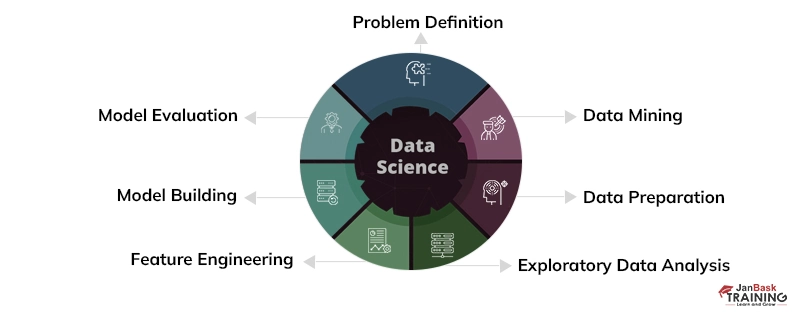
Introduction
Data scientists gather data and convert it into a tractable form, make it tell its story, and present that story to others.” Mike Loukides, the Vice President of O'Reilly Media, says this. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistics, more than 11.5 million jobs will be created in Data Science by 2026. In fact, this is just a mere estimate, and the experts say that the numbers can rise far beyond these measurements!
The era of data scientists has already begun; if you want to be a part of this ride, it’s time to start asking these questions before it's too late:
- What is data science course?
- What is the need of data science?
- What are the advantages of data science?
This and much more shall be answered in today’s blog. But, knowing the answers shall be enough? Understandably, you should first clear the basics, but what's post that? Well, then, is the entry into the real world, which is made easier through the best data science certification online by Janbask Training!
What is Data Science Course?
A data science course is not simply an educational program but a journey into data-driven decision-making and predictive analytics. Here's what you get out of going through a data science course and how crucial that is in today's data-centric society:
An Overview of What is Data Science Course:
Comprehensive Curriculum
- Advanced Statistical Methods: Beyond the usual statistics, you shall learn how to predict models which go beyond the assumptions of regular regression analysis; we study inferential statistics.
- Machine Learning and AI: These courses tackle supervised and unsupervised learning methods, neural networks, and deep learning techniques.
- Data Management: Knowledge of data warehousing, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and database manipulation.
- Basic Data Tools and Technologies: Fundamental knowledge of the latest big data platforms, even ones like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
- Data Visualization and Communication: A data science course will teach advanced methods for creating interactive dashboards and visualizations based on one's data.
Hands-on Experience
- Capstone Projects: Effortlessly showcase your expertise in a chosen domain.
- Workshops and Labs: Take your theoretical skills to the next level with actual-life workshops and labs.
- Hackathons and Competitions: Vital experiences working on real-time problems, full of challenges.
Skill Upskilling
- Thinking and Analysis: Interest in problems and derivation of adequate elucidation from data.
- Technique and Tools: Overcoming the common difficulties with essential data science tools and programming languages.
- Knowledge in Specific Field: Some classes offer additional paths like health care analytics, financial analytics, or marketing analysis of public companies.
Career Pathway
- Networking Possibilities: Connect to professionals in your interest, and alumni may provide advice or potential job leads.
- Career Services: Many programs have resume-building workshops, coaching students on handling interviews and helping them find jobs.
Target Group
- Beginning Data Scientists: For those just starting their journey in data science.
- People from Different Fields: Perfect for software engineers, statisticians, and business analysts who realize a data science shift.
Flexibility in Learning
- Part-Time vs. Full-Time: Allows working adults time to take the class or college student space.
- Portal for Online Learning: This can be done anywhere in the world today, according to his/her lessons and lectures with an Internet connection.
Quality Control & Accreditation
- Quality Assurance and University Affiliation: A reputable institution for most courses adds weight to your qualifications.
- Qualifications Recognized by Industry: When having a reputable certification added to your data science resume, you shall be accepted by significant employers, too, including Google, IBM, etc.
