Christmas Offer : Get Flat 35% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
Data storage is the fundamental function of a database. This data is used for reporting and analysis. Different tables are used to store the database's data. To the greatest extent possible, error reduction is critical. Data errors and duplicates must also be avoided. We refer to this as maintaining the integrity of the data. By imposing a variety of constraints, we safeguard the database's integrity.
In the following paragraphs, we will discuss various SQL data integrity features. Understanding the Data integrity in SQL begin with the understanding of SQL Server; you can get an insight about the same through our online SQL server training.
The overall accuracy, completeness, and dependability of data are referred to as data integrity. Error-free data can be demonstrated by the absence of variation between two instances or consecutive updates to a record.
Different types of data integrity are as follows
1) Entity Integrity
2) Domain Integrity
3) Referential Integrity
4) User-Defined Integrity

Entity Integrity: For a fixed table, entity integrity defines a row like a unique entity. The modifier column's attribute or a table's primary key is applied by entity integrity.
Domain Integrity: The authority of the data for a particular column is known as domain integrity. The size of the possible values, the data type, or the pattern can all be used to achieve domain integrity.
Referential Integrity: This constraint is used to regulate the flexibility of the rows and is described between the two tables. If a record contains related records, you are unable to delete or change a value from the table. A value that does not exist in the primary key of the primary table cannot be entered into the foreign key field of the table. However, you can define that the data are distinct by inserting a null value into the foreign key.
User-Defined Integrity: Business laws may require prompting for subsequent actions whenever a particular action occurs.
When designing a database, constraints and normalization techniques are used to ensure the integrity of the data. In the following section, we will learn in-depth how to insert these features into the database.
Next, we'll learn how to use constraints in SQL integrity check databases.
NOT NULL - Ensures that a column cannot have a NULL value
Syntax for implementing null constraint in a table using T-SQL is as follows
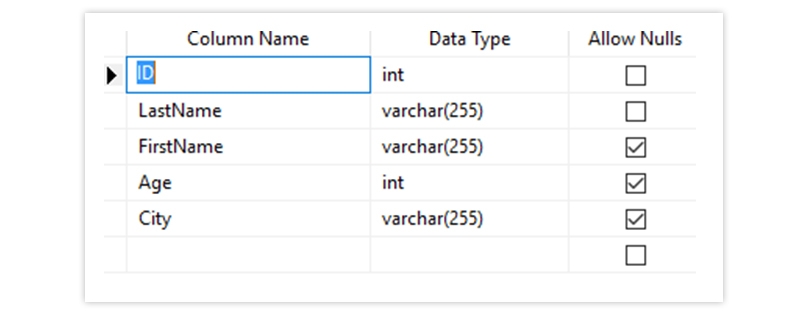
CREATE TABLE Persons (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
Age int
);
The Output Looks Like Below
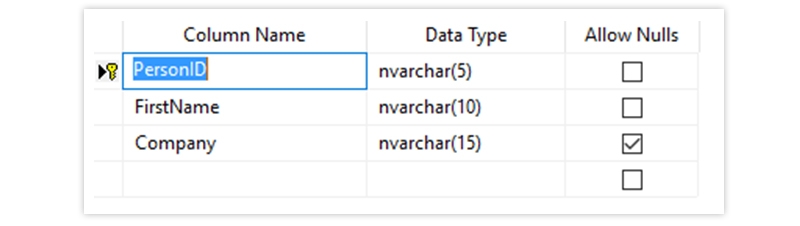
UNIQUE - Ensures that all values in a column are different
Syntax for the unique constraint is as follows
CREATE TABLE Persons1 (
ID int NOT NULL UNIQUE,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int
);
The Output Looks Like Below
PRIMARY KEY - A combination of a NOT NULL and UNIQUE. Uniquely identifies each row in a table
