handle ambiguous or uncertain information and make decisions based on degrees of truth rather than strict binary values. Fuzzy Logic is often used when precise rules or boundaries are difficult to define.
7. Data Mining: Data Mining involves the extraction of valuable insights and patterns from large datasets. It combines techniques from AI, statistics, and database systems to discover hidden relationships and trends in data. Data Mining is employed in various applications, including market analysis, fraud detection, recommendation systems, and customer segmentation.
These branches of AI represent different approaches and techniques used to solve specific problems and advance the field of Artificial Intelligence.
How Does AI Actually Work?

From self-driving cars to virtual assistants, AI-powered technologies are becoming increasingly prevalent in our daily lives. But have you ever wondered how AI actually works?
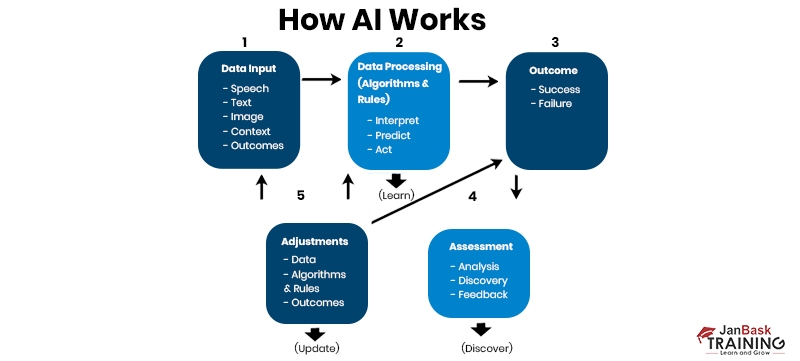
Here are underlying principles and techniques behind AI, including machine learning, neural networks, and algorithms. By understanding the fundamentals of AI, you'll gain insights into how machines can perceive, learn, reason, and make decisions. So, let's delve into the inner workings of AI and uncover the magic behind this transformative technology.The general steps involved in the functioning of AI systems are as follows:
1. Data Collection: Artificial intelligence (AI) systems necessitate pertinent data to acquire knowledge and generate forecasts or determinations. The acquisition of this information can be sourced from diverse origins, including databases, sensors, or the World Wide Web. The performance of AI algorithms is significantly impacted by the quality and quantity of data.
2. Data Preprocessing: Before feeding the data into AI algorithms, it must be cleaned, transformed, and prepared for analysis. This step involves removing noise, handling missing values, normalizing or scaling data, and performing other preprocessing techniques to ensure the data is in a suitable format for further analysis.
3. Algorithm Selection: Appropriate AI algorithms are selected depending on the task or problem at hand. These algorithms can include Machine Learning algorithms (e.g., decision trees, neural networks, support vector machines), Deep Learning models (e.g., convolutional neural networks, recurrent neural networks), or other specialized techniques such as NLP or expert systems.
4. Training or Learning: For AI systems to learn, they are trained using labeled or unlabeled data. Labeled data with known inputs and outputs are used to train the system in supervised learning. In unsupervised learning, the system learns patterns or structures from unlabeled data. Reinforcement learning involves preparing the plan through interaction with an environment, where it receives rewards or punishments based on its actions.
5. Model Building: During training, the AI system builds a model or representation of the data and its underlying patterns. This model captures the relationships and dependencies in the data and is used to make predictions or decisions.
6. Evaluation: After training the AI system, its performance is evaluated using a separate data set called the test or validation set. The evaluation metrics depend on the specific task, such as accuracy, precision, recall, or F1 score. This step helps assess the system's effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
7. Deployment and Inference: Once the AI system has been trained and evaluated, it is ready for deployment. In real-world scenarios, the system is provided with new input data, and it uses the learned model to make predictions, classify information, generate responses, or perform other tasks based on the specific application.
8. Continuous Learning and Improvement: AI systems can be designed to learn and adapt to new data and experiences continually. They can update their models over time, improving their performance and accuracy based on feedback and further information.