Who is a Data Scientist and What all Technical Aspects are Included in His Work?
The purpose of learning data science is to gain excellent expertise in unfolding and analyzing large structured and unstructured data sets.
The primary role of a data scientist involves the acquisition of intelligence to solve problems as he has studied the programming languages of computer science as well as facts inscribed in the statistics and even mathematical formulas to resolve more excellent queries in the coding field.
Tasks of Data Scientists- Data scientists work on three pillars such as collecting, analyzing large sets of structured and unstructured data to yield actionable plans for enhancing the commercial growth of the company as well as small-sized organizations.
Reasons why Data Scientists are Called as the Analytical Experts

They are often labeled as analytical experts who can efficiently utilize their skills in technology and find social science measures to search for the latest trends that help manage the data. But, to be this proficient, a learner should know well how to do data science course that they have chosen.
1. Technical Knowledge
- Solve Problems- These professionals are known for their vast knowledge, contextual understanding, and skepticism of the current assumptions to unmask the solutions to solve hidden business challenges.
- Fully Understand Coding- Data scientists are professionals who fully understand the length and breadth of the coding spectrum in computer science.
- Updated Skills- Their technical skills are highly updated as they can create projects, websites, and landing pages by performing machine learning techniques that include Python, Java, C++, and more.
- Strong Visualisation- A data scientist is also able to visualize structured as well as unstructured data and can even create business reports. The individual carries a sharp eye for carrying out the analysis of risks. Before the losses happen to the company, his compiled set of risk reports is enough to project the losses that can fall in the path of the company’s growth.
Understanding the need of data science, and accordingly preparing for the technical skills should be the motto!
2. Know the exact work of the data scientist

Extraction of Data
- Data Mining- The data scientist is also known for extracting information from numerous web servers and importing it into specific databases by mining the data.
- Efficient Cloud Computing Skills- They perform research on big-data platforms and cloud computing tools such as Amazon Web Server and efficiently structure data warehouses.
- Perfect Engineering Skills - The data scientist's software engineering skills are very sharp because he understands coding concepts and runs computer programming-made projects on different servers
- Comprehends Technical Aspects - They also understand the technical concepts of Content Delivery Networks. Thus, his help is quite fruitful to the organization in running the audio-visual business scripts in the areas where data centers are not at higher capacity.
When aiming to know what is data science course, you should also be thorough with the exact work skills that would be required.
Thorough Understanding of Data Science Tools
- Business Analyst Tools - A data scientist is someone who is already thorough with various concepts about business analytics and fully understands their usage and concept, and perhaps this is the reason why many of them prefer to use tools like R, Big Data, Hadoop, and Spark.
- Technical Experts - Data scientists are also classified as the experts who understand the life cycle probability and data analytics project lifecycle. They are also known for having information linked to the IT product's life cycle and for analyzing the project.
A data scientist is said to have excellent expertise in understanding variables and measuring the central tendency. With the severe impact of advanced data analytics on computing data statistics, one can quickly summarise the data on numerous other platforms.
3. Know the Exact Objectives for Learning Online Data Science Training
- Accessible Data Courses - One Of the main objectives or purpose of learning data science is that they offer plenty of data science courses and help one to grasp the skills revolving around R programming, Python, Data Mining, machine learning with R, Data mining and live coding with real industry experts.
- Advanced Technical Skills - Learning advanced technical skills is quite helpful in delivering unified and comprehensive training that often teaches web developers to cope with advanced concepts and skills of data science analysis. By learning these skills, they can resolve technical queries.
- Helps Organizations - The training to learn data science online offers rigorous ways of handling any structured data used to build a complex business setup and applying intuition and intelligence. In other words, it would retract meaningful conclusions that could help organizations make significant decisions for the targeted audience.
- Helpful in Creating Complex Predictive Models- Its main objective is to provide every essential detail to learners, including advanced learning. It begins by introducing the person with the right tools to frame the algorithms and complex predictive models to analyze the data and gain insights.
