Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL

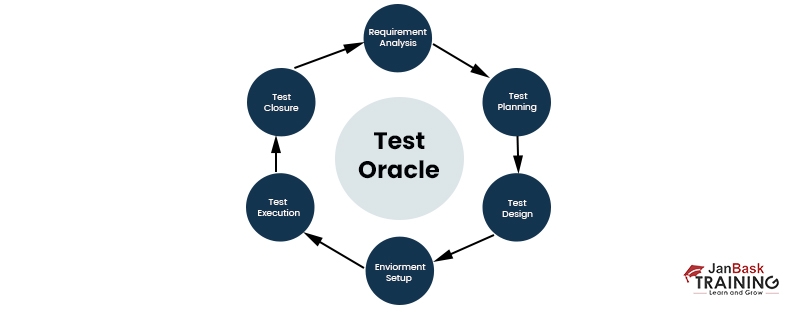
Testing depends on the approach taken at different points within the development process.
The testing process is determined by the following phases
Test control is an ongoing activity influencing test planning. The test plan may be re designed according to the information acquired from best controlling.
The test process status is determined by comparing the progress achieved against the last test plan. Necessary activities will be started accordingly.

Test Plan document explaining the scope, approach, resources and schedule of intended test activities. It includes, but is not limited to, the test items, the features to be tested, resources and contingency planning.
High test level description to be performed and the testing carried out with those levels for an organization or program.
According to the overall approach, the test efforts are divided among the test objects and the different test objectives: the choice of test methods, how and when the test activities should be done , when do we stop testing , whats the exit criteria
The set of generic specific conditions, agreed upon with the stakeholders, for permitting a process to be officially completed. The purpose of exit criteria is to prevent a task from being considered completed when there are still parts of the task outstanding which have not been finished.
Exit criteria helps when to stop testing. This should be done for each test level.
Data that is present in the system before even test is executed and affects or is affected by the component or system under test.
Input Data: A variable that is read by a system within or outside

The degree of which a specified item has been exercised by a test suite (expressed as a percentage). Mostly used on white box tests to determine code coverage.
Process of executing a test, producing actual results.
A consecutive record of suitable details about the execution of tests: when the test was executed,what was the actual outcome

QA Software Testing Training
The testing process can be divided into different stages.

Testing with V Models: A Guide to Their Application


Understanding The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in QA

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Download Syllabus
Get Complete Course Syllabus
Enroll For Demo Class
It will take less than a minute
Tutorials
Interviews
You must be logged in to post a comment