Syntax for declaring primary key is as below
CREATE TABLE Persons2 (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
CONSTRAINT PK_Person PRIMARY KEY (ID, LastName)
);
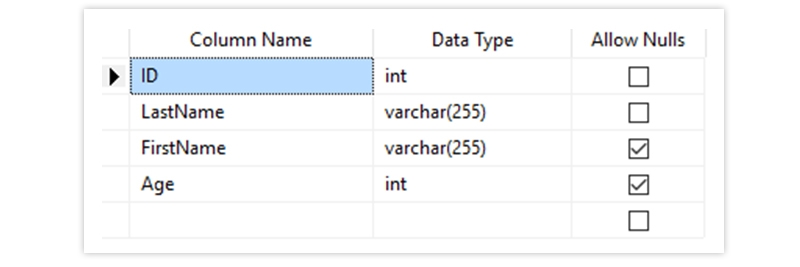
The Output Looks Like Below
FOREIGN KEY - Prevents actions that would destroy links between tables
Syntax for creating the foreign key is as below
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
OrderNumber int NOT NULL,
PersonID int FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Persons(PersonID)
);
CHECK- Ensures that the values in a column satisfy a specific condition
The syntax for SQL integrity check constraint is as below
CREATE TABLE Persons5 (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int CHECK (Age>=18)
);
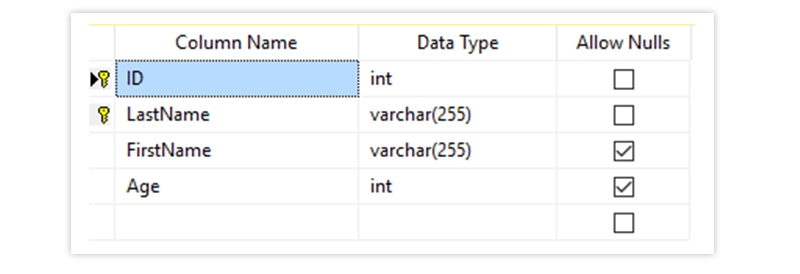
The Output is as Below
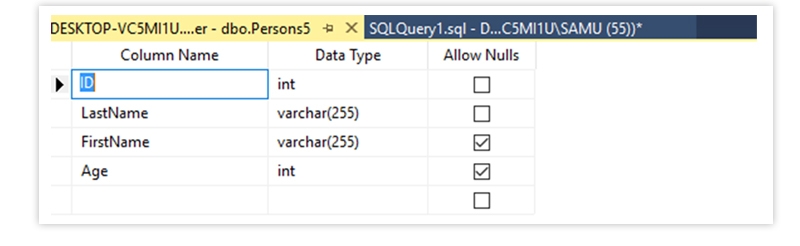
DEFAULT - Sets a default value for a column if no value is specified
The syntax for default constraint is as below and know more about how to add a default constraint when creating a table in SQL server.
CREATE TABLE Persons6 (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
City varchar(255) DEFAULT 'Sandnes'
);
The Output is as Below
CREATE INDEX - Used to create and retrieve data from the database very quickly
The syntax for create index is as below
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (column1, column2, ...);
Constraints can't handle varying data
What is data normalization? The process of removing redundant data from the table and improving its integrity is known as normalization. Additionally, normalization aids in the database's data organization. Sets the data into tabular form and removes duplicate data from relational tables in multiple steps.

Types of Normalisation
First Normal Form
Second Normal Form
Third Normal Form
Boyce Codd Normal Form
Another name for Boyce Codd Normal Form is 3.5 NF. Raymond F. Boyce and Edgar F. Codd created this superior version of 3NF to address specific anomalies that could not be resolved by 3NF.
In the above writeup, we have discussed SQL Server check database integrity. We have also discussed about different methods on how to implement SQL Server integrity check in the database. We learned about different types of constraints and also about normalization. Hope this can be an introductory text for readers who wants to study about SQL database integrity check and encourages them to study further on the topic. Additionally, we will talk about the various constraints that can be applied to a SQL Server database and why WITH CHECK CHECK CONSTRAINT is used.

SQL Testing Training

Database Files-Heart of SQL Server Database

Data Definition Language (DDL) Commands in SQL

Different Types of DBAs and Their Roles

What is Schema in SQL With Example: All You Need to Know

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Download Syllabus
Get Complete Course Syllabus
Enroll For Demo Class
It will take less than a minute
Tutorials
Interviews
You must be logged in to post a comment