- In-depth Data Science Learning - The main objective is to create a roadmap for data science training and allow one to enroll for free in in-depth data science training. It also gives a clear view of what has been expected throughout their training course on data science.
- Offers Clarity - It offers clarity to the audience in using concepts like R and Python.
Thus, the primary purpose of learning data science online lies in its consistent growth. On the other hand, data-backed industries can impart technical and sound knowledge about this field to aspiring individuals.
Moreover, within a few years, the data scientists could surely gain a master of their machine learning skills.
Data Science Training - Using R and Python
- Detailed Coverage
- Best-in-class Content
- Prepared by Industry leaders
- Latest Technology Covered
Application of Data Science in Different Industries
Now that we are slowly done with understanding what is data science course, it’s time to head on to learning data science importance in different industries:
1. Healthcare
- Infectious Disease Prediction: using statistical models to predict outbreaks; patient readmission index and potential medical risks posed by new drugs
- Drug Development: Accelerating drug discovery and development through data analysis and research.
- Personalized Medicine: tailoring treatments for different types of people based on their medical history and physical conditions.
2. Finance
- Risk Management: Building predictive models on banks to be aware of credit risks developing before it happen.
- Algorithmic Trading: High-frequency trading using machine learning algorithms and other investment strategies.
- Fraud detection: Telltale signs of fraud can be pretty unusual.
3. Trade & E-Commerce
- Customer Insights: Looking at buying trends and shopping preferences
- Inventory Management: Predictive analytics on stock levels.
- Recommendation Systems: Consumer-focused product recommendations based on data insights.
4. Internet Technology and Information Technology
- Cybersecurity: Using data analysis to detect and prevent security breaches
- Network Optimization: Using data analysis for planning network performance capacity.
- UI (User Interface) Design: Software and web interfaces that optimize for user data input based on behavior cues.
5. Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensor data represents an excellent opportunity for predicting equipment failures or operations.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Using statistics and analysis to streamline the supply chain, cutting time and costs.
- Quality Control: Automated detection of defects and monitoring of production quality.
6. Transportation and Logistics
- Demand Forecasting: Predicting the demand for transport to services.
- Vehicle Maintenance: Predictive analytics for vehicle repair.
7. Energy and Utilities
- Energy Demand Forecasting: Forecasting energy consumption helps to manage resources best.
- Smart Grid Management: The potential load on electricity distribution or grid control is optimized day to evening.
- Renewable Energy: Data on the efficiency of renewable energy sources through calculation.
8. Agriculture
- Crop Yield Prediction: Use data to predict crop yields and farming practices.
- Precision Agriculture: Using data more efficiently for agriculture watering, fertilizing, and spraying.
- Livestock Monitoring: Based on sensors and data analysis for health management of animals.
9. Entertainment and Media
- Content Personalization: Customize what is recommended for individual tastes, no matter what.
- Audience Analytics: Studying TV watcher habits and the latest trends to guide content development.
- Advertising Optimization: Data strategies, targeted advertising, and marketing campaigns.
10. Education
- Learning Analytics: Base your methods of teaching and the results on data collected from students.
- Course Recommendation Systems: Offering personalized course suggestions for learners so that they can get the most from their learning experience.
- Predictive Analytics: Discovering students likely to leave college or need special assistance.
The future of data science is evolving, and you can expect its applications to increase exponentially for all the relevant industries! Keep your eyes open; you never know an opportunity can arise anywhere.
Data Science Tools

Data Science relies mainly on various tools and technologies to analyze and process data into new insights. These tools are necessary for handling large data sets of information, running complex computations, and presenting those results in a graph. Here are some of the most popular tools used in data science:
1. Programming Languages
- Python: Widely employed due to its simple syntax and powerful libraries - such as Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn, and Matplotlib.
