09
JanYear End Sale : Get Upto 50% OFF on Live Classes + $999 Worth of Study Material FREE! - SCHEDULE CALL
We realize tables are database objects that are utilized to store data in a table. These data can be of date, strings, and numbers. These data are stored in various fields of the table. But, how SQL Server does arrange and comprehends what sort of information it is storing in the table. That is where data types come into play. SQL Server allows the developer to indicate which column in a table will hold what sort of data. For instance, if you have made a table called the employee in a database and you have a column called name in it, you can specify SQL Server to store just string or character information in that column. These details are called data types. In the following write-ups we will get to know the following-
We will also understand the requirement of having such a significant number of sub-data types under the major data types and the process of memory management related to it.
SQL Data Types portray the TYPE OF VALUE that can be stored in a column of a table. For instance, if we want a SQL table column to store just integer values, then we can characterize the information type as int.

SQL data types can be broadly divided into the following categories:
int, tinyint, bigint, float, real etc.Date, Time, Datetime, etc.char, varchar, text etc.nchar, nvarchar, ntext etc.binary, varbinary etc.clob, blob, xml, cursor, table etc.Numeric data types are numbers stored in database columns.
There are two types of numeric data types-
SQL's exact numeric data types comprise of NUMERIC (p,s) and DECIMAL(p,s) subtypes. They are exact, and we characterize them by precision (p) and scale (s). Precision is an integer that represents the total number of digits permitted in this column. These digits are in a specific radix, or number base – ie binary (base-2) or decimal (base-10). They are generally characterized by a decimal point. The scale, also an integer value represents the number of decimal spaces to the left (if positive) or right (if negative; this is once in a while utilized) of the decimal point.
CREATE TABLE test_int (
accountNo integer,
balance numeric(8,2)
);
Output

CREATE TABLE test_sql_server_decimal (
dec_col DECIMAL (4, 2),
);

Both decimal and numeric are actually the equivalent. They are the same thing with an alternate name

SMALLINT, INT, TINYINT, INT
| Datatype | Range | Storage |
| BIGINT | -263 (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808) to 263-1 (9,223,372,036,854,775,807) | 8 Bytes |
| INT | -231 (-2,147,483,648) to 231-1 (2,147,483,647) | 4 Bytes |
| SMALLINT | -215 (-32,768) to 215-1 (32,767) | 2 Bytes |
| TINYINT | 0 to 255 | 1 Bytes |
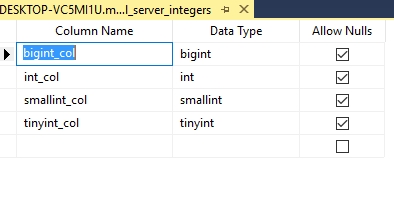
CREATE TABLE sql_server_integers
(
bigint_col bigint,
int_col INT,
smallint_col SMALLINT,
tinyint_col tinyint
);
These are values where the exactness should be saved and the scale can be floating. The approximate numeric types are DOUBLE PRECISION and FLOAT.
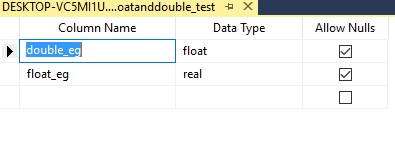
Create table floatanddouble_test ( double_eg DOUBLE PRECISION, float_eg float(2) )
The date and time data types store date and time data, and the date time offset. Examples of date and time data types are datetime, smalldatetime, date, time, datetime2, and datetimeoffset.
To store the date, data in the SQL Server table we utilize the SQL Server Date data type.
CREATE TABLE Date_Example
(
valid_from DATE NOT NULL,
valid_to DATE NOT NULL,
)

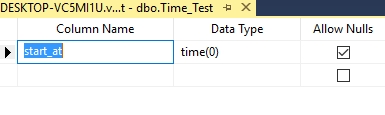
The SQL Server Time data type defines a time of a day based on a 24-hour clock.
CREATE TABLE Time_Test
(
start_at TIME(0),
)
The data type characterizes a date that is combined with a time of day with fractional seconds that is based on a 24-hour clock.
create table testdatetime
(
datetimevar datetime
)