It's important to note that the specific working of AI systems can vary depending on the algorithms, techniques, and application domains involved. The field of AI encompasses a broad range of methods and approaches, and different AI systems may have unique workflows and architectures.
Industrial Applications of Artificial Intelligence
AI has a wide range of applications across industries and domains. Some notable applications of AI include:
1. Healthcare: AI is utilized in medical imaging for the diagnosis and detection of diseases, drug discovery, personalized medicine, virtual nursing assistants, and health monitoring systems. It can assist in detecting diseases early, improving treatment plans, and enhancing patient care.
2. Finance: AI is used in fraud detection and prevention, algorithmic trading, risk assessment, credit scoring, customer service chatbots, and personalized financial recommendations. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of financial data in real-time to identify patterns and make accurate predictions.
3. Autonomous Vehicles: AI plays a crucial role in self-driving and autonomous vehicles. It enables perception systems to interpret sensor data, decision-making algorithms for navigation and route planning, and control systems for safe and efficient operation.
4. Retail and E-commerce: AI is employed in recommendation systems, personalized marketing, demand forecasting, inventory management, virtual shopping assistants, and chatbots for customer support. It enhances the shopping experience, improves customer engagement, and optimizes business operations.
5. Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is used in virtual assistants, voice recognition systems, chatbots, language translation, sentiment analysis, and text summarization. It enables machines to understand and generate human language, facilitating seamless communication and information retrieval.
6. Manufacturing and Robotics: AI and robotics are combined to automate manufacturing processes, enhance precision, optimize supply chain management, and enable collaborative robots (cobots) to work alongside humans safely. AI algorithms can improve manufacturing operations' efficiency, quality control, and predictive maintenance.
7. Cybersecurity: AI is utilized in cybersecurity for threat detection, anomaly detection, behavior analysis, and real-time response. It can identify patterns of malicious activities, protect networks and systems, and provide proactive defense against cyber threats.
8. Education: AI is used in intelligent tutoring systems, adaptive learning platforms, automated grading systems, and personalized learning experiences. It can provide customized guidance, assess student performance, and tailor educational content to individual needs.
9. Entertainment and Gaming: AI is employed in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications, character animation, game playing, content recommendation, and interactive storytelling. AI algorithms can enhance user experiences, create realistic simulations, and provide engaging entertainment.
10. Energy and Utilities: AI is used in energy grid optimization, predictive maintenance of infrastructure, demand forecasting, energy management systems, and smart grid technologies. It helps optimize energy consumption, improve efficiency, and enhance sustainability.
These are just a few examples, and AI is being applied in numerous other domains, such as agriculture, logistics, customer service, security, and more. The potential applications of AI continue to expand as technology evolves and advances.
Career Opportunities in Artificial Intelligence

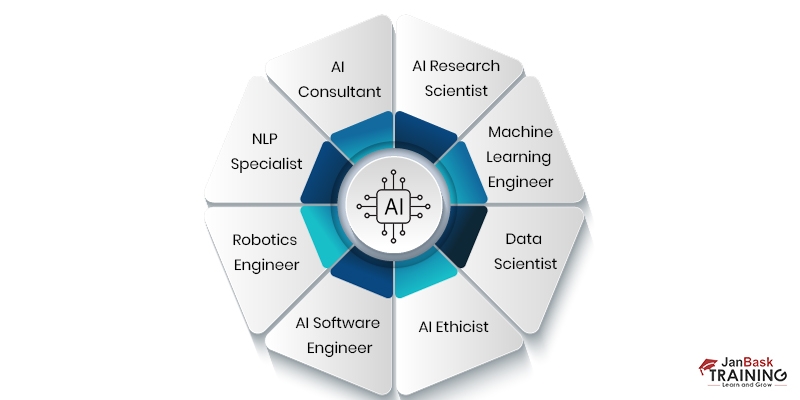
AI career prospects are vast and diverse, with growing demand for professionals skilled in various AI-related domains. Here are some promising career paths and roles in the field of AI:
1. AI Research Scientist: AI research scientists work on the cutting edge of AI, conducting research, developing new algorithms, and pushing the boundaries of AI capabilities. They often work in academia, research institutions, or advanced technology companies, contributing to developing AI theories, models, and applications.