- R: Preferred for statistical analysis with graphs. It has packages like ggplot2, dplyr, and shiny.
- SQL: Essential not just for managing databases but querying them as well.
2. Data Analysis / Processing
- Excel: For standard data manipulation and analysis.
- Jupyter Notebooks: Mainly used in Python /R code, these allow insights directly derived from data to be visualized interactively.
- Apache Spark: Known for handling significant data processing and analytics. Of course, it is beneficial if your data won't all fit into one machine.
3. Machine Learning
- TensorFlow: An open-source library built by Google, broadly employed in machine learning and deep learning applications.
- Keras: A high-level neural networks API written in Python capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.
- Scikit-learn is a Python library for machine learning that provides tools to assist data analysis and data mining.
4. Data Visualization
- Tableau: It is a powerful tool for creating interactive and shared dashboards.
- Power BI: It is Microsoft’s business analytics service, and it provides interactive data visualization and intelligence capabilities.
- Matplotlib and Seaborn: They are Python libraries to create both static graphs as well as animated or interactive ones .
5. Big Data Technologies
- Hadoop: A framework for large-scale distributed data storage and processing based on the MapReduce programming model.
- Apache Hive: A data warehouse software for managerial extensive data collections held in distributed storage
- Apache Kafka: It figures out how to speed up building real-time data pipelines, directly transmitting messages as they come in.
6. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
- PyCharm: An IDE specifically for Python with code analysis, graphical debugger, etc.
- RStudio: An IDE for R with a console, syntax-highlighting editor, and tools for plotting history debugging and workspace management.
- Visual Studio Code: A multipurpose editor supporting Python, R, and many other languages.
7. Version Control
- Git: Widely used in source code management.
- GitHub/GitLab: Platforms for Hosting Code and reviewing code, managing data science projects to building software.
Question- What is the Need of Data Science Models?
- Avail Jobs in Non - IT Sectors-The courses of data science help an individual to get standalone jobs and that is the best part of learning them. Moreover, these roles are available in the non-core IT industries too. It means that with limited learning one could easily expand his/her horizons.
- Proper Understanding of Programming Languages - The courses of data science also allow the data scientist to utilize statistical computer programming languages like R, Python, SQL, and much more to manipulate and transfer data into meaningful insights.
- Enables Web Developer to Create Models -
- Data science models allow the engineers to develop the complex predictive models by using techniques like data analysis, cleansing, ingestion, visualization, mapping as well as drawing of conclusions.
- The data science training enables web-developers to create models by using machine learning programming like clustering and decision tree learning as well as data learning algorithms that offer a different input about using the neural networks
- Learning data science models help web-developers to represent the information by efficiently using the data visualization tools and techniques.
Question- What are the Roles and Responsibilities of the Data Scientists?

Have you asked yourself why do you want to learn data science? Is it just about all the fancy terms and the higher salaries? Well, there's nothing wrong in making those your motivation, but it's essential to understand their significant share of roles and responsibilities also. The major responsibilities of the data scientist developer include building different types of machine learning algorithms and designing experiments that could be merged with existing data. It also includes analysis of the data used for pulling the business reports for the clients and colleagues and for business purposes.
- To Manage Databases - His/her job role includes developing, managing as well as the use of relational and NoSQL databases.
- Efficient Use of Data Processing Tools - The role of the data scientist also includes the efficient use of big-data processing tools like Hadoop, Spark, MapReduce, Hive, and much more.
- Efficient Understanding of Data Mining Methods - He /she can also select and deploy the data mining methods which are related to the needs of the project.
- Enable one to enhance Data Collection - Many data scientists are also able to enhance the data collection by including what all things are relevant for architecting the analytics systems.
- Helpful in Procuring Data - These tools also help a data scientist to procure, analyze, and standardize the huge data in a particular digital format that includes sales inventory, general ledger, and much more.
