10
JanYear End Sale : Get Upto 50% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
If you are one of them who don’t know how to use GitHub then this blog post is definitely designed for you. GitHub is a popular version control tool and a web-based platform. The blog will take you through multiple benefits and capabilities of the platform and you will learn the following topics throughout the post –
 To be very crisp about GitHub, this is a file or code sharing service to collaborate quickly with different people. The platform is majorly used for version control by Companies. It is generally used when multiple people are connected with one project only.
To be very crisp about GitHub, this is a file or code sharing service to collaborate quickly with different people. The platform is majorly used for version control by Companies. It is generally used when multiple people are connected with one project only.
For example, if there is one website whose code wanted to edit everyone in the team simultaneously while working on the project then the GitHub is useful. Here, GitHub will design a central repository where every team member could upload, edit, or manage the code files based on convenience.

GitHub has a plenty of advantages and this is clear from the discussion as well but people are still confused why should not we use any cloud-based CRM system? Let me explain to you why GitHub needs to prefer. Let us take the example two software developers who are working on the same project and wanted to update it continuously.
Unfortunately, the person who commits changes first will get the preference. If you are using GitHub then this is not the case. GitHub has the capability of managing changes and reflects them in an organized manner to avoid any chaos among multiple file uploads. It will create a central repository and working on the same code file is much easier than you expected.  Now you must be confused between two popular terms i.e. Git and GitHub but they are completely different. Git is a popular version control tool that gives you the flexibility to perform multiple operations to fetch data from the central server and push data to it whereas GitHub is a web-based hosting platform for version control collaboration. It allows you to host a central repository in a remote server. Here is a list of facts what makes GitHub simpler –
Now you must be confused between two popular terms i.e. Git and GitHub but they are completely different. Git is a popular version control tool that gives you the flexibility to perform multiple operations to fetch data from the central server and push data to it whereas GitHub is a web-based hosting platform for version control collaboration. It allows you to host a central repository in a remote server. Here is a list of facts what makes GitHub simpler –
Read: 4 Easy and Famous Ways To Facilitate Jenkins Management
Let us dive little deep and learn ahead how to use GitHub….
A repository is the storage space where your project survives. It can be created locally or it can be taken as the storage space on another host too. You have the flexibility of storing data in multiple formats that could be text files, image files, or any other format too. There is a quick need of repository if you have made some changes to the file and need to upload immediately. The GitHub repository can also be named as the remote repository for your project. So, let us make the things little simpler and learn how to create repository in GitHub.
Go to the https://github.com/ link first and sign up for GitHub by giving simple details only.  As soon as you create a GitHub account then click on Start a new project option as shown below in the screenshot.
As soon as you create a GitHub account then click on Start a new project option as shown below in the screenshot. 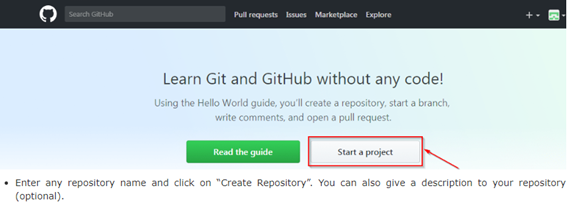 Refer the screenshot for better understanding how to create a repository.
Refer the screenshot for better understanding how to create a repository. 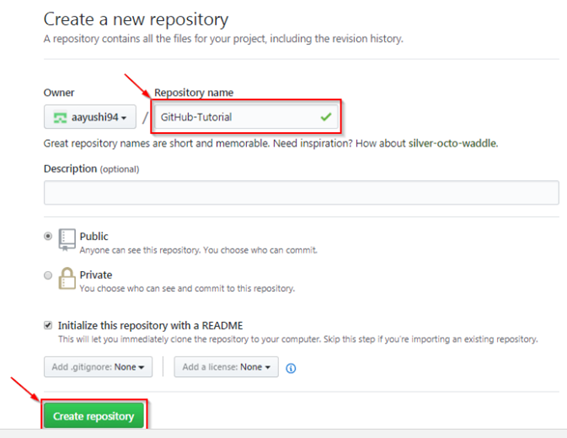 Now, if you would look at the screenshot above carefully then one GitHub repository is public by default. The private keyword signifies that anyone can view the content in the repository. The best idea is to keep the repository private and give access to selected users only. Now initialize the repository with a README file and this would be the first file stored in the repository.
Now, if you would look at the screenshot above carefully then one GitHub repository is public by default. The private keyword signifies that anyone can view the content in the repository. The best idea is to keep the repository private and give access to selected users only. Now initialize the repository with a README file and this would be the first file stored in the repository.

