09
JanYear End Sale : Get Upto 50% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
Inheritance is the most powerful and natural mechanism to structure and organize the software program. It explains how classes inherit behavior or states from superclasses. It will also explain how one class can be derived from another with the help of simple syntax as suggested by the Java programming language. Before we dive deep into the topic, let us first discuss what is Java, its history, and the features. Then we will discuss the inheritance in Java, its different types, and applications.
Java is the OOPs-based platform-independent language that is useful to create the most powerful and secure apps that may run on a single computer or it will be distributed among different servers or clients across the network. The simplicity and portability features of Java make sure that enterprises would not face any problem while designing apps related to hardware, network, or the operating system.
Java was started as the Oak programming language in 1991 by the James Gosling. The objective of the programming language was to implement a virtual machine that has a familiar notation like C and C++ but highly simpler as compared to previous programming languages.
The first version of Java was released by Sun Microsystem in 1995 with the famous tagline “Write once, run anywhere” and it becomes more popular due to its platform-compatibility features. It became more popular when it was released as the open source programming language for Java 7 version in 2006.
JVM or Java Virtual Machine is the implementation product that helps in executing programs like a real machine only. Because of JVM only, the computer programs can be executed over multiple operating systems like Linux, Unix, or Windows etc. Further, there is one Java compiler to convert the program into bytecodes that are easy to execute.
JRE or Java Runtime Environment is made up of JVM, class libraries, and necessary functions to initiate the Java programs. Basically, it provides a runtime environment to execute or run the Java programs.
Inheritance is an integral pillar of object-oriented programming and a popular mechanism where one class is allowed to inherit the properties of another class through fields or methods. Here, are some important methodologies related to the concept.
In practice, inheritance and polymorphism both concepts are used together to achieve better performance and readability of the code. To use inheritance in Java, the extends keyword is used. The syntax is given below-
Read: What is A Java Constructor? Type of Constructors & Uses in Java

Here are different types of inheritance that are support by the Java programming language –
When one subclass inherits the features of one superclass, this would be the case of Single inheritance. In the example given below, the base class A will be inherited by a subclass B. 
In the case of multi-level inheritance, a subclass that is inheriting one parent class will also act as the base class for another class. Based on the example given below, B is the subclass that is inhering the features of parent class A and acting as the base class for C subclass. 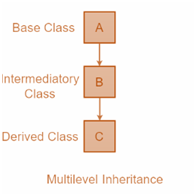
In the case of Hierarchical Inheritance, there is one base class for multiple subclasses. For the example given below, A is the base class that is inherited by multiple subclasses B, C, and D. 
In the case of multiple inheritances, there could be more than one parent classes for a given subclass. For the example given below, C is the subclass having more than one parent class i.e. A and the B. Multiple inheritances are not supported in Java through classes but this is possible through interfaces and the default implementation of methods in Java 8 and the later versions.
If two parent class has similar methods with the same signature, the default method is used to override the other. If we remove the implementation of default methods from the subclass then it will show the compiler error again.

Read: Java String Functions & Methods with Examples
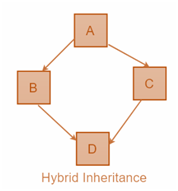
This is mix or two or more types of inheritance discussed earlier. Like the multiple inheritances, hybrid inheritance is also not supported in Java through classes but you could make it possible again through interfaces.
For the sub class, we can inherit members, hide them, replace them or supplement them with new members as per the convenience. This is possible to use the inherited members directly like you are using the other fields of a class. Apart from the inherited fields, you could always add the new attributes to make it even more powerful.
This is possible to define the new instance method for the subclass that would be given the same signature as the superclass. In this case, method overriding concept will be applicable. We could define new subclass constructors that can be invoked from the superclass with the keyword Super.
As the name suggests, this is a popular Oops concept where properties of more than one parent class can be inherited. There comes an issue when a method has the same signature in both parent class and the subclass. When a method call request is put, java compiler gets confused which method should be invoked actually either of parent class or subclass.
In the final output, there would be a compiler error that needs to resolve quickly. For this reason, Java does not support the concept of multiple inheritances of classes which is quite complex. There are other techniques too where we need the concept of multiple inheritances, so better keep the things simple and straightforward in Java.
In Java 8, multiple inheritances were made possible through interfaces and default methods that have the capability to provide the default implementation of methods. If two parent class has similar methods with the same signature, the default method is used to override the other. If we remove the implementation of default methods from the subclass then it will show the compiler error again.
The ‘final’ keyword in Java is used to restrict some functionalities. This is possible to declare classes, methods, or variables with the help of the ‘final’ keyword. In case of the inheritance, we should always declare methods using the final keyword if the implementation is same throughout the derived class. However, this is not mandatory to use the final keyword with base class only but you can use it with subclass too that is supposed to be extended by any other class.
Read: How to Create Object in Java with Examples?
At the particular time, when some class is declared as the final then it could not be inherited anymore. Here is given the example below with syntax –

When some class is declared final then its members will also follow the same culture and cannot be accessed anymore. We cannot declare the same class as abstract and final both because the abstract class is incomplete in itself and relies on other class for implementation. Further, if some method is declared as final then it could not be overridden by another and it is taken as the example of static binding. Here, you can see that final keyword can be used in different perspectives in case of inheritance in Java.
Related Post
With this detailed discussion, you must be sure on all possible aspects of inheritance, its types and how it should be used with your application. A depth understanding of the OOPs concept makes you more capable of writing a powerful program. TO know more on Java and related OOPs concepts, you should join Java certification program at JanBask Training right away and explore the endless jobs opportunities for your career.
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on Java Course
Interviews