- Implementation of Statistical Techniques - A data scientist can easily manage and implement statistical techniques such as regression analysis, statistical tests, and much more.
- Meeting with the Product Development Team - The role of data scientist also includes collaboration with the product development and engineering team.
- Upgrading Business - A data scientists can also help the company to upgrade its business strategies by using the prevalent technologies, methods, and processes too.
A data scientist is someone who could easily take the position as a technical thought leader and bridge the communication gap between the analytics and web team.
Data Science Training - Using R and Python
- Personalized Free Consultation
- Access to Our Learning Management System
- Access to Our Course Curriculum
- Be a Part of Our Free Demo Class
Question- What are the Skills Required to Become the Data Scientist
|
Technical Skills
|
- Python Coding- Python is regarded as the most common coding language that is typically seen in analyzing the data scientist role, a data scientist should have thorough knowledge about Java, Perl, C/C++.
- Hadoop Platform- A data scientist is expected to be a professional who carries greater expertise to use the cloud computing and behavior-driven models such as agile scrum method.
- SQL Database Coding- A data scientist is someone from whom everybody expects to seek the solution to arising problems of SQL queries.
- Machine Learning and AI- A data scientist is someone who is known for having in-depth knowledge about artificial intelligence and understands how decision tree models work.
- Data Visualization- A data scientist is also an experienced individual who knows about the various ways of visualizing the unstructured data.
|
|
Non-Technical Skills
|
- Communication- A data scientist also happens to be a great communicator because he needs to be persuasive while using the data visualization tools in adding the graphic appeal and also for the easy absorption by all the teams of the organization.
- Data-Driven Decision Making- A data scientist is someone who does not emphasize the final output without deciding, judging, and analyzing the information inscribed in the data sets.
- Mathematical and Statistical Acumen- A data scientist is someone who couldn't reach heights if he doesn't understand the different types of tests that are needed to be performed for interpreting the analysis of databases.
- Inner-Curiosity to learn new things- A data scientist is someone ready to learn a new set of things and can think of different ways of solving the queries within a limited time frame.
|
Know the Exact Salary of the Data Scientist and Also Know the Different Career Paths
- Data Scientist - The estimated salary of a data scientist can go beyond USD 1,00,000. It is the best because it allows a data scientist to analyze, create algorithms, administer databases, and work on different decision tree models.
- Data Analyst - The overall salary of the data analyst ranges from USD 57,202 to USD 117,000. It is one such profession where he needs to interpret and analyze the growth and decline of the business in every fiscal year.
- Data Engineers - The salary of a data engineer is estimated to be around USD 89,700, and it is a high-profile job for a data engineer. A data engineer’s work is to create various regression models on decision trees and SDLC models.
- Database Admin/Administrator - The overall salary of the database administrator lies between USD 106,912 and USD 170,000, and this job role includes administering the databases according to the information granted by the clients.
- Machine Learning Engineer - The overall salary of the machine learning engineer is expected to go beyond USD 1,20,000 because they are an expert in creating AI models and fully understand their functioning. They also have full-fledged knowledge of machine learning programs such as Python, Java, C++, and cloud computing systems.
- Data Architect - The estimated salary of a data architect is around USD145,053. Their primary task is to structure the unstructured data by resolving the SQL queries and building the base of software architecture.
- App Architect - The estimated salary of an app architect is expected to be near USD 160,000. An app architect is a professional who can design regression models by using a new set of technologies that work as the perfect way to run them on Android systems.
- Business Analyst - The overall estimated salary of the business analyst is expected to be around USD90,012 because the main work includes developing the business reports and expanding the business horizons
- Data and Analytics Manager - The overall salary of the data and analytics manager is around USD130,364, and the significant work includes analyzing and managing the data according to standardized norms.
- Business Intelligence Developer - The overall estimated salary of the business intelligence developer is between USD 89,644 to USD 135,778. He is said to be the organization's leading man because he can create and convert new leads.
Question-How to Learn Data Science Online?