2. Machine Learning Engineer: Machine Learning engineers focus on designing, implementing, and deploying machine learning systems and models. They develop algorithms, preprocess data, train models, and optimize their performance. Machine Learning engineers are in high demand across healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and autonomous vehicles.
3. Data Scientist: Data scientists leverage AI and statistical techniques to analyze large datasets, extract insights, and make data-driven decisions. They work on tasks such as data preprocessing, feature engineering, model selection, and evaluation. Data scientists are crucial in various industries for solving complex problems and driving business strategies.
4. AI Ethicist: With the increasing importance of ethical considerations in AI development and deployment, AI ethicists focus on addressing issues of bias, fairness, transparency, accountability, and privacy. They ensure that AI systems are developed and used responsibly, taking into account potential societal impact and ethical implications.
5. AI Software Engineer: AI software engineers develop and implement AI systems and applications. They build the infrastructure, design the architecture, and integrate AI models into software solutions. AI software engineers work on various projects, from developing chatbots and virtual assistants to creating computer vision systems.
6. Robotics Engineer: Robotics engineers specialize in designing and developing intelligent robotic systems. They combine AI techniques with mechanical engineering principles to create robots that can autonomously perceive and interact with their environment. Robotics engineers work in the manufacturing, healthcare, and space exploration industries.
7. NLP Specialist: Natural Language Processing specialists focus on developing algorithms and systems that enable machines to understand, process, and generate human language. They work on tasks like sentiment analysis, language translation, speech recognition, and text summarization. NLP specialists are in demand in customer service, content generation, and language technology industries.
8. AI Consultant: AI consultants provide strategic guidance and expertise in implementing AI technologies and solutions. They assess business needs, identify opportunities, and develop AI strategies aligned with organizational goals. AI consultants work with clients across various industries, helping them leverage AI for competitive advantage.
These are just a few examples of the many career paths available in AI. As AI continues to advance and permeate various sectors, the demand for AI professionals is expected to grow significantly. It's worth noting that interdisciplinary skills, such as a combination of AI and domain expertise (e.g., AI in healthcare or finance), can be precious in shaping a successful AI career.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of artificial intelligence is crucial in comprehending the scope and potential of this rapidly evolving field. From narrow AI, which dominates the current technological landscape, to the aspirational goal of strong AI, each type offers unique capabilities and implications. If you're eager to delve deeper into the world of artificial intelligence, consider exploring online Artificial Intelligence courses. These courses provide a flexible and accessible way to learn about AI concepts, algorithms, and applications from industry experts, empowering you to unlock the vast possibilities that lie within the realm of artificial intelligence. Embark on your journey today and enroll in an online artificial intelligence course to enhance your understanding and proficiency in this transformative field.
FAQs
Q: Which type of AI system is the most advanced?
Ans:- At present, reactive machines and AI systems with limited memory are the prevailing and sophisticated forms of AI systems that are presently operational. The domains of Theory of Mind AI and Self-Aware AI are presently under active investigation and advancement. Currently, we have not achieved a state where these systems exist in their complete and functional form.
Q: Can you provide examples of types of Artificial Intelligence systems for each type?
Ans:- Here are examples of types of Artificial Intelligence Systems:
- Reactive Machines: IBM's Deep Blue (chess-playing AI) and Google's AlphaGo (Go-playing AI).
- Limited Memory AI: Virtual personal assistants like Apple's Siri, Amazon's Alexa, and Google Assistant, which learn from user interactions to improve their responses.
- Theory of Mind AI: Currently, there are no AI systems that fully exhibit theory of mind capabilities. However, research and development in this area are ongoing.
- Self-Aware AI: True self-aware AI systems are purely hypothetical at this stage and do not exist in reality.
Q: What are the types of Artificial Intelligence are commonly used today?
Ans:- There are 3 types of Artificial Intelligence (AI) used today, most commonly used is Machine Learning (ML). Machine Learning involves training computer systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. It enables various applications such as image recognition, natural language processing, recommendation systems, and predictive analytics.
