Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
AWS has been spreading its services around the world since its inception, and it currently has around a million dynamic clients,. The global infrastructure of AWS is broadening so that the clients or end-users can now receive higher throughput and lower latency. AWS infrastructure is making sure that data remains in the user-specified region. It has always been ready to create infrastructure for its clients in such a way that they can fulfill their global requirements.
AWS Global Cloud infrastructure can be called the backbone of all services AWS offers and its data centers, which means it is globally available. With AWS training, grow your cloud computing technical skills and AWS concepts.

AWS Global Infrastructure Components Consist of:-
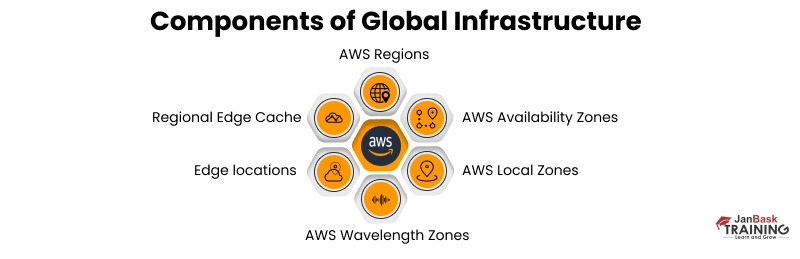
AWS Region
AWS Regions can be called the heart of the Global Cloud. These are actual physical locations all over the world. It consists of the data center clusters with the AWS availability zones. AWS region can consist of 2 or more AZs. Each AWS Region works in isolation from other AWS Regions. This helps in achieving fault tolerance and stability. Resources are not replicated across regions. We only see resources in our region when we see them in the AWS console.
Example of AWS Regions:
US East (Ohio)
US East (N. Virginia)
US West (N. California)
US West (Oregon) endpoint is the default for AWS RDS
AWS Availability Zones
An Availability Zone (AZ) is a collection of one or many data centers that provide services in an AWS Region.Each AZ contains an extra amount of connectivity, power, and networking capabilities, and an excellent geographical distance separates these individual AZs. All these individual AZs are connected through low latency and high throughput networking channels.This fine connectivity and redundancy help them provide scalable and fault-tolerant applications. As we know, AZs in a Region are isolated from each other physically, and applications in these AZs can provide high availability. Isolated metro fibers connect all Availability Zones.

AWS Local Zones
A Local Zone is an extension of an AWS Region that is geographically closer to users. Any VPC from the parent AWS Region can be extended into Local Zones.We can achieve this by creating a new subnet and assigning it to the AWS Local Zone. By doing this, we are extending the VPC to that Local Zone. this subnet works the same as the other subnets in the same vpc.These Local Zones are configured to run high-speed applications—such as media entertainment—that require low latency to service users in nearby geographic locations.
AWS Wavelength Zones
These AWS Wavelength zones provide 5G telecommunications connections inside AWS Regions. These zones provide AWS compute and storage capabilities to service provider's data centers to their 5G networks. Devices that support 5G can use apps that run in these Wavelength Zones and take advantage of 5G bandwidth.
Edge Locations
Regional Edge Cache
Customers provide workload and proper services to end users via AWS global cloud infrastructure zones and outposts in different geographical locations through the below infrastructure options: Data Centers: These are scalable and redundant.
Millisecond Latency: Data centers close to users provide single-digit millisecond latency.
5G Availability: 5G speed access with millisecond latency access for mobile devices end users.

The size of AWS is explained below as of today:
Why Cloud Infrastructure Matters?
AWS pricing varies across Regions because of different CapEx, OpEx, and regulations in different geographic locations. While configuring AWS infrastructure, organizations consider the following parameters:
AWS offers a cost calculator to estimate the expected costs of AWS services in different regions. The more complex your AWS environment is, the harder it will be to estimate your AWS global cloud infrastructure costs accurately. The cost calculator is an excellent place to estimate expected AWS regions' costs.
AWS offers an extensive collection of solutions and services across the globe. Although all its services are popular and available among all regions, not all are available across all regions. A detailed breakdown of all services and what region they are available in can be checked here on the AWS Regional Services page.
Correct AWS regions are selected based on current and future needs.
Regulatory compliance and security primarily affect the choice of AWS regions and zones where we can decide to deploy our applications. Consider the following factors.
Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory specifications like the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and state require sensitive end-user data for some specific regions.
Data Mobility: Transferring, storing, and processing user data in data centers at remote locations is sometimes considered a violation of compliance regulations, leads to lawsuits, and may also impact the brand's reputation.
Security Requirements: AWS services scatter the data over different geographical data centers to provide multi-availability zone coverage.
AWS has many Service Level Agreements (SLAs) related to cover its service uptime and penalties for service failures. More details can be found on the AWS Service Level Agreement page.

This blog provides a comprehensive guide on global infrastructure aws. Get to know what is aws global infrastructure, its components, and how and why to use them. After understanding why to choose AWS global infrastructure components and why it matters the most, you must have come to know why the demand for cloud skills will continue to grow; here is a top AWS certifications guide with required qualifications, career options, and the pay scale, for you to refer.
AWS Training For Administrators & Developers




Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Download Syllabus
Get Complete Course Syllabus
Enroll For Demo Class
It will take less than a minute
Tutorials
Interviews
You must be logged in to post a comment