The certification courses linked to the data sciences are many not one. The main aim of these courses is to introduce a new wave of logical thinking in the minds of aspiring individuals who are capable enough of imbibing a new set of skills that involves working upon agile methods in the blends with machine learning programs.
Know the Nine Best Certification Programs in Data Sciences
Certified courses in data sciences aren’t only enough in letting one grab the golden opportunity to work with the best IT giants in the world like Apple Inc, IBM, HCL, Microsoft and HP but also offer them a sharp rise in their salary. These certified courses do help professionals to secure their position in the corporate world where insecurities of losing the jobs prevail more.
- Dell EMC Proven Professional Certification Program
- Certified Analytics Professional
- SAS Academy for Data Science
- Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE)
- Cloudera Certified Associate (CCA)
- Cloudera Certified Professional: CCP Data Engineer
- Data Science Certificate – Harvard Extension School
- Amazon AWS Big Data Certification
- Oracle Certified Business Intelligence
Moreover, one can learn data science with python by enrolling in the certification courses and even get a free demo. With the help of real-life industry experts one can understand the grassroots of the technical concept that would reap many benefits to him and can add much more success to him.
So this was it, ‘why should you learn Data Science and How should you learn Data Science’. Hope you had a great time reading this blog. Write to us in the comment section below what your views are on the same.
Conclusion
Data science, as a field, is ever-growing, and it's never too early or too late to be a part of the field. We tried to cover every aspect of the data science field, right from ‘what is data science course’ to ‘advantages of data science’ that you should know.
We hope you had a great time reading this blog. If you too, are clueless about where to begin with your data science journey, then just go ahead and enroll in the best data science Certification program by JanBask Training.
FAQs
Q1. Why do you want to learn data science?
A: Data science is not just a skill; it's also the mindset of continuously learning and solving problems. Think about it like this: in this line of work, you can take a large amount of information and distill it down into actionable insight. You guide businesses and organizations strategically with this skill set. Data science gives us the power to make a difference, from predicting consumer behavior and optimizing business processes to participating in pioneering scientific research.
Q2. What is data science course?
A: A data science course meant to teach you how to manipulate data and analyze the results is nothing more than a starting point. It includes statistics learning, machine learning, and programming languages such as Python or R, as well as convenient techniques for data visualization. Such courses are designed to lay a solid foundation and equip you with the skills necessary to process, analyze, and draw predictive conclusions from structured data sources from fields such as natural sciences or social studies and unstructured ones like plain text. These courses often involve real-world case studies as the only way students can acquire practical experience.
Q3. What are the advantages of data science?
A: Data science today offers many advantages based on its insight into the tidal wave of data surrounding us. For enterprise, this means a transformation of how companies grapple with problems and opens new doors to tomorrow: predictive analysis shows what might happen next if you know why today's ratio stands out; it turns hunches into certainty. For example, data science methods in health care provide personalized treatment plans. In finance, they help detect fraud and manage risk. Five years ago, these advantages highlighted the transformative power of data science, from raw number-toting to strategic insight.
Q4. How are different industries utilizing data science-driven insights?
A: No matter what your business is, business intelligence boosts your chances of success. For instance, in retail, it's used to manage stock and study customer tastes; in transportation, there's the problem of route planning and traffic control. The entertainment field enjoys an advantage from data science: user experiences are tailored by personalized recommendations.
Q5. Why do we need data science more than ever?
A: Data is growing exponentially in the digital age. Given this, companies and organizations are awash with data that, properly handled, could lead to breakthroughs and strategic advantages. Navigating the data deluge requires data science or, in other words, tools to help look through all that data and turn information into insight.
Q6. What are the benefits of Data Science Course of JanBask Training?
A: The data science course of JanBask Training is a career-defining move! It will arm you with practical skills in big data technologies, advanced analytics, and machine learning ++, all the things that are sought after most in job markets today. With these paths, you can come and go through the doors of top tech companies or banks; you know financially what yours can be worth when you help define company policy.