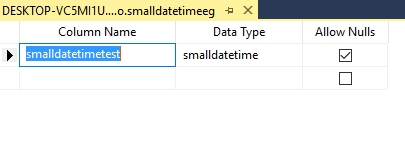
This data type characterizes a date that is combined with a time of day.
create table smalldatetimeeg
(
smalldatetimetest smalldatetime
)
The datetime variable rounds up the fractional seconds part. This is because datetime consistently rounds to increments of .000, .003, or .007 seconds. The smalldatetime variable on the other hand, rounds up the minutes part. Not simply that, the seconds part is set to zero.
The data type characterizes a date that is combined with a time of day that is based on a 24-hour clock.
create table datetime2eg
(
testdattime datetime2
)
The Datetimeoffset enables you to control any single point in time, which is a datetime value, along with an offset that specifies how much that datetime differs from UTC.
create table datetimeoffseteg
(
testdattimeoffset DATETIMEOFFSET
)

There are four diverse character data types that store character strings: char, varchar, varchar(max), and text
CHAR is a fixed length string data type, so any residual space in the field is cushioned with blanks. CHAR takes up 1 byte per character. So, a CHAR (100) field (or variable) takes up 100 bytes on disk, regardless of the string it holds
create table chartest
(
testchar char(10)
)

A varchar(n) or Variable Character Field is a set of character data of uncertain length. The term varchar refers to a data type of a field (or column) in a Database Management System which can hold letters and numbers.
create table varchartest
(
testchar varchar(50)
)
When we store data to a VARCHAR (MAX) column, behind the screen the data is handled as a TEXT value. So there is some extra processing required when dealing with a VARCHAR (MAX) value.
create table varcharmaxtest
(
testchar varchar(MAX)
)
Varchar(n) is a variable, you can assign a value to it, it can receive an int from 1 to 8000 or max.
varchar(max) is a constant, it has a value of max.
In SQL, Unicode character string data types are utilized in a circumstance where we required storing a huge data. In Unicode character string, we have an alternate type of string data types available, those are nchar,nvarchar,nvarchar(max).
Nchar is a fixed length character string and we can store maximum 4000 characters.
create table tablenchartest ( testchar nchar(500) )
Output
Nvarchar(n) is a variable length character string and we can store maximum 4000 characters.
create table tablenvarchartest
(
testchar nvarchar(500)
)

Nvarchar(max) is a variable length character string and we can store maximum 2^30-1 characters (upto 2 GB)
create table tablenvarcharmaxtest
(
testchar nvarchar(max)
)
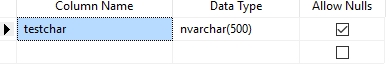
Nvarchar(n) is used for storing a variable-length unicode string. The variable, n, – for the mathematically inclined – denotes the length of the string data and this can be anything between 1 and 4,000.
The “max” in nvarchar(max) denotes a maximum storage size of 2 GB. Values stored in a nvarchar(N) are physically stored in the same way. However for the nvarchar(max) datatype , the values are treated as a TEXT value thus some additional processing is required, particularly when the size surpasses 8000.
In sql, binary data types are used to store any kind of binary data like images, word files, text files, etc. in table. In binary data types we have an option like allow users to store fixed length or variable length of bytes based on necessities.
Binary(n) is a fixed length binary data and we can store a maximum of 8000 bytes
create table tablebinarytest
(
testbinary binary(1000)
)
Output

Varbinary or variable length binary data and we can store maximum 8000 bytes
create table tablevarbinarytest
(
testvarbinary varbinary(1000)
)
Output
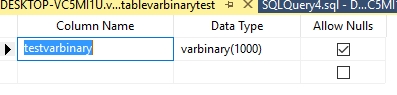
Varbinary (max) is a variable length character string and we can store maximum 2GB data
create table tablevarbinarymax
(
testvarbinary varbinary(max)
)
Output
In sql, we have an alternate data types which will not come under string data types, binary data types, date and time and numeric data types those will be called miscellaneous or other data types.
Example of miscellaneous data types are cursor,xml,table etc
The different data type has a particular memory necessity. Therefore, it makes more sense to define the column or variable with the data type it will hold for efficient utilization of memory. For instance, if you have a table called Employee where you have a column called Gender which determine whether the employee is male or female, ie M or F ,there is no point in declaring a column with a datatype varchar(50) which would use up lot of unnecessary space. Instead of declaring the column as char will be sufficient. Similarly, for a field that would contain age, datatype int will be enough
SQL Server Training & Certification

The above writeup is an extensive study of every data type that is available in SQL Server. This would give the reader a fare beat of an idea about these data types as well as the syntax to use them while creating tables. Happy querying!
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Interviews