Q: What skills are needed for Artificial Intelligence training?
Ans:- Artificial Intelligence training requires a combination of skills, including:
- Strong understanding of mathematics, including linear algebra, calculus, and probability theory.
- Proficiency in programming languages such as Python, R, or TensorFlow for implementing AI models.
- Knowledge of machine learning algorithms, neural networks, and statistical modeling.
- Data preprocessing and analysis skills, including feature engineering and data visualization.
- Problem-solving abilities and critical thinking to optimize AI models and address challenges during training.
Q: What topics are covered in an online Artificial Intelligence course?
Ans:- Online Artificial Intelligence courses cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence and its applications
- Machine learning algorithms and techniques
- Neural networks and deep learning
- Natural language processing
- Computer vision and image recognition
- Reinforcement learning
- Ethics and social implications of Artificial Intelligence
Q: What are the benefits of taking an Artificial Intelligence course online?
Ans:- Some advantages of Artificial Intelligence courses online include:
- Flexibility: You can access course materials and lectures at your own convenience, allowing for self-paced learning.
- Accessible Resources: Online courses often provide video lectures, reading materials, practical exercises, and discussion forums for interaction with instructors and peers.
- Affordability: Online courses are often more cost-effective compared to in-person alternatives, eliminating travel and accommodation expenses.
- Diverse Course Options: You can choose from a wide range of online AI courses offered by different institutions and experts, enabling you to find the best fit for your learning needs.
- Competitive Edge: The growing demand for professionals with AI skills and knowledge. By acquiring expertise in AI, you can position yourself as a valuable asset to organizations seeking to leverage AI for enhanced decision-making, automation, and innovation.
Artificial Intelligence Course
Upcoming Batches
Trending Courses
Cyber Security
- Introduction to cybersecurity
- Cryptography and Secure Communication
- Cloud Computing Architectural Framework
- Security Architectures and Models
Upcoming Class
0 day 30 Dec 2025
QA
- Introduction and Software Testing
- Software Test Life Cycle
- Automation Testing and API Testing
- Selenium framework development using Testing
Upcoming Class
-1 day 29 Dec 2025
Salesforce
- Salesforce Configuration Introduction
- Security & Automation Process
- Sales & Service Cloud
- Apex Programming, SOQL & SOSL
Upcoming Class
7 days 06 Jan 2026
Business Analyst
- BA & Stakeholders Overview
- BPMN, Requirement Elicitation
- BA Tools & Design Documents
- Enterprise Analysis, Agile & Scrum
Upcoming Class
10 days 09 Jan 2026
MS SQL Server
- Introduction & Database Query
- Programming, Indexes & System Functions
- SSIS Package Development Procedures
- SSRS Report Design
Upcoming Class
10 days 09 Jan 2026
Data Science
- Data Science Introduction
- Hadoop and Spark Overview
- Python & Intro to R Programming
- Machine Learning
Upcoming Class
3 days 02 Jan 2026
DevOps
- Intro to DevOps
- GIT and Maven
- Jenkins & Ansible
- Docker and Cloud Computing
Upcoming Class
3 days 02 Jan 2026
Hadoop
- Architecture, HDFS & MapReduce
- Unix Shell & Apache Pig Installation
- HIVE Installation & User-Defined Functions
- SQOOP & Hbase Installation
Upcoming Class
3 days 02 Jan 2026
Python
- Features of Python
- Python Editors and IDEs
- Data types and Variables
- Python File Operation
Upcoming Class
4 days 03 Jan 2026
Artificial Intelligence
- Components of AI
- Categories of Machine Learning
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Recurrent Neural Networks
Upcoming Class
18 days 17 Jan 2026
Machine Learning
- Introduction to Machine Learning & Python
- Machine Learning: Supervised Learning
- Machine Learning: Unsupervised Learning
Upcoming Class
10 days 09 Jan 2026
Tableau
- Introduction to Tableau Desktop
- Data Transformation Methods
- Configuring tableau server
- Integration with R & Hadoop
Upcoming Class
-1 day 29 Dec 2025