Q7. What's the purpose of learning Data Science?
A: You can achieve two goals by learning data science. First, familiarize yourself with the skills and techniques required to analyze large and complex data sets. Second, through acceptance, accumulated knowledge can influence decision-making and become a matter of human freedom. Learning data science is about acquiring a skill set to cut through the chaos and change raw facts into business insights that can guide and even drive commercial and scientific innovation.
Q8. How can we learn the material effectively while taking a data science course from JanBask Training?
A: To effectively tackle a data science course, the best is to involve oneself fully in what one must learn. That means not just passively listening to lectures but actively engaging with the material through coding exercises, participating in discussions, and working on projects that mimic real-world scenarios. Networking with like-minded peers can strengthen your educational experience, and getting together professionals from different areas of software development goes beyond what's available at school. The result is a broader perspective on how things work in practice and targeted feedback from Red Hat trainers who know both worlds.
Q9. What's so special about each class for data science of JanBask Training?
A: The data scientist training at JanBask offers a combination of theoretical grounding applied to practical problems. Ideally, such certifications are recognized by industry leaders. Still, they are wide-ranging regarding what's covered, including data mining (both from an educational perspective and with a strong emphasis on practice), machine learning, and algorithm development. Online classes through reputable institutions also give the flexibility and depth necessary for mastering this field.
Introduction
Careers
Data Science Vs. Different Technologies
Tools
Useful Resources
Interview
Data Science Course
Upcoming Batches
Trending Courses
Cyber Security
- Introduction to cybersecurity
- Cryptography and Secure Communication
- Cloud Computing Architectural Framework
- Security Architectures and Models
Upcoming Class
3 days 16 Jan 2026
QA
- Introduction and Software Testing
- Software Test Life Cycle
- Automation Testing and API Testing
- Selenium framework development using Testing
Upcoming Class
3 days 16 Jan 2026
Salesforce
- Salesforce Configuration Introduction
- Security & Automation Process
- Sales & Service Cloud
- Apex Programming, SOQL & SOSL
Upcoming Class
3 days 16 Jan 2026
Business Analyst
- BA & Stakeholders Overview
- BPMN, Requirement Elicitation
- BA Tools & Design Documents
- Enterprise Analysis, Agile & Scrum
Upcoming Class
10 days 23 Jan 2026
MS SQL Server
- Introduction & Database Query
- Programming, Indexes & System Functions
- SSIS Package Development Procedures
- SSRS Report Design
Upcoming Class
4 days 17 Jan 2026
Data Science
- Data Science Introduction
- Hadoop and Spark Overview
- Python & Intro to R Programming
- Machine Learning
Upcoming Class
3 days 16 Jan 2026
DevOps
- Intro to DevOps
- GIT and Maven
- Jenkins & Ansible
- Docker and Cloud Computing
Upcoming Class
-0 day 13 Jan 2026
Hadoop
- Architecture, HDFS & MapReduce
- Unix Shell & Apache Pig Installation
- HIVE Installation & User-Defined Functions
- SQOOP & Hbase Installation
Upcoming Class
3 days 16 Jan 2026
Python
- Features of Python
- Python Editors and IDEs
- Data types and Variables
- Python File Operation
Upcoming Class
11 days 24 Jan 2026
Artificial Intelligence
- Components of AI
- Categories of Machine Learning
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Recurrent Neural Networks
Upcoming Class
1 day 14 Jan 2026
Machine Learning
- Introduction to Machine Learning & Python
- Machine Learning: Supervised Learning
- Machine Learning: Unsupervised Learning
Upcoming Class
38 days 20 Feb 2026
Tableau
- Introduction to Tableau Desktop
- Data Transformation Methods
- Configuring tableau server
- Integration with R & Hadoop
Upcoming Class
3 days 16 Jan 2026