Congratulation, you have created repository in GitHub successfully in a few simple steps only. Once it is created, you can pull, push or commit changes and perform all necessary operations needed for the project.
What are the branches? With Branching, you can work on different versions in a repository at a particular time. For example, if you wanted to add a fresh feature in the development phase and wondered at the same time either you should commit changes to the main project or not. This is the situation where GitHub branching can help you to rescue.
Read: What Exactly Does A DevOps Engineer Do?
With the help of branches, this is easy to switch between multiple versions of a project. You are always free to create a new branch and add multiple features for testing without affecting the main branch. The other name for the main branch is the master branch and it is available within repository by default. Look at the image below to get a complete idea - 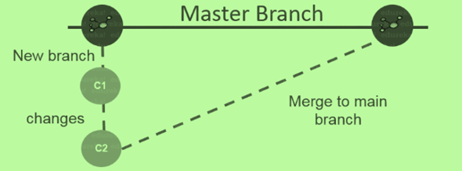 As you can see in the image, there is one master branch and one new branch added to the master branch, two set of changes are made to the new branch i.e. c1 and c2. These changes are further merged to the main branch once committed. With this discussion, it must be clear to you what is branching and how it works in GitHub.
As you can see in the image, there is one master branch and one new branch added to the master branch, two set of changes are made to the new branch i.e. c1 and c2. These changes are further merged to the main branch once committed. With this discussion, it must be clear to you what is branching and how it works in GitHub.
This is easy to create a branch in GitHub with a few simple steps only –
In this section, we will explain to you a set of commands that include Commit Command, Pull Command, and the Merge Command. Let us look at each of the commands one by one – 
This operation helps you to save changes to the file. As soon as you click on the “commit changes” option, changes will be reflected in the file immediately. This operation is necessary that helps you to identify different versions and commits made by different developers on the team. A list of changes is maintained in the repository that helps the contributors to understand the file better.
This command is useful because it notifies the users that changes are made to the file and requests other connected persons to view the changes either they are optimum or not. If they are suitable then merge the same to the master branch or give your feedback. Basically, it will compare the changes and check for conflicts as well.
Read: Famous and Easy ways To Know About Jenkins Build Job Setup
This operation will tell you how can you merge the pull requests. It is useful for merging changes to the master branch. Usually, the changes are highlighted in different colors and you can merge the same into the master branch. Keep trying these steps simultaneously while you are reading this blog how to use GitHub for your next project.

Before we learn how to clone the repository, let us first study why there is need of cloning a repository. The answer is simple if you wanted to merge the same code available in a public repository then the best option is cloning or downloading the contents directly. See the screenshot below for a better understanding – 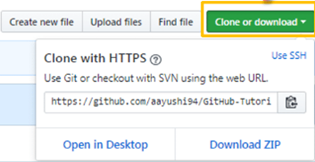 Just click on the option as given in the screenshot, and you are done!
Just click on the option as given in the screenshot, and you are done!
So, let us first discuss what is forking and why do we need forking. Take an example, where you need some code under the public repository within GitHub. For this purpose, we should fork a repository. Keep in mind these facts when you are planning to fork a repository.
Congratulations, you have forked the repository successfully with a few simple steps only. That’s all for the day and enjoyed the blog how to use GitHub with complete details. If you find this blog useful then don’t forget to check more DevOps tutorials or join DevOps Certification course at JanBask Training right away.
We have a complete database of satisfied learners worldwide and they are working on good positions too with lucrative salary packages. The training is not focused on theoretical learning but you will get hands-on expertize too on different DevOps tools like Jenkins, Puppet, Nagios, Git and more.
Read: Why Everyone’s Becoming that Certified DevOps Dude and How?
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on DevOps Course
Interviews